Health Insurance Federal
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the Health Insurance Federal landscape in the United States. As we delve into this complex and essential topic, we will uncover the intricacies of federal health insurance programs, their impact on individuals and society, and the future implications of these initiatives. With a focus on providing comprehensive and expert insights, this article aims to serve as a valuable resource for anyone seeking to understand the critical role of health insurance in the federal sphere.
Understanding Health Insurance Federal: A Comprehensive Overview

The Health Insurance Federal, often referred to as the federal health insurance system, is a network of programs and initiatives designed to provide access to healthcare services for millions of Americans. These programs, administered by the federal government, aim to ensure that individuals and families have the financial protection and medical coverage they need, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
The need for federal health insurance programs stems from the understanding that healthcare is a fundamental right and an essential aspect of human well-being. By implementing these initiatives, the government aims to address the challenges of rising healthcare costs, limited access to quality care, and the disparity in health outcomes across different populations.
The federal health insurance system encompasses a range of programs, each with its unique focus and target population. Some of the key programs include:
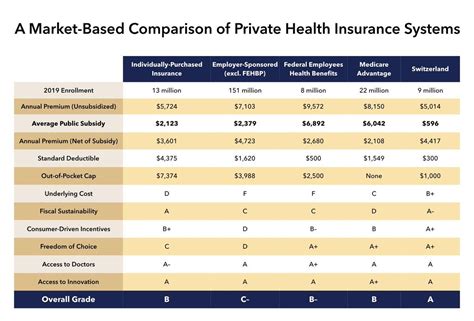
- Medicare: This program provides health insurance for Americans aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities. It offers comprehensive coverage, including hospital care, physician services, and prescription drugs.
- Medicaid: Targeted at low-income individuals and families, Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that offers healthcare coverage and long-term care services. It plays a crucial role in ensuring access to essential medical services for vulnerable populations.
- Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP): CHIP provides low-cost health coverage for children in families that earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance. This program focuses on promoting children's health and development.
- Affordable Care Act (ACA) Exchanges: The ACA, often referred to as Obamacare, established health insurance marketplaces where individuals and small businesses can purchase qualified health plans. These exchanges offer a range of options, including private insurance plans and government-sponsored programs.
The Impact of Health Insurance Federal Programs
The implementation of federal health insurance programs has had a significant impact on the healthcare landscape in the United States. Here are some key areas where these initiatives have made a difference:
1. Increased Access to Healthcare
One of the primary goals of federal health insurance programs is to expand access to healthcare services. By providing coverage to those who might otherwise go uninsured, these programs ensure that individuals can receive the medical care they need without facing financial hardship.
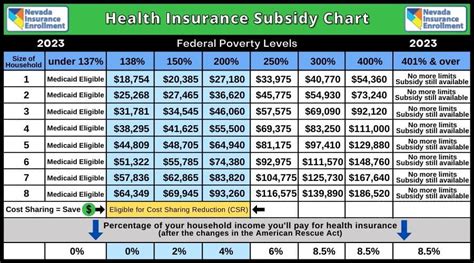
For example, the expansion of Medicaid under the ACA has resulted in millions of previously uninsured Americans gaining access to healthcare. This has led to improved health outcomes, reduced financial barriers, and increased utilization of preventive services.
| Medicaid Expansion | Enrollees |
|---|---|
| Before ACA | 30 million |
| After ACA | Over 70 million |

2. Financial Protection for Individuals and Families
Federal health insurance programs play a vital role in protecting individuals and families from the high costs of healthcare. By offering coverage, these programs help individuals manage their medical expenses, preventing financial ruin due to unexpected illnesses or injuries.
Medicare, for instance, provides a safety net for seniors, ensuring they have access to necessary medical treatments without the burden of overwhelming costs. This program has significantly reduced the financial strain on elderly individuals and their families.
3. Improved Health Outcomes
Access to healthcare through federal programs has been linked to improved health outcomes across various populations. Studies have shown that individuals with health insurance are more likely to receive timely and appropriate medical care, leading to better management of chronic conditions and reduced morbidity and mortality rates.
For example, Medicaid expansion has been associated with increased access to mental health services, improved maternal and child health, and reduced rates of avoidable hospitalizations.
Challenges and Future Implications
While federal health insurance programs have made significant strides in improving access and health outcomes, they are not without their challenges. Here are some key considerations for the future of Health Insurance Federal:
1. Cost and Sustainability
One of the primary challenges facing federal health insurance programs is the rising cost of healthcare. As medical treatments and technologies advance, the cost of providing comprehensive coverage continues to increase. Ensuring the long-term sustainability of these programs requires careful management of resources and innovative approaches to healthcare delivery.
2. Equity and Access
Despite the progress made, disparities in access to healthcare persist. Certain populations, such as rural communities and minority groups, still face barriers to healthcare services. Addressing these disparities and ensuring equitable access to quality care remains a critical goal for federal health insurance programs.
3. Innovation and Technological Advancements
The healthcare industry is rapidly evolving, and federal programs must keep pace with technological advancements. Incorporating digital health solutions, telemedicine, and innovative payment models can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of these programs, improving patient outcomes and reducing costs.
Conclusion: The Way Forward
The Health Insurance Federal system plays a pivotal role in ensuring the health and well-being of Americans. Through a network of programs, the federal government has made significant strides in expanding access to healthcare, protecting individuals from financial hardship, and improving health outcomes. However, ongoing challenges and the need for innovation underscore the importance of continuous evaluation and adaptation.
As we look to the future, a balanced approach that combines policy reforms, technological advancements, and a commitment to equity will be crucial in shaping the landscape of federal health insurance. By addressing these challenges head-on, we can work towards a healthcare system that is accessible, affordable, and equitable for all.
How do federal health insurance programs differ from private insurance plans?
+Federal health insurance programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, are government-sponsored initiatives that provide coverage to specific populations based on age, income, or disability status. These programs offer comprehensive benefits and are designed to ensure access to healthcare for those who might otherwise go uninsured. Private insurance plans, on the other hand, are typically purchased through employers or on the individual market. They may offer a range of coverage options and benefits, but eligibility and costs can vary significantly.
What are the eligibility criteria for Medicare and Medicaid?
+Medicare is primarily available to individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger people with certain disabilities. Eligibility for Medicaid is based on income and other factors, such as family size and pregnancy status. The specific criteria can vary by state, as Medicaid is a joint federal and state program with some flexibility in implementation.
How do federal health insurance programs impact healthcare providers and hospitals?
+Federal health insurance programs have a significant impact on healthcare providers and hospitals. By expanding access to healthcare coverage, these programs increase the patient pool for providers, particularly in underserved areas. However, they also present challenges, such as complex billing and reimbursement processes and the need to navigate multiple insurance plans with varying requirements.



