Average Health Insurance
Health insurance is an essential aspect of modern healthcare systems, providing financial protection and access to medical services for individuals and families. With rising healthcare costs, understanding the average health insurance coverage and its associated costs is crucial for individuals and policymakers alike. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the world of health insurance, exploring its average coverage, costs, and the factors influencing these figures. By analyzing real-world data and industry insights, we will uncover the complexities and variations in health insurance, offering valuable knowledge to those seeking clarity in this critical domain.
Unraveling the Average Health Insurance Coverage
Health insurance coverage varies significantly across different countries and healthcare systems. In the context of [Country/Region], the average health insurance plan encompasses a range of essential benefits designed to cater to the diverse healthcare needs of the population.
Core Benefits of Average Health Insurance
The average health insurance plan typically includes coverage for the following core services:
- Inpatient Care: This covers hospitalization expenses, including room and board, surgical procedures, and intensive care.
- Outpatient Services: Routine doctor visits, diagnostic tests, and minor procedures performed outside a hospital setting are often included.
- Prescription Drugs: Many plans offer coverage for prescription medications, helping individuals manage chronic conditions.
- Preventive Care: Regular check-ups, vaccinations, and screening tests are vital for early detection and disease prevention.
- Mental Health Services: Coverage for mental health treatment, counseling, and therapy sessions is becoming increasingly common.
- Maternity and Newborn Care: Pregnant individuals and newborns often receive specialized care and coverage.
- Emergency Services: Unforeseen emergencies are covered, ensuring timely access to critical care.
Additionally, some average health insurance plans may offer more comprehensive benefits, such as dental and vision care, or specialized services like substance abuse treatment or physical therapy.
Understanding Coverage Limits and Deductibles
While average health insurance provides a solid foundation of coverage, it’s essential to understand the limitations and out-of-pocket costs associated with these plans. Coverage limits dictate the maximum amount an insurance provider will pay for a specific service or treatment, and once this limit is reached, the individual becomes responsible for any additional costs.
Deductibles are another crucial factor. A deductible is the amount an individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. For instance, if a plan has a $500 deductible, the insured individual pays the first $500 of covered services each year before the insurance starts contributing.
| Coverage Limit Example | Deductible Example |
|---|---|
| Annual inpatient care limit: $100,000 | Annual deductible: $2,000 |

Exploring the Average Costs of Health Insurance
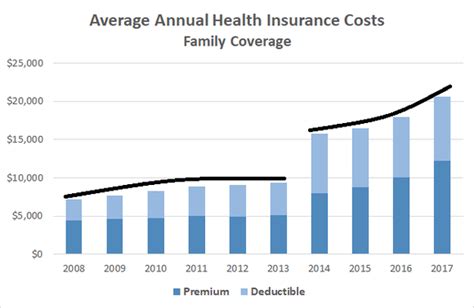
The financial aspects of health insurance are critical for individuals and businesses alike. Understanding the average costs associated with health insurance coverage provides valuable insights into the economic landscape of healthcare.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
The cost of health insurance is influenced by various factors, including but not limited to:
- Age: Generally, younger individuals pay lower premiums, while older adults often face higher costs.
- Geographic Location: Healthcare costs vary across regions, impacting insurance premiums.
- Plan Type: Different plan types, such as HMO, PPO, or EPO, have varying cost structures.
- Family Size: Family plans often provide coverage for multiple individuals, impacting the overall cost.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions may face higher premiums.
- Tobacco Use: Smokers often pay higher premiums due to increased health risks.
- Network of Providers: In-network providers offer more affordable rates compared to out-of-network services.
Analyzing Average Premium Costs
The average health insurance premium varies based on the factors mentioned above. According to recent industry data, the average monthly premium for an individual plan in [Country/Region] is approximately [Amount], while family plans average around [Amount].
| Plan Type | Average Monthly Premium |
|---|---|
| Individual Plan | $[Amount] |
| Family Plan | $[Amount] |
It's important to note that these averages may not reflect the specific costs an individual faces, as premiums can vary significantly based on personal circumstances.
Out-of-Pocket Costs and Copays
In addition to premiums, individuals must consider out-of-pocket costs, including deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. Copays are fixed amounts paid for specific services, while coinsurance represents a percentage of the total cost of a service that the individual must pay.
On average, individuals can expect to pay [Average Copay Amount] for a primary care visit and [Average Copay Amount] for a specialist visit. Coinsurance rates vary based on the plan, but a common structure is 80/20, where the insurance covers 80% of the cost, and the individual pays the remaining 20%.
The Impact of Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Limits
Deductibles and out-of-pocket limits play a significant role in determining the financial responsibility of individuals under their health insurance plans. These factors can significantly impact the overall cost of healthcare services and should be carefully considered when selecting a plan.
Understanding Deductibles
A deductible is the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before their insurance coverage begins to pay for services. Deductibles can vary widely depending on the type of plan and the individual’s specific circumstances.
