Types Of Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance, also known as permanent life insurance, is a type of financial protection that offers lifetime coverage and provides a death benefit to beneficiaries. Unlike term life insurance, which has a fixed duration, whole life insurance remains in force for the insured's entire life, as long as premiums are paid. This makes it a popular choice for individuals seeking long-term financial security and peace of mind.
The whole life insurance market has evolved significantly over the years, offering a range of policy types to cater to diverse needs and preferences. Each type comes with its own set of features, benefits, and potential drawbacks. Understanding the different types of whole life insurance policies is crucial for individuals seeking to make informed decisions about their financial future.
Traditional Whole Life Insurance

Traditional whole life insurance is the classic form of permanent life insurance. It offers a guaranteed death benefit, premium payments, and a cash value component that accumulates over time. Here’s a closer look at its key features:
- Guaranteed Death Benefit: The policy pays out a predetermined sum to the beneficiary upon the insured’s death, regardless of when it occurs.
- Level Premiums: Policyholders pay a fixed premium amount throughout their lifetime, ensuring affordability and financial predictability.
- Cash Value Accumulation: A portion of the premium goes towards building cash value, which can be borrowed against or used for various financial purposes.
- Tax Advantages: The cash value grows tax-deferred, and if withdrawn or used within policy guidelines, it may be tax-free.
Traditional whole life insurance is ideal for those seeking long-term financial security and a stable investment component. However, it may not be the most cost-effective option for individuals who don't require the investment aspect of the policy.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Guaranteed death benefit provides peace of mind.
- Stable, predictable premiums over the long term.
- Cash value accumulates tax-deferred, offering a potential source of emergency funds or retirement income.
- Builds financial discipline through consistent premium payments.
Cons:
- Higher initial premiums compared to other life insurance types.
- Cash value accumulation may be slower compared to other policies.
- Not as flexible as other whole life insurance types in terms of policy design and customization.
Universal Life Insurance

Universal life insurance is a flexible variant of whole life insurance, offering policyholders more control over premium payments and the death benefit. It combines the protection of life insurance with the potential for cash value growth. Here's an overview of its key characteristics:
- Flexible Premiums: Policyholders can adjust the amount and frequency of premium payments within certain limits, allowing for financial flexibility.
- Variable Death Benefit: The death benefit can be adjusted over time, providing the insured with the ability to increase or decrease coverage based on changing needs.
- Cash Value Growth: Similar to traditional whole life, universal life insurance policies build cash value, which can be accessed or used for various financial purposes.
- Interest Earnings: The cash value component earns interest, potentially increasing the policy's value over time.
Universal life insurance is well-suited for individuals who value flexibility in their financial planning. It allows for adjustments to coverage and premiums based on life events and changing financial goals.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Flexible premiums and death benefit adjustments provide adaptability to changing financial needs.
- Potential for higher cash value growth compared to traditional whole life.
- Offers a balance between life insurance coverage and investment potential.
- Interest earnings on cash value can provide additional financial benefits.
Cons:
- May be more complex to understand and manage compared to traditional whole life.
- Interest rates on cash value may be lower than other investment options.
- Policyholders must actively manage premiums and death benefit to avoid policy lapse.
Variable Universal Life Insurance
Variable universal life insurance (VUL) is a more dynamic form of whole life insurance, offering policyholders the ability to invest a portion of their premiums in a range of investment options. This type of policy combines the flexibility of universal life with the potential for higher investment returns.
Key Features
- Investment Options: Policyholders can choose from a variety of investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, to invest a portion of their premiums.
- Flexible Premiums and Death Benefit: Similar to universal life, VUL policies allow for adjustments in premiums and death benefit over time.
- Potential for Higher Returns: By investing in the stock market or other investment options, policyholders have the potential to earn higher returns on their cash value.
- Death Benefit Flexibility: The death benefit can be adjusted to reflect the performance of the chosen investments.
Variable universal life insurance is attractive to individuals seeking both life insurance coverage and the opportunity to grow their investment portfolio. However, it carries a higher level of risk compared to traditional or universal life insurance due to its investment-linked nature.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Offers the potential for higher investment returns compared to traditional or universal life insurance.
- Provides flexibility in premium payments and death benefit adjustments.
- Policyholders can actively manage their investment portfolio within the policy.
- May be more cost-effective for those seeking both life insurance and investment opportunities.
Cons:
Guaranteed Universal Life Insurance
Guaranteed universal life insurance (GUL) is a type of permanent life insurance that offers a fixed death benefit and a guaranteed level premium for the insured's entire life. It provides a balance between the flexibility of universal life and the stability of traditional whole life.
