What Is Marketplace Insurance On Taxes
Marketplace insurance, also known as health insurance obtained through the Health Insurance Marketplace, is a crucial aspect of the healthcare system in the United States. The Health Insurance Marketplace, established under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), provides individuals and families with access to affordable health insurance plans. When it comes to taxes, marketplace insurance plays a significant role, as it impacts tax filings and may offer certain benefits or credits. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of marketplace insurance and its implications on taxes, exploring real-world examples and offering expert insights to help you navigate this complex landscape.
Understanding Marketplace Insurance
The Health Insurance Marketplace, often simply referred to as the “Marketplace,” is an online platform where individuals and small businesses can compare and purchase health insurance plans. It serves as a centralized hub, providing a transparent and competitive environment for insurance shopping. The marketplace offers a range of plans from various insurance providers, ensuring individuals have access to diverse options tailored to their specific needs and budgets.
Marketplace insurance plans typically fall into four main categories: Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum. Each category represents a different level of coverage, with Bronze plans offering the most basic coverage and Platinum plans providing the most comprehensive benefits. The choice of plan depends on individual preferences, health needs, and financial considerations.
Tax Implications of Marketplace Insurance

Marketplace insurance and taxes are closely intertwined, as the coverage obtained through the marketplace may have tax consequences. Here’s an in-depth look at how marketplace insurance impacts your tax obligations:
Premium Tax Credits
One of the key advantages of obtaining insurance through the marketplace is the potential eligibility for premium tax credits. These credits are designed to reduce the cost of monthly insurance premiums for individuals and families with moderate incomes. The amount of the credit depends on factors such as household size, income, and the cost of insurance plans in your area.
When filing your taxes, you can claim the premium tax credit as a direct reduction of your tax liability. This means that you may receive a refund or a lower tax bill based on the credit amount. It's important to note that the credit is calculated based on your estimated income for the year, and any discrepancies between estimated and actual income may affect the final credit amount.
Reconciliation of Premium Tax Credits
To ensure fairness, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires a reconciliation process for premium tax credits. During this process, the IRS compares the estimated credit you received throughout the year with your actual credit eligibility based on your final income for the tax year.
If your estimated credit exceeded your actual eligibility, you may need to repay a portion of the excess credit received. Conversely, if your actual eligibility exceeds the estimated credit, you may be entitled to an additional refund.
Advanced Premium Tax Credits
To provide immediate financial relief, the marketplace offers the option of receiving advanced premium tax credits. With this option, a portion of your estimated premium tax credit is paid directly to your insurance provider, reducing your monthly insurance premiums. This advanced credit is then reconciled with your actual eligibility when you file your taxes.
Cost-Sharing Reductions
In addition to premium tax credits, marketplace insurance plans may also offer cost-sharing reductions for eligible individuals. These reductions lower the out-of-pocket costs associated with healthcare services, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. Cost-sharing reductions are available to individuals with lower incomes and can significantly reduce the financial burden of healthcare expenses.
Real-World Examples
To illustrate the impact of marketplace insurance on taxes, let’s consider a few hypothetical scenarios:
Scenario 1: Premium Tax Credit Eligibility
Sarah, a single individual with an annual income of 40,000, purchases a Silver marketplace insurance plan. Based on her income and the cost of plans in her area, she is eligible for a premium tax credit of 200 per month. When filing her taxes, Sarah can claim this credit, reducing her tax liability by $2,400 for the year.
Scenario 2: Advanced Premium Tax Credits
John, a family of four with a household income of 75,000, chooses to receive advanced premium tax credits for their Gold marketplace insurance plan. The advanced credit reduces their monthly premiums by 300. When filing their taxes, John’s family reconciles the advanced credit with their actual eligibility, resulting in a refund or additional credit depending on their final income for the year.
Scenario 3: Cost-Sharing Reductions
Emily, a low-income individual, enrolls in a marketplace insurance plan with cost-sharing reductions. Throughout the year, she receives reduced out-of-pocket costs for healthcare services, saving her thousands of dollars in deductibles and copayments. When filing her taxes, Emily may be eligible for additional credits or deductions based on her healthcare expenses and income.
Expert Insights and Tips
Navigating the complex relationship between marketplace insurance and taxes requires careful consideration and planning. Here are some expert insights and tips to help you maximize the benefits:
- Estimate Your Income Accurately: When applying for marketplace insurance and estimating your premium tax credit eligibility, it's crucial to provide an accurate estimate of your annual income. This ensures that you receive the appropriate credit amount and avoids potential repayment obligations during reconciliation.
- Reconciliation Awareness: Understand the reconciliation process for premium tax credits. Keep track of your estimated and actual income, as well as any changes in your insurance plan or coverage. This awareness will help you prepare for potential adjustments during tax filing.
- Explore Cost-Sharing Reductions: If you have a low income, consider exploring insurance plans with cost-sharing reductions. These reductions can significantly lower your out-of-pocket costs and provide financial relief when accessing healthcare services.
- Seek Professional Advice: The tax implications of marketplace insurance can be complex. Consider consulting a tax professional or financial advisor who specializes in healthcare-related tax matters. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances and help you optimize your tax strategy.
- Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on any changes or updates to the marketplace insurance programs and tax regulations. Stay informed about deadlines, eligibility criteria, and any new initiatives that may impact your insurance and tax obligations.
Performance Analysis and Future Implications
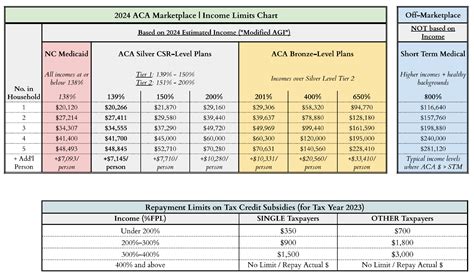
The implementation of marketplace insurance and its impact on taxes has had significant effects on the healthcare system and individuals’ financial well-being. Analysis of marketplace insurance data reveals the following insights:
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Individuals Enrolled in Marketplace Insurance | Over 12 million (as of 2021) |
| Average Premium Tax Credit Amount | $5,000 per year (as of 2021) |
| Percentage of Individuals Receiving Cost-Sharing Reductions | Approximately 25% of marketplace enrollees |
| Total Savings through Marketplace Insurance | Estimated at $28 billion for individuals and families (as of 2020) |

These numbers highlight the positive impact of marketplace insurance on individuals' access to affordable healthcare and the financial relief it provides. As the marketplace continues to evolve, future implications may include further expansion of insurance coverage options, enhanced cost-sharing reductions, and continued efforts to simplify the tax reconciliation process.
How do I know if I’m eligible for premium tax credits on marketplace insurance?
+Eligibility for premium tax credits is determined by factors such as household size, income, and the cost of insurance plans in your area. The marketplace provides tools to estimate your eligibility based on your income and family composition. It’s recommended to use these tools and consult official guidelines to assess your eligibility accurately.
Can I receive advanced premium tax credits if I have a high income?
+Advanced premium tax credits are primarily aimed at individuals and families with moderate incomes. The eligibility criteria for advanced credits may vary, but generally, higher-income households may not qualify for advanced credits. However, they may still be eligible for premium tax credits when filing their taxes.
What happens if I receive more advanced premium tax credits than I’m eligible for?
+If you receive advanced premium tax credits that exceed your actual eligibility, you may need to repay a portion of the excess credit when you file your taxes. It’s important to accurately estimate your income and reconcile the advanced credits with your actual eligibility to avoid repayment obligations.