Health Insurance Individual
In today's world, ensuring access to quality healthcare is paramount, and individual health insurance plays a pivotal role in this regard. As the cost of healthcare continues to rise, understanding the intricacies of health insurance and navigating the options available can be daunting. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the world of individual health insurance, offering valuable insights and practical information to empower individuals in making informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
The Importance of Individual Health Insurance

Individual health insurance is a critical component of personal financial planning and overall well-being. It provides individuals and their families with access to essential medical services, protecting them from potentially devastating financial burdens that unexpected health issues can bring. With rising healthcare costs, having adequate insurance coverage is more important than ever.
The peace of mind that comes with knowing one has robust health insurance is invaluable. It allows individuals to focus on their health and well-being without the constant worry of unaffordable medical bills. Moreover, individual health insurance ensures timely access to medical care, promoting early detection and treatment of health issues, which can lead to better health outcomes.
Understanding Health Insurance Plans

Health insurance plans come in various types, each with its own set of features and benefits. Understanding the different plan types is essential in choosing the right coverage that aligns with one’s unique needs and circumstances.
1. Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) Plans
PPO plans offer flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Individuals can visit any in-network provider without a referral and often have the option to see out-of-network providers as well, albeit at a higher cost. These plans typically cover a broad range of services and are known for their convenience and flexibility.
| Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Flexibility in provider choice | Wide range of in-network providers |
| Referral-free access | Convenience and time-saving |
| Out-of-network coverage | More options for specialized care |

2. Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans
HMO plans operate on a more structured network of providers. Individuals are required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within the network, who coordinates their healthcare. Referrals are necessary to see specialists, and out-of-network care is generally not covered.
| Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| PCP-centered care | Coordinated and personalized healthcare |
| In-network coverage | Lower out-of-pocket costs |
| Preventive care emphasis | Promotes early detection and management of health issues |
3. Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) Plans
EPO plans are similar to PPO plans in that they offer flexibility in provider choice, but unlike PPOs, EPOs do not provide coverage for out-of-network care. Individuals can visit any in-network provider without a referral, but if they seek care outside the network, they will have to pay the full cost.
| Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Flexibility in provider choice | Wide range of in-network providers |
| No referrals needed | Convenience and time efficiency |
| No out-of-network coverage | Lower premiums compared to PPOs |
4. Point-of-Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine elements of both HMO and PPO plans. Individuals choose a PCP and typically need referrals to see specialists. However, they also have the option to see out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
| Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| PCP-centered care | Coordinated healthcare |
| Referrals for specialists | Ensures cost-effective care |
| Out-of-network coverage | Flexibility for specialized care |
5. High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs are often paired with health savings accounts (HSAs) and are known for their cost-saving potential. These plans have higher deductibles, meaning individuals pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in. However, they offer lower premiums and the ability to save pre-tax dollars in an HSA for future medical expenses.
| Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Higher deductibles | Lower premiums |
| Health savings account (HSA) eligibility | Tax-advantaged savings for medical expenses |
| Cost-conscious individuals | Suitable for those who prioritize savings |
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing Individual Health Insurance
Selecting the right individual health insurance plan involves evaluating several critical factors. Here’s a closer look at these considerations to help guide your decision-making process.
1. Cost of Premiums
Premiums are the regular payments made to maintain health insurance coverage. They are typically paid monthly or annually and are a key factor in the overall cost of insurance. When choosing a plan, it’s essential to consider the premium costs and how they align with your budget.
Lower-cost premiums may be appealing, but they often come with higher deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses. On the other hand, plans with higher premiums might offer more comprehensive coverage and lower out-of-pocket costs. Finding the right balance between premium affordability and coverage needs is crucial.
2. Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Maximums
Deductibles are the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage begins. Out-of-pocket maximums, on the other hand, are the limit on how much you will pay for covered services in a year. These factors significantly impact the financial aspect of your health insurance.
Plans with higher deductibles and out-of-pocket maximums may result in lower premiums, making them attractive for those who prioritize saving on monthly costs. Conversely, plans with lower deductibles and maximums provide more immediate coverage but may have higher premiums.
