Insurance For Insurance Brokers
In the world of insurance, where professionals navigate a complex web of policies and risks, ensuring adequate protection for insurance brokers themselves is an essential yet often overlooked aspect. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of insurance for insurance brokers, shedding light on the unique challenges and tailored solutions that exist within this niche.
Understanding the Need for Insurance
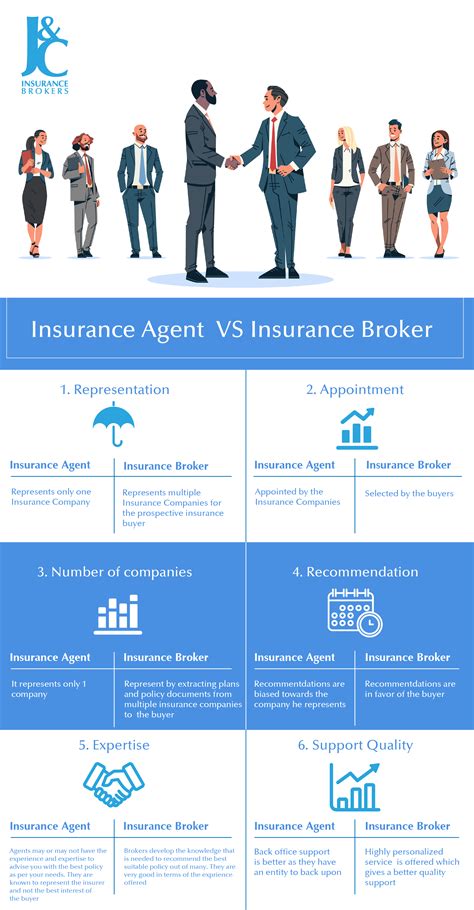
Insurance brokers play a pivotal role in the industry, acting as intermediaries between clients and insurance companies. Their expertise lies in assessing risks, providing tailored coverage, and offering guidance to ensure individuals and businesses are adequately protected. However, with great responsibility comes the potential for liability, making insurance an indispensable tool for brokers to safeguard their operations and reputation.
The nature of an insurance broker's work involves handling sensitive client information, negotiating complex contracts, and providing professional advice. Any oversight, error, or omission can lead to significant financial and legal consequences. This makes having robust insurance coverage a necessity rather than an option.
Key Risks Faced by Insurance Brokers
The risks insurance brokers face are diverse and can arise from various aspects of their practice. Here's an overview of some common risks:
- Professional Liability (Errors & Omissions): This covers brokers for claims arising from mistakes, negligence, or oversights in providing professional services. For instance, failing to advise a client on a crucial coverage aspect could lead to a claim.
- Breach of Privacy and Data Protection: With access to sensitive client data, brokers must ensure its security. A data breach or unauthorized access could result in significant legal and financial penalties.
- Contractual Disputes: Misinterpretation or misrepresentation of contract terms can lead to disputes with clients or insurance companies, potentially resulting in legal action.
- Regulatory Compliance: Non-compliance with industry regulations and standards can attract penalties and reputational damage. Brokers must stay updated with evolving regulations to avoid such pitfalls.
- Employee Misconduct: While rare, instances of employee fraud or misconduct can have severe consequences for a brokerage firm.
Given these risks, having comprehensive insurance coverage is not just a wise decision but a critical one for the sustainability and reputation of an insurance brokerage firm.
Types of Insurance for Brokers

The insurance landscape for brokers is diverse, offering tailored solutions to address the unique risks they face. Here's an in-depth look at the primary types of insurance available to insurance brokers:
1. Professional Liability Insurance (Errors & Omissions)
This is the cornerstone of insurance coverage for brokers. It provides protection against claims arising from professional services rendered or not rendered. For instance, if a broker fails to advise a client on a critical coverage aspect, leading to a financial loss, the client can file a claim against the broker. Professional liability insurance steps in to cover the costs associated with defending such claims, including legal fees and any settlements or judgments awarded against the broker.
Key aspects of professional liability insurance include:
- Retroactive Coverage: This feature ensures protection for past acts or omissions, which is crucial as claims can arise years after the service was provided.
- Prior Acts Coverage: Brokers switching insurance carriers can opt for this coverage to ensure protection for work done prior to the new policy's effective date.
