Elder Care Insurance Cost

As the world's population ages, the demand for elder care services is on the rise, and with it, the need for financial planning to cover these expenses. Elder care insurance, also known as long-term care insurance, is a critical component of this planning, offering a safety net for individuals and their families. This article delves into the intricacies of elder care insurance, exploring its costs, benefits, and the factors that influence its pricing.
Understanding Elder Care Insurance
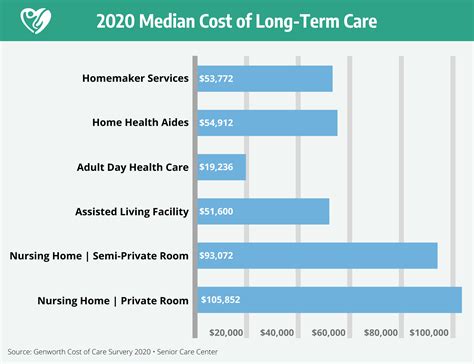
Elder care insurance is a type of coverage designed to help individuals manage the costs associated with long-term care, which may become necessary as they age. This care can range from assistance with daily activities like bathing and dressing to more complex medical needs. The policyholder typically pays premiums over time, and in return, the insurance provider covers a portion or all of the costs of long-term care services, depending on the policy’s terms.
The benefits of elder care insurance are significant. It provides peace of mind, knowing that future care needs are financially secured. It also allows individuals to maintain their independence and receive care in their preferred setting, whether that's at home, in an assisted living facility, or a nursing home. Furthermore, it can alleviate the financial burden on family members who might otherwise need to cover these expenses.
Factors Influencing Cost

The cost of elder care insurance is influenced by a variety of factors, each of which can significantly impact the overall premium. Understanding these factors is key to making informed decisions about coverage.
Age at Purchase
One of the most significant determinants of elder care insurance cost is the age at which the policy is purchased. Generally, the younger an individual is when they buy the policy, the lower the premiums. This is because younger individuals are less likely to require long-term care in the immediate future, and insurance companies price their policies based on the likelihood of a claim being made.
For example, a 55-year-old might pay an annual premium of $1,500 for a basic elder care insurance policy, while a 65-year-old might pay $2,200 for the same coverage. The difference in cost reflects the increased likelihood that the older individual will require long-term care sooner.
Health and Lifestyle Factors
An individual’s health and lifestyle can also play a role in the cost of elder care insurance. Insurance providers often consider an applicant’s health history, including any pre-existing conditions or chronic illnesses. Those with a history of serious health issues may face higher premiums or may even be denied coverage altogether.
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking or a high-risk occupation, can also influence premiums. For instance, a smoker may pay 20% more for their elder care insurance policy compared to a non-smoker, all other factors being equal. Similarly, individuals in high-risk occupations, such as construction workers, might face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of accidents or injuries.
Policy Benefits and Coverage Limits
The specific benefits and coverage limits of an elder care insurance policy also impact its cost. Policies with more comprehensive benefits, such as coverage for a wider range of services or higher daily or monthly benefit amounts, will typically be more expensive. Similarly, policies with longer benefit periods (the length of time the policy will pay for care) will generally cost more than those with shorter benefit periods.
For instance, a policy with a daily benefit of $200 and a 3-year benefit period might cost $1,800 annually, while a policy with a $300 daily benefit and a 5-year benefit period could cost $3,000 per year. The increased cost reflects the greater financial protection offered by the latter policy.
Inflation Protection
Many elder care insurance policies include inflation protection, which accounts for the rising costs of healthcare over time. This feature ensures that the policy’s benefits keep pace with inflation, so the coverage remains adequate even as healthcare costs increase. However, inflation protection typically adds to the overall cost of the policy.
A policy with a 3% inflation protection rider might cost 10% more than a similar policy without this feature. The additional cost provides peace of mind, ensuring that the policy's benefits will be sufficient to cover future long-term care costs, even as healthcare inflation rises.
Waiver of Premium
Some elder care insurance policies include a waiver of premium benefit. This means that if the policyholder becomes eligible for long-term care, they won’t have to continue paying premiums during the period they’re receiving benefits. While this feature provides added financial security, it can also increase the overall cost of the policy.
A policy with a waiver of premium benefit might cost 15% more than a similar policy without this feature. The higher cost reflects the additional financial protection offered by the waiver of premium, ensuring that individuals receiving long-term care benefits don't also have to worry about paying their insurance premiums.
Real-World Examples
To provide a clearer picture of elder care insurance costs, let’s look at some real-world examples. These illustrate how different factors can influence the cost of coverage.
Example 1: Age at Purchase
John, a 50-year-old, purchases an elder care insurance policy with a daily benefit of 150 and a 3-year benefit period. His annual premium is 1,200. If John had waited until he was 60 to purchase the same policy, his annual premium might have been $1,800, reflecting the increased likelihood of needing long-term care at a later age.
Example 2: Health and Lifestyle Factors
Sarah, a 55-year-old, applies for elder care insurance. She’s a non-smoker and has no significant health issues. Her annual premium for a policy with a daily benefit of 200 and a 4-year benefit period is 1,600. However, if Sarah had a history of smoking or a chronic health condition, her premium could be 25% higher, at $2,000, reflecting the increased risk to the insurance provider.
Example 3: Policy Benefits and Coverage Limits
Michael, a 60-year-old, is comparing two elder care insurance policies. Policy A has a daily benefit of 250 and a 3-year benefit period, while Policy B has a daily benefit of 350 and a 5-year benefit period. Michael’s annual premium for Policy A is 2,000, while for Policy B, it's 3,500. The increased cost of Policy B reflects the higher daily benefit and longer benefit period, providing more comprehensive coverage.
Performance Analysis and Future Implications
Elder care insurance policies have proven to be a valuable financial tool for individuals seeking to plan for their long-term care needs. The performance of these policies is generally measured by their ability to provide adequate coverage when needed and their cost-effectiveness over time.
For instance, a study conducted by the American Association for Long-Term Care Insurance found that among policyholders who had made claims, the average daily benefit amount was $161, with the policy covering an average of 3.6 years of care. This highlights the effectiveness of elder care insurance in providing financial support during extended periods of care.
Looking to the future, the demand for elder care insurance is expected to grow significantly. The aging population, coupled with increasing healthcare costs, will drive more individuals to seek financial protection through these policies. Insurance providers are likely to adapt their offerings to meet this demand, potentially introducing more flexible and customizable policies to cater to a wider range of needs and budgets.
Additionally, there may be increased focus on preventative care and wellness programs within elder care insurance. By encouraging healthy lifestyles and early intervention, insurance providers can help policyholders maintain their independence for longer and reduce the need for long-term care, which would benefit both the policyholders and the insurance companies.
Conclusion

