How Does Insurance Work
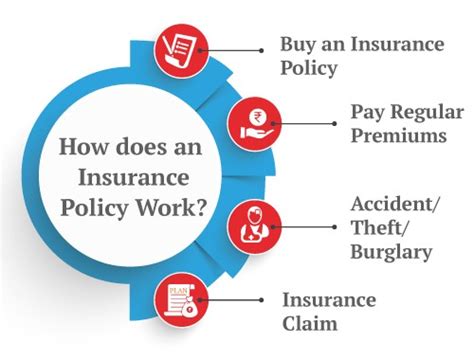
Understanding how insurance works is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Insurance is a financial safeguard that provides protection against various risks and uncertainties. It serves as a vital tool to mitigate potential losses and ensures financial stability in the face of unforeseen events. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate workings of insurance, exploring its fundamental principles, key components, and the impact it has on our lives.
The Basics of Insurance

At its core, insurance is a contract between an individual or entity (the policyholder) and an insurance company. This contract, known as an insurance policy, outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurance provider agrees to compensate the policyholder for specific losses or damages.
The concept of insurance revolves around the idea of risk pooling. Insurance companies collect premiums from a large number of policyholders, each contributing a small amount based on their chosen coverage and level of risk. By aggregating these premiums, insurers create a pool of funds that can be used to pay claims when policyholders experience covered losses.
Key Principles of Insurance
- Indemnity: The principle of indemnity states that insurance aims to compensate policyholders for their actual losses. The goal is to restore the policyholder to their pre-loss financial position, not to provide a windfall gain.
- Utmost Good Faith: Both parties in an insurance contract must act with utmost good faith. Policyholders are required to provide accurate and complete information about their risks, while insurers must clearly explain the terms and conditions of the policy.
- Insurable Interest: Insurable interest refers to the policyholder’s legitimate interest in the insured item or person. For example, a homeowner has an insurable interest in their property, and a parent has an insurable interest in their child’s life.
- Subrogation: In the event of a claim, the insurance company may have the right to step into the policyholder’s shoes to pursue legal action against the party responsible for the loss. This principle ensures that the insurer can recover the paid claim from the liable party.
Types of Insurance and Their Coverage
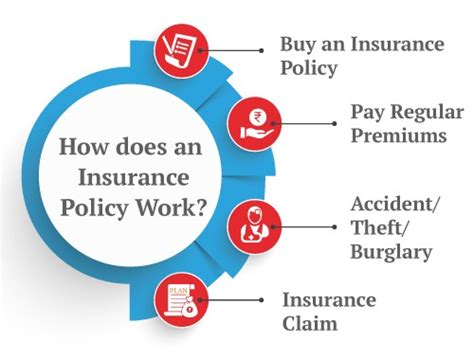
Insurance is a versatile tool, offering protection across a wide range of areas. Here are some common types of insurance and their key features:
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides financial protection to the policyholder’s beneficiaries upon their death. It can help cover funeral expenses, outstanding debts, and provide a financial safety net for loved ones. There are two main types of life insurance:
- Term Life Insurance: This type of policy provides coverage for a specific term, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. It offers pure protection without any cash value accumulation. Term life insurance is often more affordable than permanent life insurance.
- Permanent Life Insurance: Permanent policies, such as whole life or universal life insurance, provide lifetime coverage and accumulate cash value over time. The cash value can be borrowed against or withdrawn, providing additional financial flexibility.
Health Insurance
Health insurance is designed to cover medical expenses, ensuring individuals have access to necessary healthcare services without incurring excessive financial burden. Common types of health insurance include:
- Individual Health Insurance: These plans are purchased by individuals or families to cover their healthcare needs. They offer a range of benefits, including coverage for doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care.
- Group Health Insurance: Many employers offer group health insurance plans as part of their employee benefits package. These plans often provide more comprehensive coverage at a lower cost due to the larger pool of insured individuals.
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance provides financial protection in the event of accidents, theft, or damage to a vehicle. It is typically mandatory by law and can include coverage for:
- Liability Coverage: This covers the policyholder’s legal responsibility for bodily injury or property damage caused to others in an accident.
- Collision Coverage: Pays for damages to the policyholder’s vehicle in the event of an accident, regardless of fault.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Covers non-collision-related incidents, such as theft, vandalism, natural disasters, or damage caused by animals.
Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance is essential for protecting one’s home and personal belongings. It typically covers:
- Dwelling Coverage: Provides financial protection for the structure of the home.
- Personal Property Coverage: Covers the policyholder’s personal belongings, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
- Liability Coverage: Protects the homeowner against lawsuits and medical expenses if someone is injured on their property.
Business Insurance
Businesses face unique risks, and insurance plays a critical role in safeguarding their operations. Some common types of business insurance include:
- General Liability Insurance: Covers a wide range of risks, including property damage, bodily injury, and legal defense costs.
- Product Liability Insurance: Protects businesses against claims arising from defective products.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Also known as errors and omissions insurance, it covers legal costs and damages arising from professional mistakes or negligence.
The Insurance Claims Process
When a policyholder experiences a covered loss, they can file a claim with their insurance company to seek compensation. The claims process involves several key steps:
Step 1: Reporting the Claim
Policyholders must promptly report the loss to their insurance company. This can be done by contacting the insurer’s customer service or claims department, either online or over the phone. It’s important to provide accurate and detailed information about the incident.
Step 2: Claims Investigation
Once a claim is reported, the insurance company initiates an investigation to assess the extent of the loss and determine its validity. This may involve inspecting the damaged property, reviewing police reports, or gathering medical records, depending on the type of claim.
Step 3: Claims Adjustment
During the claims adjustment phase, the insurance company evaluates the claim and determines the amount of compensation to be paid. This process considers the policy’s coverage limits, deductibles, and any applicable exclusions.
Step 4: Payment of Claims
If the claim is approved, the insurance company will make the necessary payments to the policyholder or the third party involved in the incident. Payments can be made in various forms, such as checks, direct deposits, or repairs to the damaged property.
Risk Assessment and Premium Calculation
Insurance companies carefully assess the risks associated with each policyholder to determine the appropriate premium. Factors such as age, health, location, and driving record influence the level of risk and, consequently, the premium.
Actuaries, professionals specializing in risk assessment, use statistical models and historical data to calculate premiums. These models consider the likelihood of an insured event occurring and the potential cost of claims. By accurately assessing risk, insurance companies can set premiums that reflect the true cost of providing coverage.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Younger individuals may have higher premiums for certain types of insurance due to their increased risk of accidents or health issues. |
| Health Status | Pre-existing medical conditions or a history of health issues can impact health insurance premiums. |
| Location | The geographic location of the insured property or vehicle can affect premiums due to factors like crime rates, natural disasters, or traffic congestion. |
| Driving Record | Auto insurance premiums are influenced by an individual's driving history, including any accidents or traffic violations. |

