What Is Tax Credit For Health Insurance

Understanding tax credits for health insurance is crucial for individuals and families navigating the complex world of healthcare and finances. These credits can provide significant relief, making health coverage more accessible and affordable. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of tax credits for health insurance, exploring how they work, who qualifies, and their impact on healthcare accessibility.
The Role of Tax Credits in Healthcare
Tax credits have emerged as a vital tool in promoting equitable access to healthcare. By reducing the financial burden of health insurance premiums, these credits empower individuals to secure essential coverage. This guide will unravel the complexities surrounding tax credits, offering a clear understanding of their function and benefits.
Understanding Tax Credits for Health Insurance

Tax credits for health insurance are designed to offset the cost of insurance premiums, offering a direct reduction in the amount individuals owe in taxes. This mechanism aims to encourage enrollment in health insurance plans, particularly among those who might otherwise struggle to afford coverage. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) administers these credits, making them accessible to eligible individuals and families.
Eligibility Criteria
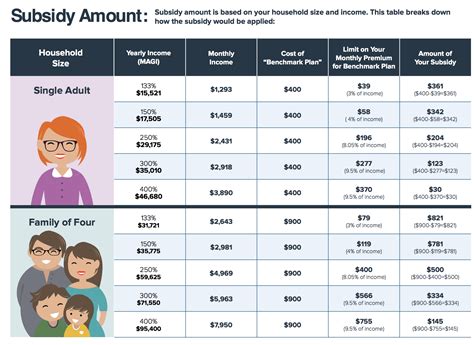
Eligibility for tax credits is primarily determined by income. Individuals and families with incomes between 100% and 400% of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL) are generally eligible. The FPL varies based on family size and geographic location. For instance, in 2023, the FPL for a single individual is 13,080, while for a family of four, it's 27,720. These income thresholds are crucial in determining eligibility and the extent of the tax credit.
| Income Range | Percentage of FPL |
|---|---|
| 100% - 150% | Low-income |
| 150% - 200% | Lower-middle-income |
| 200% - 250% | Middle-income |
| 250% - 400% | Higher-middle-income |
How Tax Credits Work
Tax credits for health insurance can be claimed in two ways: as an advance credit or a reconciliation credit. The advance credit allows individuals to receive the credit directly from the insurance company, reducing their monthly premium payments. In contrast, the reconciliation credit is claimed when filing taxes, providing a refund or reducing the amount owed.
The amount of the tax credit depends on various factors, including income, family size, and the cost of health insurance in the individual's area. Generally, the credit increases as income decreases, ensuring that those with lower incomes receive more substantial assistance. Additionally, the credit amount is adjusted based on the cost of insurance, ensuring it remains affordable even in regions with higher premiums.
Impact on Healthcare Accessibility
Tax credits for health insurance have had a profound impact on healthcare accessibility. By making insurance more affordable, these credits have encouraged enrollment, particularly among younger, healthier individuals who might otherwise opt out of coverage. This has helped to diversify the risk pool, leading to more stable insurance markets and lower premiums for all.
Moreover, tax credits have played a crucial role in reducing the number of uninsured individuals, particularly in states that have expanded Medicaid coverage. The combination of tax credits and Medicaid expansion has resulted in significant gains in coverage, improving access to healthcare services and financial protection for millions of Americans.
Navigating the Application Process
Applying for tax credits for health insurance involves several steps. Individuals can apply through the Health Insurance Marketplace, either during the annual Open Enrollment Period or if they qualify for a Special Enrollment Period due to specific life events. The application process involves providing detailed income and family information to determine eligibility and the appropriate credit amount.
Verification and Enforcement
To ensure the integrity of the tax credit system, the IRS employs robust verification processes. This includes cross-referencing income and family information with other government databases and conducting periodic reviews. Additionally, the IRS has the authority to audit tax returns and recoup excessive credits if eligibility requirements are not met.
Advantages and Challenges
Tax credits for health insurance offer numerous advantages, including increased accessibility, affordability, and stability in the insurance market. However, challenges remain, particularly in ensuring that eligible individuals are aware of and take advantage of these credits. Outreach and education efforts are crucial in maximizing the impact of tax credits and ensuring that those in need receive the assistance they are entitled to.
Future Implications and Policy Considerations
The future of tax credits for health insurance is closely tied to healthcare policy developments. As healthcare reform continues to evolve, the role and structure of tax credits may change. Potential policy considerations include expanding eligibility criteria, increasing credit amounts, and exploring new mechanisms to further enhance accessibility and affordability.
Furthermore, ongoing research and data analysis are essential to understand the full impact of tax credits on healthcare accessibility and financial protection. By closely monitoring the outcomes of these credits, policymakers can make informed decisions to optimize their effectiveness and reach.
How often can I apply for tax credits for health insurance?
+
You can apply for tax credits during the annual Open Enrollment Period, typically lasting for a few months each year. Additionally, you may qualify for a Special Enrollment Period if you experience certain life events, such as losing job-based coverage or getting married.
Are tax credits only available for private insurance plans?
+
No, tax credits can also be applied to coverage through Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). These credits help make these public insurance programs more affordable for eligible individuals and families.
Can I receive tax credits if I already have job-based insurance coverage?
+
In most cases, no. Tax credits are primarily designed for individuals and families who do not have access to affordable employer-sponsored insurance. However, there are exceptions, such as if your job-based coverage is considered unaffordable based on your income.