Types Of Healthcare Insurance
Healthcare insurance is a vital aspect of modern life, providing individuals and families with financial protection and access to essential medical services. With the rising costs of healthcare, having adequate insurance coverage is more important than ever. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various types of healthcare insurance, exploring their features, benefits, and considerations to help you make informed decisions about your healthcare needs.
Understanding the Landscape of Healthcare Insurance
Healthcare insurance is a complex system designed to cover the costs associated with medical care, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and various medical procedures. The primary goal is to ensure individuals can access the necessary healthcare services without facing financial hardship.
The types of healthcare insurance available can vary depending on the country and its healthcare system. In this article, we will focus on the United States, where healthcare insurance plays a significant role in the healthcare landscape. Understanding the different options is crucial for individuals and families to navigate the complex world of healthcare and make choices that align with their specific needs and circumstances.
Key Types of Healthcare Insurance

Healthcare insurance comes in various forms, each with its own set of features and coverage options. Here are some of the most common types of healthcare insurance:
1. Private Health Insurance
Private health insurance is typically purchased by individuals or provided through employers. It offers a wide range of coverage options and is often customized to meet the specific needs of the insured. Private plans can be comprehensive, covering a broad spectrum of medical services, or they can be more focused, targeting specific areas like dental or vision care.
One of the key advantages of private health insurance is the flexibility it offers. Policyholders can choose from various networks, including PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), and POS (Point of Service) plans. These networks determine the healthcare providers and facilities the insured can access, with PPOs typically offering the most flexibility in provider choice.
Private insurance plans also come with different cost structures. Some plans have higher premiums but lower deductibles, while others may have lower premiums with higher out-of-pocket costs. The choice depends on individual preferences and expected healthcare needs.
2. Medicare
Medicare is a government-funded healthcare program primarily designed for individuals aged 65 and older. However, it also covers certain younger individuals with specific disabilities or conditions. Medicare is divided into different parts, each covering various aspects of healthcare:
- Part A (Hospital Insurance): Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, and some home healthcare services.
- Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers outpatient medical services, including doctor visits, lab tests, and some preventive care.
- Part C (Medicare Advantage): These are private insurance plans approved by Medicare, offering an alternative to traditional Medicare. They often include additional benefits beyond Parts A and B.
- Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Provides coverage for prescription medications, with various plan options available.
Medicare offers a safety net for older adults and those with specific health conditions, ensuring they have access to necessary medical care without facing overwhelming financial burdens.
3. Medicaid
Medicaid is another government-funded healthcare program, but unlike Medicare, it is primarily designed for individuals and families with low incomes and limited resources. Medicaid coverage can vary from state to state, as each state administers its own program within federal guidelines.
Medicaid provides comprehensive healthcare coverage, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and various other medical services. It often covers a wider range of services compared to private insurance, making it an essential safety net for those who cannot afford private coverage.
4. Employer-Sponsored Insurance
Many individuals in the United States receive their healthcare insurance through their employers. Employer-sponsored insurance plans are typically offered as part of an employee benefits package. These plans can vary widely in terms of coverage and cost, as employers have the flexibility to choose the insurance provider and design the plan.
Employer-sponsored insurance often comes with the advantage of lower premiums, as employers contribute to the cost. Additionally, these plans may have a broader network of providers, making it easier for employees to access healthcare services without incurring high out-of-pocket expenses.
5. Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance plans are designed to provide temporary coverage for individuals who may be between jobs, transitioning between plans, or facing other short-term gaps in coverage. These plans typically have a limited duration, often lasting less than a year, and offer more basic coverage compared to long-term plans.
While short-term plans can be a cost-effective solution for temporary coverage needs, they often come with restrictions and limitations. For instance, they may have higher out-of-pocket costs, exclude pre-existing conditions, and have limited coverage for certain services. It's important to carefully review the terms and conditions before opting for a short-term plan.
6. High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
High-deductible health plans are a type of insurance plan with a higher deductible compared to traditional plans. The deductible is the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. HDHPs are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), which allow individuals to save pre-tax dollars to cover their healthcare expenses.
HDHPs can be a cost-effective option for individuals who anticipate minimal healthcare needs, as they typically have lower premiums. However, it's important to consider the potential risks of higher out-of-pocket costs if unexpected medical expenses arise.