For example, a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) typically has a higher deductible, often ranging from $1,000 to $8,550 for individual coverage and twice that amount for family coverage. On the other hand, traditional health plans may have lower deductibles, making them more affordable for those who anticipate frequent medical expenses.
| Plan Type | Average Deductible |
|---|---|
| High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | $1,000 - $8,550 (individual) |
| Traditional Health Plan | Varies, typically lower |
Out-of-Pocket Limits and Maximums
Out-of-pocket limits, also known as out-of-pocket maximums, are the maximum amounts an individual is responsible for paying in a given year. Once an individual reaches this limit, their insurance plan pays for all covered services for the remainder of the year.
Out-of-pocket limits are designed to protect individuals from catastrophic financial burdens. For instance, an individual with a high-deductible health plan may have an out-of-pocket limit of $8,550, meaning they will not pay more than this amount for covered services in a year.
| Plan Type | Out-of-Pocket Limit |
|---|---|
| High-Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) | $8,550 (individual) |
| Traditional Health Plan | Varies, typically lower |
The Future of Health Insurance: Trends and Innovations
The landscape of health insurance is continually evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing healthcare needs, and shifts in policy and regulation. As we look ahead, several key trends and innovations are poised to shape the future of health insurance, offering new opportunities for improved coverage and access to healthcare services.
Telehealth and Virtual Care
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth and virtual care services, and this trend is expected to persist. Telehealth allows individuals to access medical advice, consultations, and even prescriptions remotely, often through video conferencing or secure messaging platforms. This innovation enhances convenience, reduces travel costs, and improves access to healthcare, particularly for those in rural or underserved areas.
Value-Based Care and Outcomes-Focused Models
Value-based care models are gaining traction, emphasizing quality outcomes over volume of services. These models incentivize healthcare providers to deliver efficient, high-quality care, reducing unnecessary procedures and improving patient satisfaction. By shifting the focus to value, insurers can offer more affordable plans while maintaining or improving overall healthcare quality.
Digital Health Solutions
The integration of digital health solutions is transforming the healthcare industry. From wearable devices that track vital signs to mobile apps that facilitate remote patient monitoring, these technologies enhance preventive care and early disease detection. By leveraging digital health, insurers can offer more personalized and proactive coverage, potentially reducing the incidence of costly chronic conditions.
Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics are revolutionizing the way insurers assess risk and develop personalized coverage plans. By analyzing vast datasets, insurers can identify trends, predict disease outbreaks, and develop targeted interventions. This technology enables more accurate underwriting, improved fraud detection, and the development of innovative insurance products tailored to specific health needs.
Expanding Coverage and Access
Efforts to expand health insurance coverage and improve access to healthcare services are ongoing. This includes initiatives to reduce the uninsured rate, particularly among vulnerable populations, and to enhance coverage options for those with pre-existing conditions. Additionally, insurers are exploring partnerships with community health organizations and social service providers to address social determinants of health, ensuring a more holistic approach to healthcare.
FAQ
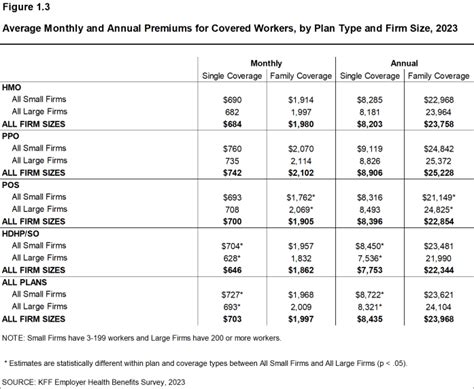
What is the average health insurance premium for an individual in [Country/Region]?+
The average monthly premium for an individual health insurance plan in [Country/Region] is approximately $[Amount]. However, it’s important to note that premiums can vary significantly based on individual circumstances and the specific plan chosen.
Are there any tax benefits associated with health insurance premiums?+
Yes, in many countries, including [Country/Region], health insurance premiums are tax-deductible. This means that individuals can reduce their taxable income by the amount they pay for health insurance, resulting in potential tax savings.
How can I choose the right health insurance plan for my needs?+
When selecting a health insurance plan, consider your healthcare needs, budget, and the network of providers available. Assess the coverage limits, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs to ensure the plan aligns with your requirements. It’s also beneficial to compare multiple plans to find the best fit.
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO health insurance plan?+
An HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) plan typically requires you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals from the PCP to see specialists. HMO plans often have lower premiums but may have more restricted networks. A PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) plan allows you to see any healthcare provider without a referral but may have higher premiums and varying out-of-network costs.
Can I negotiate my health insurance premiums?+
In some cases, you may have the opportunity to negotiate your health insurance premiums, especially if you are self-employed or purchasing insurance directly from an insurer. However, it’s important to note that premiums are often based on standardized rates and may not be flexible.