3. Network of Providers
The network of healthcare providers covered by your insurance plan is a critical consideration. Ensure that your preferred doctors, specialists, and hospitals are in-network to avoid unexpected out-of-network charges. Check the plan’s directory and verify the inclusion of your desired providers.
If you have specific healthcare needs or regularly see certain specialists, confirming their inclusion in the network is essential. Additionally, consider the plan's out-of-network coverage, as it may provide some flexibility if your preferred providers are not in-network.
4. Coverage for Pre-Existing Conditions
Health insurance plans are required by law to cover pre-existing conditions without any exclusions or waiting periods. However, it’s important to verify this coverage with your chosen plan to ensure you have protection for any existing health issues.
Understanding how your plan handles pre-existing conditions can prevent surprises and ensure you receive the necessary care without financial penalties. Review the plan's benefits and exclusions to confirm comprehensive coverage for pre-existing conditions.
5. Prescription Drug Coverage
Prescription medications are an essential component of healthcare, and their coverage can vary significantly between plans. Some plans offer comprehensive coverage for a wide range of medications, while others may have limited options or higher copays.
Review the plan's formulary, which lists the medications covered and their associated costs. Consider your current and potential future medication needs to ensure the plan provides adequate coverage without excessive out-of-pocket expenses.
6. Preventive Care Benefits
Preventive care is a vital aspect of maintaining good health and catching potential issues early on. Look for plans that offer comprehensive preventive care benefits, including screenings, immunizations, and wellness programs.
Many insurance plans provide these services at little to no cost, promoting early detection and management of health issues. Consider the preventive care offerings of different plans to ensure they align with your wellness goals and needs.
7. Maternity and Pediatric Care
If you’re planning to start or expand your family, it’s crucial to evaluate the maternity and pediatric care benefits of potential insurance plans. These benefits can vary widely, so understanding what’s covered is essential.
Look for plans that offer comprehensive maternity coverage, including prenatal care, delivery, and postpartum support. For pediatric care, ensure the plan covers well-child visits, immunizations, and any specialized care your child may need.
8. Mental Health and Substance Abuse Coverage
Mental health and substance abuse treatment are vital components of overall healthcare. When choosing a plan, verify that it covers mental health services, including therapy, counseling, and medication management. Additionally, confirm that substance abuse treatment is included, as this coverage can vary between plans.
Ensuring comprehensive coverage for these services is crucial for maintaining mental well-being and accessing necessary treatment options.
Shopping for Individual Health Insurance: A Step-by-Step Guide
Navigating the process of shopping for individual health insurance can be complex, but with a systematic approach, you can find the plan that best meets your needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through this process.
Step 1: Evaluate Your Healthcare Needs
Start by assessing your current and potential future healthcare needs. Consider factors such as chronic conditions, regular medications, specialist visits, and any anticipated medical procedures. Understanding your needs will help you choose a plan that provides adequate coverage.
Step 2: Research Plan Options
Explore the different plan types available, such as PPOs, HMOs, and HDHPs. Research their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks to determine which plan type aligns best with your needs. Utilize online resources, insurance brokers, or health insurance marketplaces to gather information.
Step 3: Compare Premiums and Out-of-Pocket Costs
Compare the premiums and out-of-pocket costs of various plans. Assess how these costs fit within your budget and consider the balance between premiums and deductibles. Remember that lower premiums often come with higher out-of-pocket expenses, so find the right balance for your financial situation.
Step 4: Verify Provider Network Coverage
Check the plan’s provider network to ensure your preferred doctors, specialists, and hospitals are included. Verify that your current healthcare providers are in-network to avoid unexpected out-of-network charges. If you have specific healthcare needs, confirm that the plan covers the necessary specialists.
Step 5: Review Benefits and Coverage Details
Thoroughly review the plan’s benefits and coverage details. Pay attention to exclusions and limitations to ensure the plan covers all your anticipated healthcare needs. Look for comprehensive coverage for pre-existing conditions, prescription medications, and any specialized care you may require.
Step 6: Consider Additional Benefits
Evaluate the additional benefits offered by each plan, such as wellness programs, telemedicine services, or fitness incentives. These perks can enhance your overall healthcare experience and provide added value.