- Extended Reporting Periods (Tail Coverage): Tail coverage provides an extended period of coverage after a policy has ended, offering protection against claims arising from work done during the policy period.
2. Cyber Liability Insurance
With the increasing reliance on digital systems and the rise in cyber threats, cyber liability insurance has become essential for insurance brokers. This coverage protects against a range of cyber-related risks, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and social engineering schemes.
Key aspects include:
- Data Breach Response: Covers the costs associated with responding to a data breach, including notification to affected parties, credit monitoring services, and legal fees.
- Network Security and Privacy Liability: Protects against claims arising from network failures, data loss, or privacy breaches.
- Cyber Extortion: Covers costs related to cyber-related extortion, such as ransomware demands.
3. Commercial General Liability Insurance
Commercial general liability insurance provides broad protection for a range of common risks faced by businesses, including insurance brokers. It covers bodily injury, property damage, and personal and advertising injury claims.
Key aspects include:
- Premises Liability: Covers claims arising from accidents or injuries that occur on a brokerage's premises.
- Products and Completed Operations: Protects against claims related to products or services provided by the brokerage.
- Advertising Injury: Covers claims arising from the brokerage's advertising activities, such as libel or slander.
4. Employment Practices Liability Insurance
Employment practices liability insurance (EPLI) is designed to protect insurance brokers from claims made by employees, former employees, or job applicants alleging wrongful employment practices. This includes claims of discrimination, harassment, wrongful termination, or failure to hire.
Key aspects include:
- Defense Costs: Covers the legal costs associated with defending against employment-related claims.
- Settlements and Judgments: Provides coverage for any settlements or judgments awarded against the brokerage as a result of employment-related claims.
- Wage and Hour Claims: Protects against claims related to wage and hour violations, such as overtime disputes.
5. Directors and Officers Liability Insurance
Directors and officers liability insurance (D&O) protects the personal assets of a brokerage's directors and officers from claims arising from their management decisions and actions. This coverage is particularly important for brokerages with a board of directors or key decision-makers.
Key aspects include:
- Entity Coverage: Provides protection for the brokerage itself against claims made against its directors and officers.
- Personal Coverage: Covers the personal assets of directors and officers, ensuring they are not personally liable for covered claims.
- Defense Costs: Covers legal fees associated with defending against covered claims.
The Importance of Tailored Insurance Solutions
Given the diverse nature of insurance brokerage operations, a one-size-fits-all approach to insurance is rarely effective. Each brokerage has unique risks and exposures based on its size, clientele, geographic location, and range of services offered. As such, a tailored insurance program is essential to ensure adequate protection.
Key Considerations for Tailored Insurance Solutions
- Business Size and Structure: Larger brokerages with multiple locations and a diverse range of services may require more comprehensive coverage than smaller, niche brokerages.
- Client Profile: The type of clients a brokerage serves can significantly impact the nature of risks. For instance, a brokerage specializing in high-net-worth individuals may face different challenges compared to one serving small businesses.
- Geographic Location: Regional differences in regulations, climate, and industry norms can influence the types of risks a brokerage faces.
- Range of Services: A brokerage offering a broad range of services, from personal lines to complex commercial coverage, may need a more intricate insurance program than one specializing in a single niche.
Working with an experienced insurance broker who understands the unique risks and needs of the insurance industry can be invaluable in designing a tailored insurance program. They can guide brokers through the process of assessing risks, selecting appropriate coverages, and negotiating the best terms and conditions with insurance carriers.
The Role of Insurance Brokers in Their Own Insurance
Insurance brokers play a critical role in their own insurance journey. They are the experts in navigating the complex world of insurance, and their knowledge and connections can significantly influence the outcome of their insurance program.
Key Responsibilities of Insurance Brokers in Their Own Insurance
- Risk Assessment: Brokers should conduct a thorough assessment of their own risks, considering their business operations, client base, and potential exposures. This self-analysis is the foundation for building an effective insurance program.
- Coverage Selection: Based on the identified risks, brokers should select the appropriate types and levels of coverage. This process involves understanding the nuances of different insurance policies and how they apply to their specific situation.
- Carrier Selection: Choosing the right insurance carrier is crucial. Brokers should consider carriers' financial strength, reputation, and track record in paying claims. They should also assess the carrier's appetite for the specific risks faced by insurance brokers.
