Fmcsa Insurance And Licensing

The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and compliance of the commercial motor vehicle industry in the United States. One of the key aspects of FMCSA's regulatory framework is the insurance and licensing requirements that commercial motor carriers must adhere to. These regulations are designed to protect the public, prevent accidents, and ensure that motor carriers operate within the law.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of FMCSA insurance and licensing, exploring the intricacies of these requirements, the benefits they offer, and the potential consequences of non-compliance. By understanding these regulations, commercial motor carriers can navigate the complex landscape of FMCSA regulations and operate their businesses safely and successfully.
Understanding FMCSA Insurance Requirements
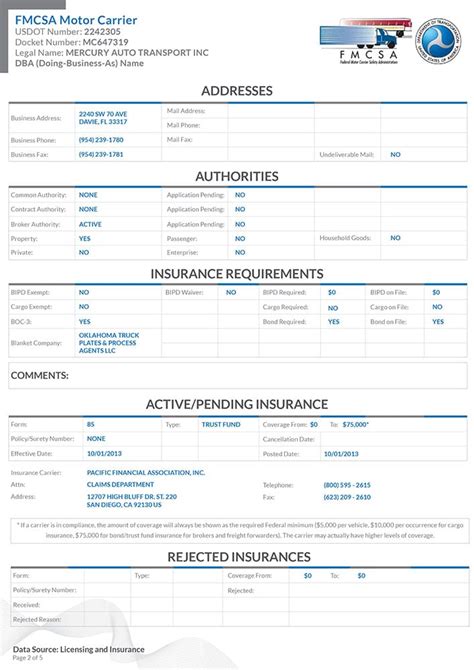
FMCSA mandates that all commercial motor carriers operating in interstate commerce must maintain adequate insurance coverage to protect the public and mitigate the financial risks associated with motor vehicle accidents. These insurance requirements are tailored to the unique risks and challenges faced by the commercial motor vehicle industry.
Minimum Liability Coverage
The FMCSA sets specific minimum liability insurance coverage limits that motor carriers must meet. These limits vary based on the type of operation and the commodities transported. For instance, carriers transporting certain hazardous materials may be subject to higher liability limits.
| Operation Type | Minimum Liability Coverage |
|---|---|
| Property-carrying vehicles | $750,000 for vehicles with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) of 10,001 pounds or more |
| Passenger-carrying vehicles | $5 million for vehicles designed to transport 16 or more passengers, including the driver |
| HazMat and passenger carriers | $5 million for vehicles transporting hazardous materials and passenger vehicles designed to transport 9 to 15 passengers, including the driver |

These minimum liability limits are designed to ensure that motor carriers can provide adequate compensation in the event of an accident. It's important to note that these limits are subject to periodic review and adjustment by the FMCSA to keep pace with inflation and changing risk profiles.
Types of Insurance Coverage
In addition to liability insurance, FMCSA requires motor carriers to carry other types of insurance coverage to address specific risks. These include:
- Bodily Injury and Property Damage Liability: This coverage protects against claims arising from bodily injury or property damage caused by the motor carrier's operations.
- Cargo Insurance: Motor carriers transporting goods are required to have cargo insurance to cover losses or damages to the cargo during transportation.
- Physical Damage Insurance: This coverage protects the motor carrier's own vehicles against damage or theft.
- Workers' Compensation Insurance: Motor carriers must provide workers' compensation insurance to cover injuries or illnesses sustained by employees while performing their duties.
Filing Insurance Certificates
Motor carriers are required to file insurance certificates with the FMCSA to demonstrate their compliance with the insurance requirements. These certificates must be filed using the appropriate forms and must include specific details about the insurance coverage, including policy limits, effective dates, and the name of the insurance company.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failing to maintain the required insurance coverage can result in severe consequences for motor carriers. The FMCSA has the authority to conduct audits and inspections to ensure compliance. If a motor carrier is found to be operating without the required insurance coverage, the FMCSA may take enforcement actions, including:
- Imposing civil penalties and fines.
- Placing the motor carrier out-of-service until compliance is achieved.
- Revoking or suspending the carrier's operating authority.
- Referring the matter to law enforcement for potential criminal prosecution.
Moreover, motor carriers that operate without the required insurance coverage may face significant financial risks in the event of an accident. They may be held personally liable for damages, which can lead to financial ruin and legal repercussions.
FMCSA Licensing: The Essential Steps

