Types Of Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance is an essential aspect of modern healthcare systems, providing individuals and families with financial protection and access to necessary medical services. With a wide range of options available, understanding the different types of health insurance plans is crucial for making informed decisions about coverage. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the various health insurance plans, their features, and how they cater to diverse healthcare needs.
Understanding Health Insurance Plans
Health insurance plans serve as a financial safety net, ensuring individuals can receive medical treatment without incurring excessive costs. These plans are designed to cover a range of healthcare services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care. The type of plan you choose depends on various factors such as your health status, budget, and preferred level of flexibility and coverage.
Key Types of Health Insurance Plans
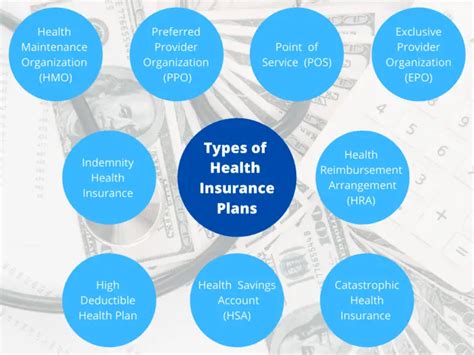
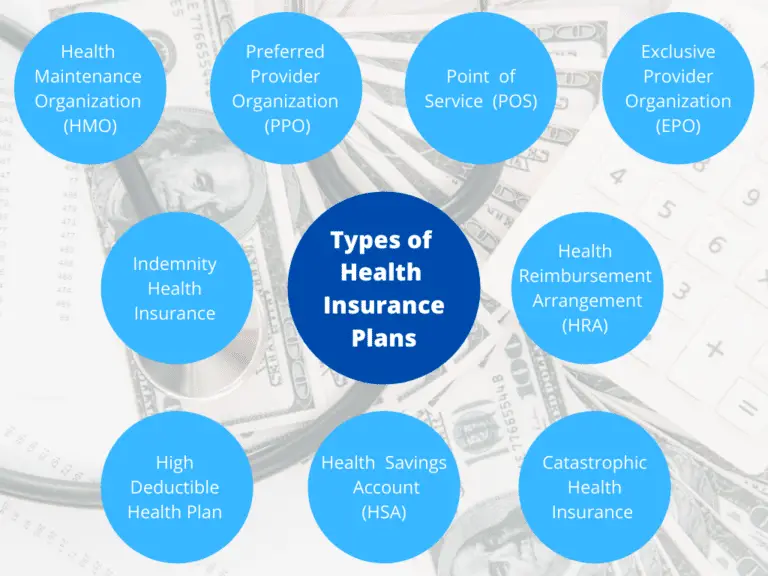
The health insurance landscape is diverse, offering several plan types to cater to different needs. Here’s an overview of the most common types of health insurance plans:
1. Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)
HMOs are known for their cost-effectiveness and emphasis on preventive care. With an HMO plan, you choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates your healthcare. Referrals are required to see specialists, and you typically pay lower out-of-pocket costs. HMOs often have a network of preferred providers, and services outside this network may not be covered.
Key Features:
- Low premiums and deductibles.
- Emphasis on preventive care and wellness.
- Requires referrals for specialist visits.
- May have limited flexibility in choosing providers.
2. Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)
PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing you to choose from a network of preferred providers. You can visit specialists without referrals, and out-of-network services may be covered at a higher cost. PPOs strike a balance between cost and flexibility, making them a popular choice.
Key Features:
- Greater flexibility in choosing providers.
- No referrals needed for specialists.
- Typically covers out-of-network services (at a higher cost)
- Mid-range premiums and deductibles.
3. Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs)
EPOs are similar to PPOs but with a more restricted network. You have the freedom to choose from a network of providers without referrals, but services outside this network are typically not covered. EPOs are a cost-effective option for those who prefer a smaller network of trusted providers.
Key Features:
- Smaller, exclusive provider network.
- No referrals needed for in-network providers.
- Out-of-network services are generally not covered.
- Lower premiums compared to PPOs.
4. Point of Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs. You choose a primary care physician and typically need referrals for specialists. However, you have the flexibility to choose in-network or out-of-network providers, with varying levels of coverage and cost.
Key Features:
- Hybrid of HMO and PPO features.
- Requires referrals for specialists.
- Flexibility to choose in-network or out-of-network providers.
- Cost and coverage vary based on provider choice.
5. High Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
HDHPs are known for their high deductibles but offer lower premiums. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing you to save money tax-free for healthcare expenses. HDHPs are suitable for those who prioritize lower monthly costs and have the means to cover initial expenses.
Key Features:
- Lower premiums but higher deductibles.
