Medical & Health Insurance

The landscape of medical and health insurance is a complex and ever-evolving field, playing a crucial role in the lives of individuals and families worldwide. With rising healthcare costs and the need for accessible, quality medical services, understanding the intricacies of this industry is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of medical and health insurance, exploring its key components, benefits, and implications.
Understanding Medical and Health Insurance
Medical and health insurance, often referred to simply as health insurance, is a type of insurance coverage that provides financial protection against the high costs of medical care. It ensures that individuals have access to necessary healthcare services without facing catastrophic financial burdens. This form of insurance has become an integral part of modern healthcare systems, offering a safety net for unexpected illnesses, accidents, and routine medical needs.
Key Features of Medical Insurance
Medical insurance policies vary widely, but they typically share some fundamental characteristics. Firstly, they offer coverage for a range of medical services, including hospitalization, doctor visits, diagnostic tests, and prescription medications. Many policies also provide coverage for preventive care, such as vaccinations and annual check-ups, promoting proactive health management.
Additionally, medical insurance often includes provisions for pre-existing conditions. This is a crucial aspect, ensuring that individuals with existing health issues are not denied coverage or charged exorbitant premiums. However, the specific terms and conditions regarding pre-existing conditions can vary significantly between different insurance providers and policy types.
The Importance of Health Insurance
The significance of health insurance extends beyond financial protection. It ensures that individuals have access to a network of healthcare providers, giving them the freedom to choose doctors and specialists based on their needs and preferences. This network of providers is a key advantage, as it offers a wide range of medical expertise and facilities, enhancing the quality of care received.
Furthermore, health insurance plays a vital role in promoting early diagnosis and treatment. By covering preventive care and encouraging regular check-ups, it helps identify health issues in their early stages when they are often more treatable and less costly. This proactive approach not only improves health outcomes but also reduces the long-term financial burden on both individuals and the healthcare system.
| Coverage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Hospitalization | Covers expenses related to inpatient care, including room and board, surgeries, and specialized treatments. |
| Outpatient Care | Provides coverage for doctor visits, diagnostic tests, and minor procedures performed outside of a hospital setting. |
| Prescription Drugs | Offers financial assistance for prescription medications, often with discounts or fixed copays. |
| Preventive Care | Includes coverage for vaccinations, annual check-ups, and other preventive measures to maintain good health. |

Types of Medical Insurance

The medical insurance market offers a diverse range of policy options, catering to the unique needs and circumstances of different individuals and families. Understanding these different types is essential for making informed decisions about coverage.
Individual vs. Group Health Insurance
One of the most fundamental distinctions in health insurance is between individual and group plans. Individual health insurance is purchased by a single person or a family, providing coverage tailored to their specific needs. On the other hand, group health insurance is typically offered through employers, covering a larger number of people, often with more comprehensive benefits and lower premiums.
Group insurance plans are generally more cost-effective due to the larger pool of participants, which spreads the risk and keeps premiums lower. They also often include additional benefits, such as dental and vision coverage, and may offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
Public vs. Private Health Insurance
Another critical distinction is between public and private health insurance. Public health insurance is typically government-funded and administered, offering coverage to specific segments of the population, such as low-income individuals, seniors, or those with disabilities. Examples include Medicare and Medicaid in the United States.
In contrast, private health insurance is purchased from private insurance companies and is often more customizable, allowing individuals to choose their level of coverage and benefits. Private insurance plans can be more expensive, but they offer greater flexibility and may provide access to a wider range of healthcare providers.
Managed Care Plans
Managed care plans are a popular type of health insurance, known for their cost-effectiveness and structured approach to healthcare. These plans typically involve a network of healthcare providers, and enrollees are encouraged to use these providers to maximize their benefits.
There are several subtypes of managed care plans, each with its own characteristics:
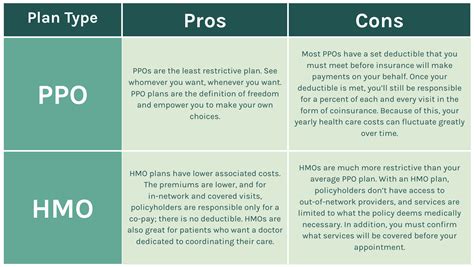
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within their network. The PCP acts as a gatekeeper, referring members to specialists within the network. HMOs generally have lower out-of-pocket costs but may have more limited provider choices.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs offer more flexibility, allowing members to choose any healthcare provider, both in and out of network. However, using in-network providers typically results in lower out-of-pocket costs. PPOs strike a balance between cost and provider choice.
- Point-of-Service (POS) Plans: POS plans combine features of HMOs and PPOs. Members start with a PCP within the network but can seek care outside the network if necessary. POS plans offer flexibility but may have higher costs for out-of-network care.
Key Terms and Concepts
Navigating the world of medical insurance requires an understanding of various terms and concepts. Here are some of the key definitions to know:
- Premium: The amount paid regularly (usually monthly) to maintain health insurance coverage.
- Deductible: The amount an insured person must pay out of pocket before the insurance company begins to pay its share of the covered medical expenses.
- Copayment (Copay): A fixed amount an insured person pays out of pocket for a covered medical service, usually at the time of service.
- Coinsurance: The percentage of costs an insured person must pay out of pocket after the deductible has been met.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The maximum amount an insured person must pay out of pocket in a year for covered services. Once this limit is reached, the insurance company pays for all covered services.
- Network: A group of healthcare providers, such as doctors, hospitals, and specialists, who have a contract with the insurance company to provide services to its members at a discounted rate.
- Exclusions: Specific services or treatments that are not covered by the insurance policy.
The Impact of Medical Insurance on Healthcare Access
Medical insurance has a profound impact on the accessibility and affordability of healthcare. It ensures that individuals can obtain necessary medical services without facing financial hardship. With insurance coverage, people are more likely to seek timely medical care, leading to better health outcomes and a reduced burden on the healthcare system as a whole.
Improving Healthcare Outcomes
Health insurance plays a pivotal role in improving healthcare outcomes. By providing coverage for a wide range of medical services, it encourages individuals to seek regular check-ups, screenings, and timely treatment for illnesses and injuries. This proactive approach to healthcare not only improves individual well-being but also helps identify and manage chronic conditions effectively.
Furthermore, health insurance often includes provisions for mental health and substance abuse treatment, ensuring that individuals have access to comprehensive care. This holistic approach to healthcare is crucial in addressing the complex needs of patients and promoting overall wellness.
Addressing Health Disparities
Health insurance is a critical tool in addressing health disparities, which are differences in health status or access to healthcare between populations. By offering coverage to underserved communities, such as low-income individuals and minorities, health insurance helps bridge the gap in healthcare access and outcomes.
For example, public health insurance programs like Medicaid play a vital role in providing coverage to vulnerable populations. These programs ensure that individuals who may not be able to afford private insurance have access to essential healthcare services, reducing the impact of socioeconomic factors on health.
Challenges and Future Prospects

