How Much Is Long Term Insurance

Long-term insurance is a crucial financial instrument designed to provide individuals and businesses with protection and stability over an extended period. In the context of insurance, the term "long-term" typically refers to policies that offer coverage for an extended duration, often spanning several years or even decades. These policies are tailored to meet specific long-term needs and goals, making them an essential component of comprehensive financial planning.
The cost of long-term insurance, often referred to as the premium, is a multifaceted consideration that is influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding these factors is key to making informed decisions about your insurance coverage. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of long-term insurance premiums, exploring the key determinants and offering insights into how you can navigate this critical aspect of financial planning.
Understanding the Cost of Long-Term Insurance

The cost of long-term insurance is a complex calculation, influenced by various elements that reflect the risk profile and specific needs of the policyholder. Here’s a breakdown of the primary factors that contribute to the premium structure of long-term insurance policies.
Risk Assessment
Insurance companies meticulously assess the risk associated with insuring an individual or entity. This process, known as underwriting, involves evaluating a wide range of factors that could potentially impact the likelihood of a claim being made. For long-term insurance, these assessments are particularly comprehensive, as they aim to forecast risks over an extended period.
Key considerations in the risk assessment process include:
- Age: Generally, younger individuals are considered lower risk, as they are less likely to require immediate medical attention or claim payouts.
- Health Status: Pre-existing medical conditions or a history of chronic illnesses can significantly influence the premium, as they indicate a higher likelihood of future healthcare needs.
- Lifestyle Factors: Habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or participation in high-risk sports can elevate the premium, as they are associated with increased health risks.
- Family Medical History: Genetic predispositions to certain conditions can impact the premium, especially for long-term health or life insurance policies.
Coverage Type and Duration
The type of coverage chosen and the duration for which it is required are fundamental in determining the cost of long-term insurance. Different types of coverage offer varying levels of protection and, consequently, carry different price tags.
Some common types of long-term insurance coverage include:
- Life Insurance: This provides a lump-sum payment to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured individual. The premium depends on factors like the insured's age, health, and the chosen coverage amount.
- Health Insurance: Designed to cover medical expenses, this type of insurance is essential for long-term healthcare planning. Premiums can vary based on the level of coverage (e.g., basic, comprehensive), deductibles, and the age and health of the insured.
- Long-Term Care Insurance: This coverage caters to the costs associated with long-term care, often for the elderly or those with chronic conditions. Premiums are influenced by the extent of coverage, the daily benefit amount, and the elimination period (the time before benefits kick in).
- Disability Insurance: Offering income protection in the event of a disability, this insurance type ensures financial stability. Premiums are affected by factors such as the benefit amount, the length of the benefit period, and the insured's occupation.
Policy Features and Riders
Long-term insurance policies often come with optional features or riders that can enhance the coverage but also increase the premium. These features are designed to tailor the policy to the specific needs of the policyholder.
Common riders and features include:
- Waiver of Premium: This rider waives the policy's premium payments if the insured becomes disabled, ensuring continued coverage without additional financial burden.
- Accelerated Death Benefit: Allows a portion of the death benefit to be paid out if the insured is diagnosed with a terminal illness, providing financial assistance during a challenging time.
- Guaranteed Insurability Option: Enables the policyholder to increase the coverage amount at specific future dates without providing additional evidence of insurability.
- Cost of Living Adjustment: Adjusts the policy's benefits to keep pace with inflation, ensuring that the coverage remains adequate over time.
Market Competition and Company Reputation
The insurance market is highly competitive, with numerous companies offering a wide range of policies. The reputation and financial stability of the insurance provider can influence the premium rates. Companies with a strong track record of financial stability and customer satisfaction may charge slightly higher premiums, reflecting the security and reliability they offer.
Inflation and Interest Rates
Economic factors such as inflation and interest rates can also impact the cost of long-term insurance. Inflation can affect the cost of claims over time, while interest rates can influence the returns on the premiums invested by insurance companies. These economic variables are often reflected in the premiums charged by insurance providers.
Factors Influencing Long-Term Insurance Premiums
Understanding the specific factors that influence long-term insurance premiums is essential for making informed decisions about your coverage. Here’s a deeper look at some of these key influencers.
Age and Health Status
Age is a primary determinant of insurance premiums. Younger individuals typically pay lower premiums, as they are generally in better health and have a lower likelihood of requiring immediate healthcare services. However, as individuals age, their health status becomes a more significant factor.