The Future of Insurance

The insurance industry is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer needs. Here are some key trends shaping the future of insurance:
Digital Transformation
Insurance companies are increasingly embracing digital technologies to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations. Online portals, mobile apps, and chatbots enable policyholders to manage their policies, file claims, and receive real-time updates.
Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance
In the auto insurance sector, telematics devices are being used to track driving behavior and offer usage-based insurance. These devices monitor factors like driving speed, acceleration, and mileage, allowing insurers to offer more personalized premiums based on actual driving habits.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing risk assessment and claims processing. These technologies enable insurers to analyze vast amounts of data, detect patterns, and make more accurate predictions, leading to improved underwriting and fraud detection.
Parametric Insurance
Parametric insurance is an innovative approach that provides rapid payouts based on predefined parameters, such as weather conditions or natural disaster events. This type of insurance is particularly useful in situations where traditional claims processes may be delayed or challenging.
Collaborative Insurance Models
Insurance companies are exploring collaborative models, such as peer-to-peer insurance, where policyholders share risks and pool resources. These models offer a more community-based approach to insurance, leveraging technology and blockchain to facilitate secure transactions.
Conclusion
Insurance is an essential tool for managing risk and protecting our financial well-being. By understanding the principles, types, and processes involved in insurance, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to secure their future. As the insurance industry continues to evolve, staying abreast of the latest trends and innovations will be crucial for both policyholders and insurers alike.
What happens if I fail to disclose relevant information during the insurance application process?
+Failing to disclose relevant information can lead to the insurance company denying your claim or even canceling your policy. It’s important to be honest and provide accurate details to ensure your coverage remains valid.
Can I switch insurance companies if I find a better deal?
+Absolutely! You have the freedom to shop around and compare insurance policies. If you find a more suitable or cost-effective option, you can switch insurance companies by canceling your existing policy and purchasing a new one.
How often should I review my insurance coverage?
+It’s recommended to review your insurance coverage annually or whenever significant life changes occur, such as buying a new home, getting married, or starting a business. Regular reviews ensure your coverage remains adequate and aligned with your current needs.