What Is Healthcare Insurance

Healthcare insurance, often simply referred to as health insurance, is a fundamental aspect of modern healthcare systems, playing a crucial role in ensuring access to medical services and financial protection for individuals and families. In essence, it is a contract between an individual or a group and an insurance company, where the insured party pays a premium in exchange for coverage of specified health-related expenses.
This vital coverage system has become an indispensable part of healthcare across the globe, offering a safety net against the often overwhelming costs of medical treatment. The benefits extend far beyond the financial aspect, as it also provides peace of mind and access to essential healthcare services without the fear of unaffordable expenses.
With the complexity of modern medical care and the ever-increasing costs, understanding healthcare insurance is more important than ever. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to healthcare insurance, exploring its various facets, benefits, and implications.
Understanding Healthcare Insurance

Healthcare insurance is a complex financial tool designed to manage the risks and costs associated with medical care. At its core, it operates on the principle of risk pooling, where a group of individuals pays premiums to cover the potential health expenses of any one member. This shared responsibility ensures that the financial burden of illness or injury is spread across the entire group, thus providing a form of financial protection for all involved.
The key players in this system include the insured individual or group, the insurance company, healthcare providers such as doctors and hospitals, and often, a third-party administrator (TPA) who manages the claims and reimbursements. Each of these parties has a specific role and set of responsibilities within the insurance process.
Types of Healthcare Insurance
Healthcare insurance comes in various forms, each designed to cater to different needs and circumstances. Here’s an overview of the primary types of healthcare insurance:
- Individual Health Insurance: This type of insurance is purchased by an individual directly from an insurance company. It offers coverage for the policyholder and, in some cases, their family members. Individual plans can be customized to meet specific needs and often have a range of coverage options.
- Group Health Insurance: Often provided by employers as part of employee benefits, group health insurance covers a group of people, typically employees and their dependents. This type of insurance is usually more affordable due to the larger pool of individuals and is often a significant incentive for employees.
- Medicare: A federal program in the United States, Medicare provides health insurance for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities. It's a vital component of the U.S. healthcare system, ensuring that older Americans have access to necessary medical care.
- Medicaid: Also a U.S. federal program, Medicaid provides health coverage to certain low-income individuals and families. It's jointly funded by the federal and state governments, with each state administering its own Medicaid program under federal guidelines.
- Private Health Insurance: This type of insurance is purchased directly from a private insurance company and is often used as a supplement to other forms of insurance. It can provide additional coverage for services not covered by other plans or offer more comprehensive benefits.
Key Components of Healthcare Insurance