Elder care insurance is a critical component of financial planning for older adults. By understanding the factors that influence its cost, individuals can make informed decisions about their coverage and ensure they have the financial protection they need to manage the costs of long-term care. As the industry evolves to meet the changing needs of an aging population, elder care insurance will continue to play a vital role in ensuring the financial security and independence of seniors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average cost of elder care insurance per month or year?
+
The average cost of elder care insurance can vary significantly based on factors such as age, health, and the level of coverage desired. On average, a 55-year-old might pay between 1,500 to 2,500 annually for a basic policy, while a 65-year-old could pay upwards of 3,000 to 5,000 annually for a more comprehensive policy. Monthly costs would range from about 125 to 200 for the 55-year-old and 250 to 400 for the 65-year-old.
How does the cost of elder care insurance compare to other types of insurance, like health insurance or life insurance?
+
Elder care insurance is generally more expensive than health insurance, especially for younger individuals. This is because health insurance primarily covers acute medical conditions, while elder care insurance covers long-term care needs that may span years. Life insurance, on the other hand, can be more or less expensive than elder care insurance depending on the coverage and policy type. However, life insurance and elder care insurance serve different purposes and cannot be directly compared.
Can I customize my elder care insurance policy to fit my specific needs and budget?
+
Yes, elder care insurance policies are often customizable. You can choose the daily or monthly benefit amount, the benefit period (how long the policy will pay for care), and whether you want inflation protection or a waiver of premium. These choices will impact the overall cost of the policy, allowing you to find a balance between the coverage you need and what you can afford.
Are there any tax benefits associated with elder care insurance policies?
+
Yes, in many countries, premiums paid for elder care insurance policies may be tax-deductible, especially if the policy is part of a broader long-term care plan. However, tax laws can vary by jurisdiction, so it’s important to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific benefits available in your area.
What happens if I need long-term care but haven’t purchased elder care insurance?
+
If you require long-term care and don’t have elder care insurance, you’ll likely have to pay for these services out-of-pocket. This can be financially burdensome, as the cost of long-term care can quickly add up. Some individuals may qualify for government assistance programs, but these often have strict eligibility criteria and may not cover all care-related expenses.