Key Characteristics
- Fixed Death Benefit: The policy guarantees a predetermined death benefit, ensuring beneficiaries receive a specified amount upon the insured’s death.
- Guaranteed Level Premiums: Policyholders pay a fixed premium amount throughout their lifetime, providing financial predictability.
- Cash Value Growth: GUL policies build cash value over time, which can be used for various financial purposes, such as retirement income or emergency funds.
- Simplicity: GUL policies are often simpler to understand and manage compared to other whole life insurance types.
Guaranteed universal life insurance is an appealing option for individuals seeking a straightforward, stable life insurance policy with a guaranteed death benefit and level premiums. It provides a balance between the flexibility of universal life and the investment potential of variable universal life.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Offers a guaranteed death benefit, providing peace of mind.
- Level premiums ensure financial predictability over the long term.
- Cash value growth provides a potential source of funds for various financial needs.
- Simpler to understand and manage compared to other whole life insurance types.
Cons:
- May not offer the same level of flexibility as universal or variable universal life.
- Cash value growth may be slower compared to other policies with investment components.
- Limited customization options compared to more flexible whole life insurance types.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Indexed universal life insurance (IUL) is a type of permanent life insurance that links the policy's cash value to the performance of a specific index, typically a stock market index. It combines the stability of whole life insurance with the potential for higher investment returns.
Key Features
- Index-Linked Cash Value: The policy’s cash value is tied to the performance of a chosen stock market index, allowing for potential higher returns.
- Limited Risk Exposure: While the cash value can grow based on the index’s performance, it is typically protected from market downturns, offering a balance between risk and stability.
- Flexible Premiums and Death Benefit: Similar to universal life insurance, IUL policies allow for adjustments in premiums and death benefit over time.
- Potential for Tax-Deferred Growth: The cash value grows tax-deferred, providing a potential source of tax-efficient retirement income.
Indexed universal life insurance is an attractive option for individuals seeking a balance between life insurance coverage and investment potential. It offers the potential for higher returns while mitigating some of the risks associated with direct stock market investments.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Potential for higher investment returns compared to traditional whole life.
- Provides protection from market downturns, offering stability.
- Offers tax-deferred growth on cash value, which can be used for various financial purposes.
- Flexible premiums and death benefit adjustments allow for financial adaptability.
Cons:
- May be more complex to understand and manage compared to traditional whole life.
- Performance is linked to the chosen index, which may not always provide the desired returns.
- Policyholders must actively manage premiums and death benefit to avoid policy lapse.
Final Thoughts on Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance, in its various forms, offers a range of options to meet diverse financial needs and preferences. From the stability of traditional whole life to the flexibility of universal and variable universal life, there is a policy type to suit every individual's circumstances. It's essential for policyholders to carefully consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and the long-term implications of each policy type before making a decision.
As with any financial decision, seeking professional advice and thoroughly understanding the terms and conditions of the policy is crucial. Whole life insurance can be a powerful tool for financial security and wealth accumulation, but it requires careful consideration and ongoing management to maximize its benefits.
FAQ
What is the primary advantage of whole life insurance over term life insurance?
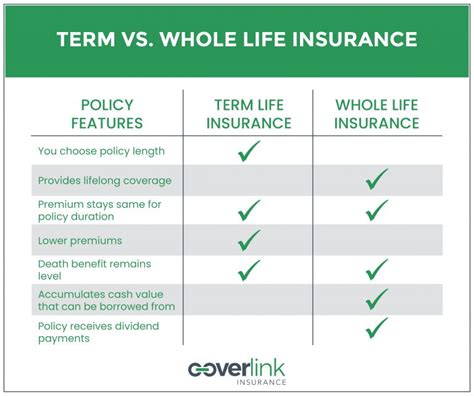
+Whole life insurance offers lifetime coverage, ensuring a guaranteed death benefit to beneficiaries. Term life insurance, on the other hand, has a fixed duration and may not provide coverage throughout an individual’s entire life.
How do premiums for whole life insurance compare to term life insurance?
+Whole life insurance typically has higher initial premiums compared to term life insurance. However, term life insurance premiums can increase significantly as the policyholder ages, while whole life insurance premiums remain level over time.
Can whole life insurance policies be customized to meet specific needs?
+Yes, certain types of whole life insurance, such as universal and variable universal life, offer flexibility in terms of premium payments and death benefit adjustments. This allows policyholders to tailor the policy to their changing financial needs and goals.