- Policy Negotiation: Brokers can leverage their expertise to negotiate favorable terms and conditions with insurance carriers. This includes discussing coverage limits, deductibles, exclusions, and any unique endorsements or riders that may be necessary.
- Renewal Management: The insurance landscape is dynamic, and brokers should stay updated on market trends and changes in their own business to ensure their insurance program remains adequate and cost-effective. This involves regular reviews and potential adjustments to coverage during policy renewals.
Future Trends and Innovations in Insurance for Brokers
The insurance industry is continually evolving, and the landscape for insurance brokers is no exception. Here are some key trends and innovations that are shaping the future of insurance for brokers:
1. Digital Transformation
The digital revolution is transforming the way insurance is bought and sold. Online platforms and digital tools are making it easier for brokers to compare policies, obtain quotes, and manage their insurance programs. This trend is expected to continue, with an increasing emphasis on digital convenience and efficiency.
2. Cyber Risk Management
With the rise in cyber threats, cyber risk management is becoming a critical aspect of insurance for brokers. This involves not just having adequate cyber liability insurance, but also implementing robust cyber security measures and incident response plans. Brokers are increasingly expected to demonstrate their commitment to data security as a condition of insurance coverage.
3. Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance
Telematics and usage-based insurance are gaining traction in the insurance industry. These technologies allow insurance carriers to monitor driving behavior in real-time, offering personalized insurance rates based on actual usage. While initially popular in auto insurance, these technologies are now being explored for other lines of business, including professional liability insurance for brokers.
4. Parametric Insurance
Parametric insurance is an innovative approach that provides coverage based on predefined parameters rather than traditional indemnity-based coverage. In the context of insurance brokers, parametric insurance could offer coverage for business interruption or cyber events, providing quick payouts based on predefined triggers.
5. Risk Mitigation Services
Insurance carriers are increasingly offering risk mitigation services as part of their insurance offerings. For brokers, this could mean access to specialized tools, resources, and training to help identify and mitigate risks. These services aim to reduce the likelihood of claims, thereby lowering insurance premiums and enhancing the overall risk profile of the brokerage.
Conclusion
Insurance for insurance brokers is a complex yet critical aspect of the industry. By understanding the unique risks faced by brokers and tailoring insurance solutions accordingly, brokers can ensure their operations are protected, their clients are served effectively, and their reputations remain intact. As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and innovations will be key to staying ahead of the curve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main benefits of having professional liability insurance for insurance brokers?
+
Professional liability insurance, also known as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance, is a critical safeguard for insurance brokers. It provides financial protection against claims arising from mistakes, negligence, or omissions in the provision of professional services. This coverage is essential as it can cover the legal costs associated with defending against such claims, as well as any settlements or judgments awarded against the broker. By having professional liability insurance, brokers can protect their financial stability and reputation, ensuring they can continue to operate their business without the threat of crippling financial losses due to a single claim.
How does cyber liability insurance benefit insurance brokers specifically?
+
In today’s digital age, cyber liability insurance has become increasingly crucial for insurance brokers. As brokers handle sensitive client data, they are vulnerable to a range of cyber threats, including data breaches, ransomware attacks, and social engineering schemes. Cyber liability insurance provides coverage for the costs associated with responding to such incidents, including legal fees, credit monitoring services, and ransom payments. Additionally, it can provide crisis management support and help brokers restore their systems and data, ensuring business continuity. By having cyber liability insurance, brokers can demonstrate their commitment to data security and protect their clients’ information, thereby maintaining their trust and confidence.
What are some common exclusions in insurance policies for insurance brokers, and how can they be mitigated?
+
Insurance policies for insurance brokers often come with certain exclusions, which are specific situations or risks that are not covered by the policy. Common exclusions may include intentional misconduct, fraudulent acts, criminal acts, or claims arising from violations of intellectual property rights. To mitigate the impact of these exclusions, brokers should thoroughly review their policies, ensuring they understand the limitations of their coverage. They should also consider purchasing additional endorsements or riders to expand their coverage for specific risks. Additionally, brokers can take proactive measures to minimize the likelihood of excluded events, such as implementing robust internal controls, regularly training staff on ethical practices, and maintaining a strong culture of compliance within their organization.