While medical insurance has undoubtedly improved access to healthcare, it also faces several challenges. Rising healthcare costs, complex policy structures, and varying levels of coverage can create barriers for individuals seeking insurance. Additionally, the insurance market is dynamic, with ongoing debates and reforms shaping its future.
Affordability and Accessibility
One of the primary challenges in medical insurance is ensuring affordability and accessibility. Premiums, deductibles, and copays can be substantial, especially for individuals with low incomes or pre-existing conditions. Finding the right balance between comprehensive coverage and affordable premiums is a constant challenge for insurers and policymakers.
To address this, many countries are exploring innovative solutions, such as high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) paired with health savings accounts (HSAs). HDHPs offer lower premiums, while HSAs allow individuals to save pre-tax dollars for medical expenses, providing a financial buffer for unexpected healthcare costs.
The Future of Medical Insurance
The future of medical insurance is poised for significant changes and innovations. As technology advances, we can expect to see more digital health solutions, such as telemedicine and wearable health devices, integrated into insurance coverage. These advancements will likely improve access to care, especially in rural or underserved areas, and provide insurers with valuable data for risk assessment and claim management.
Furthermore, the concept of value-based insurance design (VBID) is gaining traction. VBID focuses on encouraging the use of cost-effective, high-value services by reducing cost-sharing for these services. This approach aims to improve health outcomes while controlling costs, making healthcare more affordable and accessible for all.
Conclusion
Medical and health insurance is a complex but essential component of modern healthcare systems. It provides financial protection, enhances access to quality care, and promotes proactive health management. While challenges persist, ongoing innovations and reforms offer a glimpse into a future where healthcare is more affordable, accessible, and tailored to individual needs.
As we navigate the evolving landscape of medical insurance, staying informed about our options and understanding the intricacies of coverage is crucial. Whether through public or private insurance, managed care plans, or emerging digital health solutions, the goal remains the same: to ensure that everyone has the opportunity to lead a healthy and fulfilling life.
How does health insurance impact healthcare costs for individuals?
+Health insurance plays a crucial role in managing healthcare costs for individuals. By providing coverage for medical services, it helps individuals avoid the financial burden of paying for these services out of pocket. While insurance plans come with premiums, deductibles, and copays, the overall cost is typically much lower than paying for healthcare services without insurance. Additionally, insurance coverage encourages individuals to seek preventive care and timely treatment, which can help identify and manage health issues early on, preventing more costly and complex treatments down the line.
What are the benefits of managed care plans in health insurance?
+Managed care plans, such as Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), offer several benefits. They typically have lower premiums compared to traditional indemnity plans, making them more affordable for many individuals and families. Managed care plans also emphasize preventive care and early intervention, which can lead to better health outcomes and lower long-term healthcare costs. Furthermore, these plans often have a network of healthcare providers, ensuring that enrollees have access to a range of medical services without having to navigate the complexities of the healthcare system alone.
How does health insurance contribute to overall public health?
+Health insurance plays a significant role in promoting public health. By providing coverage for a wide range of medical services, including preventive care, it encourages individuals to seek regular check-ups, screenings, and timely treatment for illnesses and injuries. This proactive approach to healthcare helps identify and manage health issues early on, preventing more serious conditions and reducing the overall burden on the healthcare system. Additionally, health insurance often includes coverage for mental health and substance abuse treatment, addressing critical aspects of public health that can impact individuals’ well-being and productivity.