Personal Health Insurance Cost
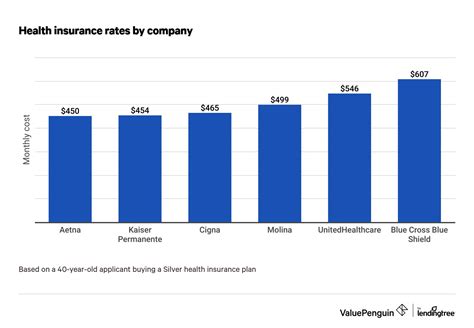
The cost of personal health insurance is a significant concern for individuals and families, especially in regions where healthcare is primarily financed through private insurance. With rising medical expenses and the complexities of insurance plans, understanding the factors that influence insurance premiums is crucial for making informed decisions. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of personal health insurance costs, providing a comprehensive guide to help individuals navigate this critical aspect of their financial well-being.
Unraveling the Factors Behind Personal Health Insurance Costs
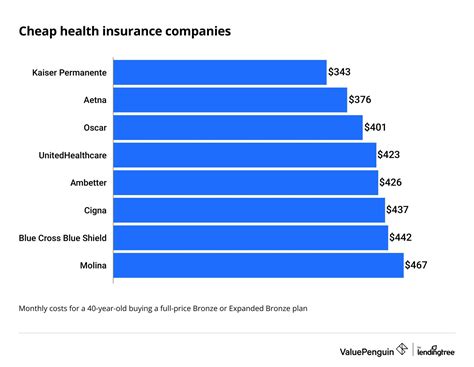
The price of personal health insurance is influenced by a multitude of variables, each playing a unique role in determining the overall cost. These factors are often interconnected and can vary significantly based on individual circumstances and the specific insurance market.
Demographic Factors
Demographics, such as age, gender, and location, are fundamental determinants of health insurance costs. Generally, younger individuals tend to pay lower premiums as they are statistically less likely to require extensive medical care. Conversely, older adults, particularly those over 65, often face higher premiums due to increased healthcare needs associated with aging.
Gender can also impact insurance costs, with insurers often charging different rates for men and women based on historical patterns of healthcare utilization. For instance, women may face higher premiums due to pregnancy-related care and certain gender-specific health conditions.
Location is another critical factor. The cost of living and the availability of healthcare services in a particular region can significantly influence insurance premiums. Areas with higher concentrations of healthcare facilities and specialists may have higher insurance costs, while more rural or less populated regions might offer more affordable options.
| Demographic Factor | Impact on Premium |
|---|---|
| Age | Premiums generally increase with age due to increased healthcare needs. |
| Gender | Insurers may charge different rates based on gender-specific healthcare utilization patterns. |
| Location | Cost of living and availability of healthcare services can drive insurance costs. |

Medical History and Pre-Existing Conditions
An individual’s medical history is a pivotal factor in determining insurance premiums. Those with a history of serious illnesses or chronic conditions often face higher premiums or may even be denied coverage altogether. Pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or certain mental health disorders, can significantly impact the cost of insurance, as they indicate a higher likelihood of future healthcare needs.
Insurers carefully evaluate an applicant's medical history to assess the risk associated with providing coverage. This risk assessment process, known as underwriting, considers the severity and stability of any pre-existing conditions. For instance, a well-managed chronic condition might result in only a slight increase in premiums, while a more severe or unstable condition could lead to significantly higher costs or even coverage denial.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices and behaviors can also influence the cost of personal health insurance. Individuals who engage in risky behaviors, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or participation in extreme sports, often face higher premiums. These activities are associated with increased health risks and, consequently, higher healthcare costs.
Furthermore, lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor dietary habits can contribute to various health issues over time. Insurers take these factors into account when assessing an individual's risk profile, as they can lead to chronic diseases and more frequent healthcare utilization.
Plan Design and Coverage Options
The design and coverage options of a health insurance plan are key determinants of its cost. Plans vary significantly in terms of the services they cover, the providers included in their networks, and the level of financial protection they offer. Generally, plans with broader coverage and more extensive provider networks tend to be more expensive.
Deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance are essential components of insurance plans that impact the out-of-pocket costs for policyholders. Plans with higher deductibles (the amount an individual must pay before insurance coverage kicks in) often have lower premiums, as policyholders are expected to shoulder more financial responsibility for their healthcare. Conversely, plans with lower deductibles typically have higher premiums, providing more immediate coverage but potentially resulting in higher out-of-pocket costs over time.
The scope of coverage, including whether the plan covers prescription drugs, mental health services, or specialized treatments, also influences the premium. Plans with comprehensive coverage for a wide range of services tend to be more expensive than those with more limited coverage.
| Plan Design Factor | Impact on Premium |
|---|---|
| Coverage Scope | Comprehensive plans covering a wide range of services often have higher premiums. |
| Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Costs | Higher deductibles usually result in lower premiums, while plans with lower deductibles often have higher premiums. |
| Provider Networks | Plans with larger, more extensive provider networks tend to be more expensive. |
Market Competition and Regulation
The insurance market’s competitive landscape and regulatory environment also play a role in determining health insurance costs. In highly competitive markets, insurers may offer more affordable plans to attract customers, while less competitive markets might result in higher premiums due to limited options.
Regulatory policies, such as mandates requiring insurers to cover specific services or conditions, can influence the structure and cost of insurance plans. Additionally, state and federal regulations regarding premium rating methods and insurer financial requirements can impact the overall affordability of health insurance.
Strategies for Managing Personal Health Insurance Costs

Navigating the complexities of personal health insurance costs can be challenging, but there are strategies individuals can employ to manage these expenses effectively.
