Disability Insurance Definition
Disability insurance, often referred to as DI, is a crucial form of protection that provides financial support to individuals who become disabled and are unable to work. It serves as a safety net, ensuring that individuals can maintain a certain level of income and meet their financial obligations even when faced with a disability that prevents them from earning an income through traditional employment.
In today's world, where accidents, illnesses, and unforeseen circumstances can strike anyone, disability insurance has become an essential component of personal financial planning. It offers peace of mind, knowing that you and your loved ones are protected from the potentially devastating financial impact of a disability.
Understanding Disability Insurance: A Comprehensive Overview
Disability insurance is designed to replace a portion of an individual's income when they become unable to work due to a disability. This income protection is particularly vital for those whose livelihood depends on their ability to perform specific tasks or engage in certain occupations. The primary goal of DI is to provide a financial safety net, ensuring that individuals can continue to meet their basic needs and maintain their standard of living during a period of disability.
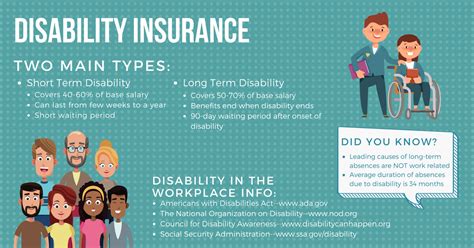
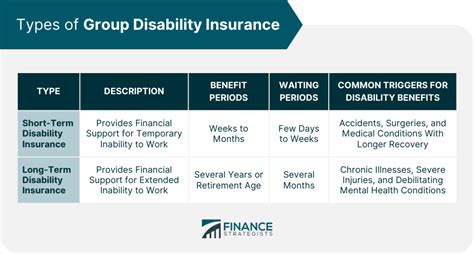
The coverage offered by disability insurance can be categorized into two main types: short-term disability insurance and long-term disability insurance. Short-term coverage typically provides benefits for a period ranging from a few weeks to a few months, covering temporary disabilities such as injuries or illnesses that require a brief recovery period. On the other hand, long-term disability insurance offers coverage for more extended periods, often lasting years, and is designed to support individuals with chronic or severe disabilities that significantly impact their ability to work.
Key Features and Benefits of Disability Insurance
One of the standout features of disability insurance is its flexibility. Policies can be tailored to meet the specific needs and circumstances of the individual. This customization allows for variations in coverage amounts, benefit durations, and eligibility criteria, ensuring that the policy aligns with an individual's income, occupation, and personal financial goals.
Another significant advantage of disability insurance is its tax benefits. In many cases, the premiums paid for DI policies are tax-deductible, reducing the overall cost of coverage. Additionally, the benefits received from a disability insurance policy are typically tax-free, providing a valuable source of income without the added burden of taxation during a challenging period.
Moreover, disability insurance often includes optional riders that enhance the basic coverage. These riders can include provisions such as future purchase options, which allow individuals to increase their coverage amount without providing additional evidence of insurability, or residual disability benefits, which provide a reduced benefit amount for individuals who can return to work on a part-time basis.
| Coverage Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Short-Term Disability | Provides temporary income replacement for brief disabilities, typically offering benefits for a few weeks to months. |
| Long-Term Disability | Offers financial support for extended periods, often covering severe or chronic disabilities that last for years. |
| Flexible Coverage | Policies can be customized to fit individual needs, allowing for variations in coverage amounts, benefit durations, and eligibility criteria. |
| Tax Advantages | Premiums are often tax-deductible, and benefits received are generally tax-free, providing a valuable source of income without additional taxation. |
| Optional Riders | Enhance basic coverage with features like future purchase options and residual disability benefits, offering additional flexibility and support. |

It's important to note that disability insurance is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The specific terms and conditions of a policy can vary widely depending on the insurance provider and the individual's circumstances. It's crucial to carefully review the policy details, including the definition of disability, the benefit amount, the elimination period (the time between the onset of disability and the start of benefit payments), and any exclusions or limitations that may apply.
The Role of Disability Insurance in Financial Planning

Incorporating disability insurance into a comprehensive financial plan is a strategic move that demonstrates a proactive approach to managing potential risks. It ensures that individuals and their families are prepared for the financial challenges that may arise due to a disability, providing a critical layer of protection against income loss.
For individuals who rely on their income to meet daily expenses, save for the future, and maintain their financial obligations, disability insurance is an indispensable tool. It bridges the gap between an individual's earning capacity and their ability to work, offering a stable source of income during a period of disability. This financial stability is particularly crucial when considering the unexpected expenses that often accompany a disability, such as medical bills, rehabilitation costs, and potential home modifications.
Choosing the Right Disability Insurance Policy
When selecting a disability insurance policy, it's essential to consider various factors. These include the individual's occupation, income level, and personal financial goals. For instance, individuals in high-risk occupations or those with specialized skills may require more extensive coverage to protect their earning potential. Additionally, the policy's benefit amount, benefit duration, and elimination period should align with the individual's financial needs and circumstances.
It's also crucial to assess the financial strength and reputation of the insurance provider. A stable and reputable insurer ensures that policyholders can rely on the insurer's ability to pay out claims when needed. Furthermore, understanding the policy's exclusions and limitations is vital to ensure that the coverage meets the individual's specific needs.
In conclusion, disability insurance is a vital component of financial planning, offering a safety net for individuals and their families during times of disability. By providing income protection, disability insurance ensures that individuals can maintain their financial stability and peace of mind, even in the face of unexpected circumstances. With a well-chosen policy, individuals can navigate the challenges of a disability with greater financial resilience and security.
How does disability insurance differ from other types of insurance, such as health insurance or life insurance?
+Disability insurance differs from health insurance and life insurance in its primary focus. Health insurance primarily covers medical expenses associated with illnesses or injuries, while life insurance provides a financial benefit to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death. In contrast, disability insurance is designed to replace a portion of an individual’s income when they become unable to work due to a disability, ensuring financial stability during a challenging period.
What are some common exclusions or limitations in disability insurance policies that individuals should be aware of?
+Common exclusions and limitations in disability insurance policies may include pre-existing conditions, self-inflicted injuries, disability due to war or military service, and disabilities resulting from illegal activities. It’s crucial to carefully review the policy’s fine print to understand any specific exclusions that may apply to your situation.
How can individuals ensure they choose a reputable disability insurance provider?
+When selecting a disability insurance provider, individuals should consider the insurer’s financial strength and stability. Reputable rating agencies, such as A.M. Best or Standard & Poor’s, provide ratings that assess an insurer’s financial health. Additionally, researching customer reviews and experiences can offer valuable insights into the insurer’s reputation and claim settlement process.