Healthcare insurance is a complex system, with several key components that work together to provide coverage and manage costs. Understanding these components is essential for navigating the insurance landscape effectively.
Premiums
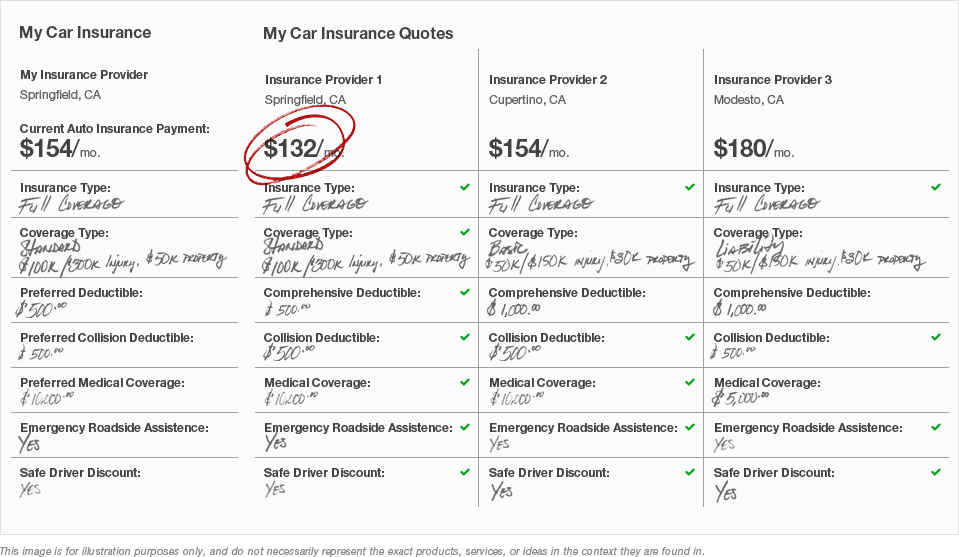
Premiums are the regular payments made by the insured to the insurance company. These payments are typically made monthly, quarterly, or annually, and they represent the cost of maintaining the insurance coverage. The amount of the premium can vary significantly based on factors such as the type of insurance, the level of coverage, the age and health of the insured, and the region in which they reside.
Deductibles
A deductible is the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. For example, if an insurance policy has a 1,000 deductible, the insured must pay the first 1,000 of covered medical expenses before the insurance company starts to pay its share. Deductibles can vary widely, and higher deductibles usually result in lower premiums.
Copayments (Copays)
Copays are fixed amounts the insured pays for a covered medical service, usually at the time of service. For instance, a doctor’s visit might have a copay of $25, which the patient pays directly to the healthcare provider. Copays can vary based on the type of service and the insurance plan.
Coinsurance
Coinsurance is a percentage of the total cost of a covered healthcare service that the insured must pay. For example, an insurance policy might have a 20% coinsurance clause, meaning the insured pays 20% of the cost of a covered service, while the insurance company pays the remaining 80%. Coinsurance typically comes into play after the deductible has been met.
Coverage Limits and Exclusions
Insurance policies often have limits on the amount they will pay for certain services or treatments. These limits can be annual, lifetime, or specific to a particular condition or treatment. Additionally, insurance policies may exclude certain services, treatments, or conditions from coverage. It’s crucial to understand these limits and exclusions to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
Benefits of Healthcare Insurance
Healthcare insurance offers a multitude of benefits, both tangible and intangible, that contribute to the overall well-being of individuals and society as a whole. These benefits extend beyond the immediate financial protection and peace of mind that insurance provides.
Financial Protection
Perhaps the most significant benefit of healthcare insurance is the financial protection it offers. Medical care, especially for serious conditions or injuries, can be extremely costly. Without insurance, individuals may face substantial financial burdens that can lead to debt or even bankruptcy. Insurance helps mitigate these risks by covering a portion or all of the costs associated with medical treatment.
Access to Healthcare Services
Healthcare insurance plays a crucial role in ensuring access to healthcare services. With insurance, individuals can seek medical care without worrying about the immediate financial impact. This access is particularly vital for preventive care, which can help identify and address health issues early on, potentially preventing more serious and costly health problems down the line.
Peace of Mind
Knowing that one has healthcare insurance can provide a significant sense of security and peace of mind. Individuals don’t have to worry about the financial implications of unexpected illnesses or injuries, allowing them to focus on their health and recovery without the added stress of potential financial ruin.
Enhanced Healthcare Quality
Insurance often leads to improved healthcare quality. Insured individuals are more likely to seek regular check-ups and screenings, which can help detect health issues early and improve overall health outcomes. Additionally, insurance often covers a wide range of services, from primary care to specialized treatments, ensuring that individuals have access to the care they need.
Network of Healthcare Providers
Most healthcare insurance plans come with a network of preferred healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and other medical facilities. These networks can offer lower costs and better quality of care, as insurance companies negotiate rates with these providers. This network system also makes it easier for insured individuals to find and access healthcare services.
Challenges and Future of Healthcare Insurance
While healthcare insurance offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges that impact its effectiveness and accessibility. Understanding these challenges is crucial for navigating the current landscape and shaping the future of healthcare insurance.
Cost of Healthcare Insurance
The cost of healthcare insurance is a significant challenge, with premiums, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket expenses rising faster than wages for many individuals and families. This increase in costs can make insurance unaffordable for some, leading to underinsurance or even lack of coverage altogether.
Underinsurance and Gaps in Coverage
Underinsurance occurs when individuals have insurance but it doesn’t provide adequate coverage for their needs. This can lead to high out-of-pocket expenses and financial hardship, particularly for those with chronic conditions or serious illnesses. Gaps in coverage can also arise, leaving certain services or treatments uncovered, which can result in unexpected costs.
Administrative Complexity
The administrative processes involved in healthcare insurance can be complex and time-consuming. From understanding policy terms and conditions to filing claims and managing reimbursements, the process can be daunting for many individuals. This complexity can lead to errors, delays, and frustration, impacting the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the insurance system.
Future Implications and Innovations
The future of healthcare insurance is likely to see continued innovation and change. With the increasing focus on value-based care and the integration of technology, insurance companies are exploring new ways to improve access, quality, and affordability. This includes the use of digital tools for claims processing, the development of new insurance models, and a greater emphasis on preventive care and wellness.
Addressing the Challenges
Addressing the challenges in healthcare insurance requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes policies and initiatives aimed at controlling healthcare costs, improving insurance coverage and affordability, and simplifying administrative processes. Additionally, a focus on consumer education and empowerment can help individuals make more informed choices about their insurance coverage and healthcare decisions.
Conclusion

Healthcare insurance is a vital component of modern healthcare systems, offering financial protection, access to healthcare services, and peace of mind for individuals and families. While it faces challenges, such as rising costs and administrative complexity, ongoing innovations and reforms are working to address these issues and improve the overall effectiveness and accessibility of healthcare insurance.
By understanding the key components, benefits, and challenges of healthcare insurance, individuals can make more informed decisions about their coverage and navigate the healthcare system with greater confidence and security.
What are some common exclusions in healthcare insurance policies?
+Common exclusions in healthcare insurance policies can vary, but often include pre-existing conditions, cosmetic procedures, certain types of mental health treatment, and alternative or complementary therapies. It’s essential to review the policy’s exclusions carefully to understand what’s covered and what’s not.
How can I choose the right healthcare insurance plan for my needs?
+Choosing the right healthcare insurance plan involves considering factors such as your health needs, the cost of premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, the network of providers, and the coverage limits and exclusions. It’s beneficial to compare different plans and seek advice from insurance experts or financial advisors to make an informed decision.
What are some tips for reducing healthcare insurance costs?
+To reduce healthcare insurance costs, consider enrolling in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) with a health savings account (HSA), taking advantage of wellness programs and preventive care services, and comparing quotes from multiple insurance companies. Additionally, staying healthy and avoiding unnecessary medical treatments can help keep costs down.