Health status is a critical consideration in long-term insurance. Pre-existing medical conditions or a history of chronic illnesses can lead to higher premiums, as these factors indicate an increased likelihood of future healthcare needs. For example, individuals with a history of heart disease or diabetes may face higher premiums for long-term health insurance policies.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Factors
Lifestyle choices and behaviors can significantly impact the cost of long-term insurance. Habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or participation in high-risk sports are often associated with increased health risks. As a result, individuals engaging in these activities may be considered higher-risk and charged higher premiums.
For instance, smokers may face higher premiums for life insurance, as smoking is linked to various health complications. Similarly, individuals who regularly engage in extreme sports or high-risk activities may see their premiums for disability or health insurance increase, reflecting the elevated risk of injury or illness.
Family Medical History
Genetic factors play a role in determining long-term insurance premiums. If an individual has a family history of certain medical conditions, such as heart disease or cancer, it can impact the premium for life or health insurance. Insurance companies carefully evaluate family medical histories to assess the potential risks associated with insuring an individual.
For example, if an individual's parents or siblings have a history of cardiovascular disease, the insurance company may view this as a risk factor and adjust the premium accordingly. This is particularly relevant for long-term health insurance, as it aims to provide coverage for an extended period of an individual's life.
Policy Type and Coverage Level
The type of long-term insurance policy and the level of coverage chosen significantly impact the premium. Different types of policies, such as life insurance, health insurance, long-term care insurance, and disability insurance, serve distinct purposes and carry varying costs.
The level of coverage, whether it's the death benefit in life insurance, the daily benefit amount in long-term care insurance, or the benefit period in disability insurance, directly influences the premium. Higher coverage levels typically result in higher premiums, as they provide greater financial protection.
Optional Riders and Policy Add-ons
Long-term insurance policies often offer optional riders or add-ons that can enhance the coverage but also increase the premium. These features are designed to cater to the specific needs of the policyholder and provide additional layers of protection.
Some common optional riders and add-ons include:
- Accidental Death Benefit: This rider provides an additional payout in the event of an accidental death, on top of the standard death benefit.
- Critical Illness Rider: Pays a lump sum if the insured is diagnosed with a specified critical illness, such as cancer or stroke.
- Income Protection Rider: Offers a monthly income benefit if the insured becomes disabled and is unable to work.
- Inflation Protection: Automatically adjusts the policy's benefits to keep pace with inflation, ensuring that the coverage remains adequate over time.
Economic Factors
Economic conditions, such as inflation and interest rates, can indirectly influence the cost of long-term insurance. Inflation affects the cost of claims over time, as medical expenses and other financial needs tend to increase with inflation. Insurance companies factor in these rising costs when setting premiums.
Interest rates also play a role, as insurance companies often invest a portion of the premiums they collect. When interest rates are high, insurance companies can earn more from these investments, which can lead to slightly lower premiums. Conversely, in a low-interest-rate environment, premiums may be slightly higher to compensate for reduced investment returns.
Navigating Long-Term Insurance Costs
Understanding the factors that influence long-term insurance premiums is the first step toward making informed decisions about your coverage. Here are some strategies to help you navigate the cost of long-term insurance effectively.
Shop Around and Compare Policies
The insurance market is highly competitive, and premiums can vary significantly between providers. It’s essential to shop around and compare policies from different companies to find the best value for your needs. Online insurance marketplaces and comparison websites can be valuable tools for this process.
When comparing policies, pay close attention to the coverage details, exclusions, and any additional riders or add-ons. Ensure that you're comparing policies with similar levels of coverage to make an accurate assessment of the value and cost.
Consider Bundle Discounts
Many insurance companies offer bundle discounts when you purchase multiple policies from them. For instance, if you have your home and auto insurance with the same provider, you may be eligible for a discount on your long-term care or disability insurance. Bundle discounts can provide significant savings over time, so it’s worth exploring this option.
Optimize Your Health and Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing your health effectively can have a positive impact on your long-term insurance costs. Insurance companies often offer discounts or reduced premiums to individuals who take proactive steps to improve their health.
Here are some strategies to consider:
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for various health issues. Quitting smoking can lead to lower premiums for life and health insurance.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of certain health conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight can positively impact your insurance costs.
- Manage chronic conditions: If you have a pre-existing medical condition, effectively managing it through medication, regular check-ups, and lifestyle changes can demonstrate stability and reduce insurance risks.
- Participate in wellness programs: Some insurance companies offer discounts or premium reductions for individuals who participate in wellness programs, such as fitness tracking or healthy lifestyle challenges.
Choose the Right Coverage Level
Selecting the appropriate level of coverage is crucial to ensuring you have adequate protection without paying for unnecessary benefits. It's important to strike a balance between having enough coverage to meet your needs and keeping premiums affordable.