Understanding Your Healthcare Needs
The first step in managing health insurance costs is to assess your individual and family healthcare needs. Consider your current health status, any pre-existing conditions, and your expected healthcare utilization over the coming year. Understanding your healthcare needs will help you choose a plan that provides adequate coverage without unnecessary expenses.
If you anticipate significant healthcare expenses, such as ongoing treatment for a chronic condition or an upcoming major medical procedure, ensure your insurance plan covers these services adequately. Conversely, if you're generally healthy and don't anticipate major healthcare needs, a plan with a higher deductible and lower premiums might be a more cost-effective option.
Comparing Plans and Providers
Shopping around and comparing different health insurance plans and providers is essential to finding the most affordable option that meets your needs. Utilize online comparison tools and resources, and reach out to insurance brokers or agents who can provide personalized advice based on your specific circumstances.
When comparing plans, pay close attention to the coverage details, including the types of services covered, the providers in the network, and the out-of-pocket costs such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. Ensure the plan you choose aligns with your healthcare needs and preferences.
Exploring Discounts and Subsidies
Many insurers offer discounts and subsidies to make health insurance more affordable. These discounts may be available for various reasons, such as maintaining continuous coverage, paying premiums on time, or enrolling in specific wellness programs.
Additionally, individuals with lower incomes may qualify for government-sponsored programs that provide financial assistance for health insurance premiums. These programs, such as Medicaid or the Affordable Care Act's premium tax credits, can significantly reduce the cost of health insurance, making coverage more accessible for those with limited financial resources.
Adopting a Healthy Lifestyle
Leading a healthy lifestyle can not only improve your overall well-being but also help reduce your health insurance costs. Insurers often offer incentives and discounts for policyholders who maintain healthy habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding risky behaviors like smoking.
Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help prevent certain chronic diseases and reduce your overall healthcare needs, potentially leading to lower insurance premiums over time. This approach aligns with the concept of "wellness incentives," which many insurers are now incorporating into their plans to encourage policyholders to prioritize their health.
Utilizing Preventive Care Services
Many health insurance plans cover a range of preventive care services, such as annual physical exams, immunizations, and screenings for various health conditions. Taking advantage of these services can help detect potential health issues early on, when they are often more treatable and less costly to manage.
Preventive care is a cornerstone of modern healthcare and is often covered at little to no cost under most insurance plans. By staying on top of your preventive care needs, you can not only improve your health but also potentially reduce your future healthcare expenses, leading to more affordable insurance premiums.
The Future of Personal Health Insurance Costs
The landscape of personal health insurance is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in medical technology, shifts in healthcare delivery models, and changes in regulatory environments. As we look to the future, several key trends and developments are likely to shape the cost of health insurance.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in healthcare technology are expected to continue transforming the industry, potentially leading to more efficient and cost-effective healthcare delivery. Telemedicine, for instance, has gained significant traction during the COVID-19 pandemic, offering a convenient and often more affordable alternative to in-person medical visits. As telemedicine becomes more widespread, it could help reduce the overall cost of healthcare, benefiting both consumers and insurers.
Additionally, the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in healthcare can lead to more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans, potentially reducing the need for costly and invasive procedures. These technological advancements could help contain healthcare costs, which would ultimately impact the affordability of personal health insurance.
Value-Based Care Models
The shift towards value-based care models, where healthcare providers are reimbursed based on patient health outcomes rather than the volume of services provided, is gaining momentum. This approach aims to incentivize providers to deliver high-quality, efficient care, potentially reducing overall healthcare costs.
Value-based care models often involve coordinated care teams, including primary care physicians, specialists, and other healthcare professionals, who work together to manage a patient's health. By emphasizing prevention, early intervention, and efficient treatment, these models could lead to more affordable healthcare, which would positively impact personal health insurance costs.
Regulatory Changes and Market Dynamics
The regulatory environment and market dynamics surrounding personal health insurance are subject to ongoing changes, which can significantly impact insurance costs. For instance, policy changes at the state or federal level, such as modifications to premium rating methods or mandates for covering specific services, can influence the structure and affordability of insurance plans.
Market competition also plays a crucial role in determining insurance costs. As the healthcare insurance market becomes more competitive, insurers may be incentivized to offer more affordable plans to attract customers. On the other hand, in less competitive markets, consumers might face higher insurance costs due to limited options.
Consumer Empowerment and Education
As consumers become more educated about their healthcare options and costs, they are increasingly driving demand for more transparent and affordable healthcare services. This shift in consumer behavior is expected to continue, potentially leading to greater pressure on healthcare providers and insurers to offer more cost-effective solutions.
Empowered consumers are more likely to shop around for the best insurance deals, compare plan options, and make informed decisions about their healthcare needs. This increased consumer engagement can drive market competition, leading to more innovative and affordable health insurance options.
How do insurance companies determine the cost of health insurance plans?
+Insurance companies use a variety of factors to determine the cost of health insurance plans, including demographic characteristics like age, gender, and location; medical history and pre-existing conditions; lifestyle factors such as smoking or extreme sports participation; plan design and coverage options; and market competition and regulation.
Are there any strategies to reduce the cost of personal health insurance?
+Yes, individuals can employ several strategies to manage health insurance costs, such as understanding their healthcare needs and choosing an appropriate plan; comparing different plans and providers to find the best value; exploring discounts and subsidies; adopting a healthy lifestyle; and utilizing preventive care services to stay on top of their health.
What role does technology play in the future of health insurance costs?
+Advancements in healthcare technology, such as telemedicine and AI, are expected to lead to more efficient and cost-effective healthcare delivery. These innovations could help reduce overall healthcare costs, which would positively impact the affordability of personal health insurance.