In addition to insurance requirements, FMCSA also mandates that motor carriers obtain the appropriate licenses and registrations to operate legally. These licensing requirements ensure that motor carriers meet specific safety and operational standards.
Obtaining a USDOT Number
The first step in the FMCSA licensing process is obtaining a unique United States Department of Transportation (USDOT) number. This number is required for all motor carriers operating in interstate commerce and is used to identify and track the carrier’s safety and operational records.
Motor carriers can apply for a USDOT number online through the FMCSA's website. The application process involves providing detailed information about the carrier's operations, including the types of vehicles used, the commodities transported, and the carrier's safety and compliance history.
Registering with the FMCSA
After obtaining a USDOT number, motor carriers must register with the FMCSA. This registration process involves submitting additional information, such as the carrier’s safety program, drug and alcohol testing policies, and maintenance and inspection procedures.
The FMCSA registration process ensures that motor carriers have the necessary systems and procedures in place to operate safely and comply with federal regulations. It also allows the FMCSA to monitor and enforce safety standards across the industry.
Operational Authority and Registration
Depending on the type of operation, motor carriers may also need to obtain specific operational authority and registration. For instance, carriers transporting hazardous materials must obtain a Hazardous Materials Safety Permit (HMSP) from the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA), a division of the Department of Transportation.
Additionally, motor carriers may need to register with state and local authorities, especially if they operate within a specific state or region. These registrations ensure that motor carriers comply with state and local regulations, which may have additional requirements beyond federal standards.
Safety Fitness Determination
The FMCSA conducts periodic safety audits and reviews of motor carriers to assess their safety performance and determine their safety fitness. This process, known as a Safety Fitness Determination (SFD), evaluates the carrier’s safety management controls, driver qualifications, vehicle maintenance, and operational practices.
Based on the SFD, the FMCSA may assign a safety rating to the motor carrier, which can be Satisfactory, Conditional, or Unsatisfactory. A Conditional or Unsatisfactory rating may trigger additional enforcement actions or require the carrier to take corrective actions to improve its safety performance.
Benefits of FMCSA Compliance
While FMCSA insurance and licensing requirements may seem burdensome, they offer several significant benefits to both motor carriers and the public at large.
Enhanced Safety
The primary benefit of FMCSA compliance is enhanced safety on the roads. By ensuring that motor carriers maintain adequate insurance coverage and adhere to strict safety standards, the FMCSA reduces the risk of accidents and mitigates the potential consequences of such incidents.
Well-insured and safety-conscious motor carriers are less likely to engage in risky behaviors, such as overloading vehicles, fatigued driving, or neglecting vehicle maintenance. This not only protects the public but also reduces the financial and legal risks faced by motor carriers themselves.
Legal and Financial Protection
FMCSA compliance provides motor carriers with essential legal and financial protection. By maintaining the required insurance coverage, motor carriers can avoid personal liability and financial ruin in the event of an accident. The insurance coverage ensures that claims for damages or injuries are handled promptly and fairly, reducing the carrier’s exposure to costly litigation.
Additionally, FMCSA licensing ensures that motor carriers operate within the law, avoiding potential legal consequences and fines for non-compliance. By adhering to FMCSA regulations, motor carriers can focus on their core business operations without the distraction and risk of legal challenges.
Improved Reputation and Customer Confidence
FMCSA compliance also enhances a motor carrier’s reputation and builds customer confidence. Customers and shippers prefer to work with carriers that demonstrate a commitment to safety and compliance. By meeting FMCSA requirements, motor carriers can attract and retain customers, build a positive brand image, and establish themselves as reliable and trustworthy partners.
Conclusion: The Importance of FMCSA Compliance
FMCSA insurance and licensing requirements are critical components of the commercial motor vehicle industry’s regulatory framework. By understanding and adhering to these requirements, motor carriers can operate safely, protect their businesses, and contribute to a safer transportation system.
The FMCSA's comprehensive approach to insurance and licensing ensures that motor carriers are financially protected, operate within the law, and maintain high safety standards. This not only benefits the motor carriers themselves but also the public, shippers, and other stakeholders who rely on a safe and efficient transportation network.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the consequences of operating without the required FMCSA insurance coverage?
+Operating without the required FMCSA insurance coverage can result in severe consequences, including civil penalties, out-of-service orders, revocation or suspension of operating authority, and potential criminal prosecution. Motor carriers may also face significant financial risks and personal liability in the event of an accident.
How often do motor carriers need to renew their insurance certificates with the FMCSA?
+Motor carriers must ensure that their insurance certificates are up-to-date and valid at all times. It is recommended to renew insurance policies and file new certificates with the FMCSA at least 30 days before the expiration of the current policy to avoid any gaps in coverage.
Can motor carriers be held personally liable for accidents if they operate without insurance coverage?
+Yes, motor carriers can be held personally liable for accidents if they operate without the required insurance coverage. The FMCSA regulations are designed to protect the public, and carriers that fail to comply with insurance requirements may face financial ruin and legal repercussions.
What happens if a motor carrier receives a Conditional or Unsatisfactory safety rating from the FMCSA?
+A Conditional or Unsatisfactory safety rating from the FMCSA indicates that the motor carrier has significant safety deficiencies. The FMCSA may require the carrier to take corrective actions, implement new safety programs, or face enforcement actions, such as fines or operating restrictions, until the carrier improves its safety performance.
How can motor carriers stay updated on FMCSA insurance and licensing requirements?
+Motor carriers can stay informed about FMCSA insurance and licensing requirements by regularly reviewing the FMCSA’s official website and publications. The FMCSA provides updates, guidance, and resources to help carriers understand and comply with the latest regulations. Additionally, carriers can consult with insurance brokers and legal experts specializing in transportation law for tailored advice.