Considerations and Choosing the Right Plan
When selecting a healthcare insurance plan, several factors come into play. Here are some key considerations to guide your decision-making process:
- Coverage Needs: Assess your healthcare needs and those of your family. Consider factors like chronic conditions, prescription medications, and the likelihood of needing specialized care.
- Cost: Evaluate the premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums. Understand how these costs align with your budget and financial capabilities.
- Provider Network: Review the network of healthcare providers and facilities covered by the plan. Ensure that your preferred doctors and hospitals are included in the network.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: If you rely on prescription medications, ensure the plan covers your specific drugs and has a pharmacy network that includes your preferred pharmacies.
- Additional Benefits: Some plans offer extra benefits like dental, vision, or mental health coverage. Consider whether these additional benefits are important to you.
- Plan Flexibility: Evaluate the flexibility of the plan, including the ability to change doctors or access out-of-network providers if necessary.
Additionally, it's essential to research and compare different insurance providers and plans to find the one that best fits your needs. Seek advice from insurance brokers or financial advisors who can provide expert guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Navigating the Future of Healthcare Insurance
The healthcare insurance landscape is constantly evolving, with new innovations and challenges emerging. As technology advances, the industry is moving towards more digital and personalized solutions, offering greater convenience and efficiency. Telehealth services, for instance, have gained prominence, allowing individuals to access healthcare remotely, especially during times of limited mobility or increased health risks.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics is revolutionizing the way healthcare insurance is administered. These technologies can improve risk assessment, identify patterns in healthcare utilization, and enhance the overall efficiency of insurance processes. As a result, insurance providers can offer more tailored and cost-effective plans, benefiting both policyholders and the healthcare system as a whole.
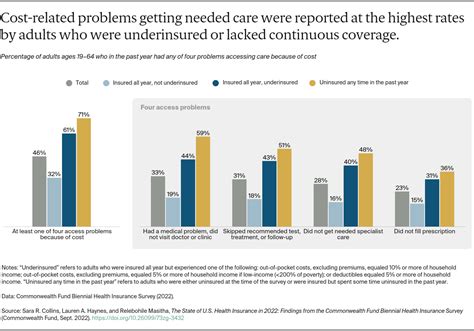
Despite these advancements, the rising costs of healthcare remain a significant challenge. Insurance providers, policymakers, and healthcare stakeholders are actively working to address this issue through various initiatives. These efforts include promoting preventive care, incentivizing healthy lifestyles, and exploring innovative payment models that focus on value-based care rather than volume-based services.
Conclusion

Healthcare insurance is a complex but essential component of modern healthcare systems. Understanding the different types of insurance available empowers individuals to make informed choices about their healthcare coverage. Whether it’s private insurance, government-funded programs like Medicare and Medicaid, or employer-sponsored plans, each option offers unique benefits and considerations.
As the healthcare industry adapts to new challenges and opportunities, staying engaged and proactive in your healthcare decisions is more important than ever. By staying informed and seeking expert advice, you can navigate the complex world of healthcare insurance with confidence, ensuring you have the coverage you need to access quality medical care.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid?
+Medicare is primarily designed for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with specific disabilities or conditions. It covers a range of healthcare services and is divided into different parts (A, B, C, and D). Medicaid, on the other hand, is intended for individuals and families with low incomes and limited resources. It provides comprehensive healthcare coverage, but the specific benefits can vary from state to state.
Can I have both Medicare and Medicaid coverage?
+Yes, it is possible to have dual eligibility for both Medicare and Medicaid. This is often referred to as “Medi-Medi” coverage. Individuals who qualify for both programs can benefit from the combined coverage, which can provide more comprehensive healthcare services and reduced out-of-pocket costs.
What are the advantages of employer-sponsored insurance plans?
+Employer-sponsored insurance plans offer several advantages. They typically come with lower premiums due to the employer’s contribution. These plans often have a broader network of healthcare providers, making it easier for employees to access medical services without incurring high out-of-pocket expenses. Additionally, employer-sponsored plans may offer additional benefits and incentives, such as wellness programs or discounted gym memberships.