- Can be paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- Suitable for individuals with limited healthcare needs.
- May require careful budgeting for healthcare expenses.
6. Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance plans offer temporary coverage for those facing gaps in their long-term coverage. These plans are typically more affordable but have limited benefits and may not cover pre-existing conditions.
Key Features:
- Affordable temporary coverage.
- Limited benefits and coverage.
- May exclude pre-existing conditions.
- Suitable for bridging coverage gaps.
7. Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare and Medicaid are government-sponsored health insurance programs in the United States. Medicare is primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, while Medicaid caters to low-income individuals and families. These programs provide essential coverage and often come with additional benefits.
Key Features:
- Medicare: Coverage for older adults.
- Medicaid: Coverage for low-income individuals and families.
- Comprehensive benefits and low out-of-pocket costs.
- Government-funded, with specific eligibility criteria.
Comparative Analysis: Choosing the Right Plan
Selecting the right health insurance plan involves considering your personal circumstances and healthcare needs. Here’s a comparative analysis to help you make an informed decision:
| Plan Type | Flexibility | Cost | Preventive Care |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | Limited (requires referrals) | Low premiums and deductibles | Emphasis on preventive care |
| PPO | High (no referrals needed) | Mid-range premiums and deductibles | Balanced approach |
| EPO | Moderate (in-network only) | Lower premiums | Focus on network providers |
| POS | Hybrid (referrals for specialists) | Varies based on provider choice | Balanced approach |
| HDHP | Varies (depends on HSA) | Lower premiums, higher deductibles | May have limited coverage |
| Short-Term | Limited (temporary coverage) | Affordable | Basic coverage |
| Medicare/Medicaid | Varies (based on program) | Low out-of-pocket costs | Comprehensive benefits |

Performance Analysis: Real-World Examples
To illustrate the impact of different health insurance plans, let’s consider a few real-world scenarios:
Scenario 1: Young Professional with Limited Healthcare Needs
Plan Choice: High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) with Health Savings Account (HSA)
A young professional with minimal healthcare needs may opt for an HDHP to save on premiums. By contributing to an HSA, they can cover initial expenses and save for future healthcare costs. This plan provides flexibility and the potential for long-term financial benefits.
Scenario 2: Family with Regular Healthcare Visits
Plan Choice: Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
A family with regular doctor visits and a preference for specific providers might choose a PPO. This plan offers flexibility in choosing providers without referrals and provides coverage for a range of services, ensuring the family’s healthcare needs are met without excessive costs.
Scenario 3: Older Adult on Fixed Income
Plan Choice: Medicare (Part A and Part B)
An older adult on a fixed income may opt for Medicare, a government-sponsored program. Medicare provides comprehensive coverage with low out-of-pocket costs, ensuring access to necessary healthcare services without financial strain.
Future Implications: The Evolving Landscape of Health Insurance

The health insurance landscape is dynamic, influenced by advancements in medicine, changes in healthcare regulations, and evolving consumer needs. Here are some key trends and future implications to consider:
- Telehealth and Digital Health: The integration of telehealth services and digital health technologies is expected to continue, offering convenient access to healthcare and potentially reducing costs.
- Value-Based Care: There is a growing focus on value-based care models, where providers are incentivized to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care. This shift may lead to more efficient healthcare delivery and improved patient outcomes.
- Consumer Engagement: Health insurance providers are increasingly emphasizing consumer engagement and education. This includes offering resources and tools to help individuals make informed healthcare decisions and manage their health more effectively.
- Customized Plans: The future may see a shift towards more personalized health insurance plans. With advancements in data analytics, insurers could offer tailored plans based on individual health profiles and preferences, optimizing coverage and cost.
- Global Health Coverage: As the world becomes more interconnected, there may be a growing demand for health insurance plans that offer international coverage. This would benefit individuals who travel frequently or work globally, ensuring seamless access to healthcare regardless of location.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I choose the right health insurance plan for my needs?
+
Consider factors such as your health status, budget, and preferred level of flexibility. Assess your healthcare needs and compare plans based on coverage, cost, and provider networks. Seek advice from insurance experts or brokers to make an informed decision.
What are the benefits of having health insurance?
+
Health insurance provides financial protection, ensuring you can access necessary medical care without incurring overwhelming costs. It covers a range of services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and medications, making healthcare more affordable and accessible.
Can I change my health insurance plan if I’m not satisfied?
+
Yes, you have the option to switch health insurance plans during the annual open enrollment period or if you experience a qualifying life event, such as marriage, divorce, or a change in employment. Review your options and make changes to find a plan that better suits your needs.