When determining the right coverage level:
- Assess your financial goals and obligations: Consider your financial responsibilities, such as mortgage payments, education costs for your children, or supporting elderly parents. Ensure that your insurance coverage aligns with these financial goals.
- Review your existing assets and savings: Evaluate your current financial assets, including savings, investments, and other forms of wealth. This will help you determine how much insurance coverage you truly need.
- Consult with a financial advisor: A financial professional can provide valuable guidance on determining the appropriate coverage level based on your specific circumstances.
Understand Policy Exclusions and Limitations
It's crucial to thoroughly understand the exclusions and limitations of your long-term insurance policy. Exclusions refer to specific situations or circumstances that are not covered by the policy, while limitations define the maximum amount the insurance company will pay out in certain situations.
Common exclusions in long-term insurance policies may include pre-existing conditions, self-inflicted injuries, or participation in high-risk activities. Limitations might specify the maximum daily benefit for long-term care insurance or the maximum benefit period for disability insurance.
Consider the Long-Term Value
When evaluating the cost of long-term insurance, it’s important to consider the long-term value it provides. While premiums may seem high initially, the protection and peace of mind offered by long-term insurance can be invaluable in the face of unforeseen circumstances.
Long-term insurance policies are designed to provide financial stability and security over an extended period. They can protect your family's financial well-being in the event of a sudden illness, disability, or death. By considering the long-term benefits, you can make a more informed decision about the value of the insurance coverage.
Case Study: Analyzing Long-Term Insurance Costs
To illustrate the factors that influence long-term insurance premiums, let’s consider a hypothetical case study of John, a 35-year-old individual looking to purchase long-term health insurance.
John’s Risk Profile
John is a non-smoker and maintains a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet. He has no history of chronic illnesses and visits his primary care physician annually for check-ups. John’s risk profile is generally favorable, which should lead to competitive insurance rates.
Coverage Options and Costs
John is interested in a comprehensive health insurance policy that covers a wide range of medical expenses, including hospital stays, outpatient care, and prescription medications. He compares policies from three reputable insurance providers, considering factors such as coverage limits, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums.
| Insurance Provider | Monthly Premium | Coverage Limit | Deductible | Out-of-Pocket Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provider A | $350 | $1,000,000 | $2,000 | $6,000 |
| Provider B | $320 | $800,000 | $1,500 | $5,000 |
| Provider C | $380 | $1,200,000 | $2,500 | $7,000 |
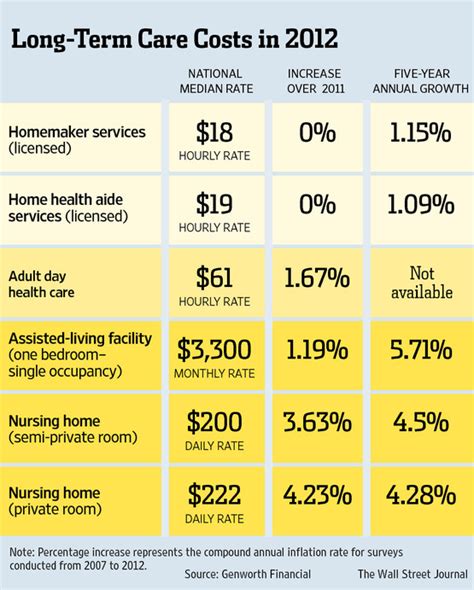
Analyzing the Premiums
In this case study, we can see that the monthly premiums vary between the three providers, ranging from 320 to 380. The differences in premiums are influenced by several factors, including the coverage limits, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums.
Provider A offers the highest coverage limit ($1,000,000) and a higher deductible ($2,000), which results in a slightly higher premium of $350 per month. Provider B, with a lower coverage limit ($800,000) and a lower deductible ($1,500), offers a slightly lower premium of $320 per month. Provider C, despite having the highest coverage limit ($1,200,000), also has a higher deductible ($2,500) and a higher out-of-pocket maximum ($7,000), resulting in the highest premium of $380 per month.
Making an Informed Decision
When deciding between these options, John should consider his specific healthcare needs and financial situation. If he anticipates frequent medical expenses or has a history of costly medical procedures, the higher coverage limit and higher premium of Provider A might be the best choice. On the other hand, if he’s generally healthy and expects fewer medical expenses, the lower premium and more affordable coverage of Provider B could be a more suitable option.
Additionally, John should carefully review the policy details, including any exclusions or limitations, to ensure that the coverage aligns with his expectations. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance professional can also provide valuable guidance in making this important decision.