Step 7: Assess Customer Service and Claims Process
Research the insurance provider’s reputation for customer service and claims handling. Look for reviews and ratings to ensure the company is responsive and efficient in processing claims. A positive customer service experience can make a significant difference in your overall satisfaction with the plan.
Step 8: Enroll in Your Chosen Plan
Once you’ve found the plan that best meets your needs, enroll during the open enrollment period or a qualifying life event. Provide all necessary information and documentation, and ensure you understand the effective date of your coverage.
Individual Health Insurance: Navigating Open Enrollment and Special Enrollment Periods
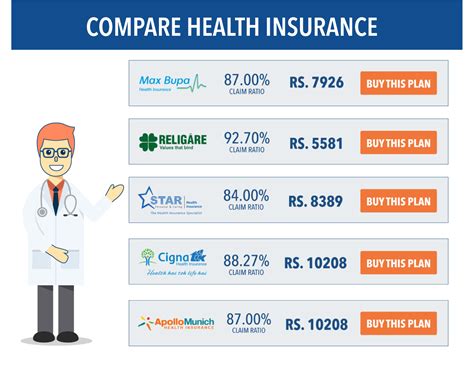
Understanding the enrollment process for individual health insurance is crucial to ensuring timely and effective coverage. Open enrollment periods and special enrollment periods are key components of this process, and knowing when and how to enroll can make all the difference.
Open Enrollment Periods
Open enrollment periods are designated times when individuals can enroll in or make changes to their health insurance coverage for the upcoming year. These periods are typically set annually and provide a window of opportunity for individuals to assess their insurance needs and make informed decisions.
It's essential to stay informed about the open enrollment dates for your specific plan or region. Missing the open enrollment period can result in a lack of coverage for the upcoming year or limited options for obtaining insurance.
Special Enrollment Periods
Special enrollment periods are outside the regular open enrollment window and are triggered by specific life events. These events can include losing job-based coverage, getting married or divorced, having a baby, or moving to a new area.
Special enrollment periods provide a critical opportunity for individuals to obtain health insurance coverage outside of the regular open enrollment period. It's important to be aware of these events and act promptly to ensure uninterrupted coverage.
Qualifications for Special Enrollment
To qualify for a special enrollment period, you must experience a qualifying life event. These events are typically significant changes in your life that affect your health insurance needs. Here are some common qualifying events:
- Loss of job-based coverage
- Change in marital status
- Birth or adoption of a child
- Moving to a new area
- Gaining citizenship or legal residency
- Loss of other qualifying health coverage
It's crucial to keep track of these events and understand their implications for your health insurance coverage. Being proactive and timely in responding to these changes can ensure you have the coverage you need when you need it.
Enrolling Outside of Open Enrollment
If you miss the open enrollment period and do not qualify for a special enrollment period, you may still have options for obtaining health insurance coverage. Some states offer expanded enrollment periods or alternative plans with year-round enrollment.
Additionally, short-term health insurance plans can provide temporary coverage until the next open enrollment period. However, it's important to note that these plans typically have limited benefits and may not cover pre-existing conditions.
The Role of Subsidies and Tax Credits
Health insurance subsidies and tax credits are vital financial aids that can significantly reduce the cost of individual health insurance. These benefits are designed to make insurance more affordable for individuals and families, ensuring access to essential healthcare services.
Eligibility for Subsidies and Tax Credits
Eligibility for health insurance subsidies and tax credits is primarily determined by household income. Individuals and families with lower incomes are more likely to qualify for these financial aids, as they are intended to make insurance coverage more accessible.
The exact income thresholds for eligibility can vary depending on the specific program and region. It's important to research and understand the income requirements for your area to determine if you qualify for subsidies or tax credits.
How Subsidies and Tax Credits Work
Health insurance subsidies are provided directly to insurance companies to reduce the cost of premiums for eligible individuals. These subsidies can cover a portion of the premium, making insurance more affordable and accessible.
Tax credits, on the other hand, are applied at tax time to reduce the amount of taxes owed. These credits can provide a significant financial benefit, especially for those with lower incomes who may not have large tax liabilities.
Applying for Subsidies and Tax Credits
To apply for health insurance subsidies and tax credits, you typically need to complete an application during the open