Supplementary Insurance

Supplementary insurance is an additional layer of coverage that individuals can opt for to enhance their existing insurance policies. It is designed to fill in the gaps and provide extra financial protection for specific healthcare needs or unforeseen circumstances. This type of insurance has gained popularity due to its ability to offer comprehensive coverage beyond what is typically provided by primary insurance plans.
In today's complex healthcare landscape, understanding the nuances of supplementary insurance is crucial. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the world of supplementary insurance, exploring its benefits, how it works, and its relevance in modern healthcare systems. By the end of this article, readers will have a clear understanding of why supplementary insurance is an essential consideration for anyone seeking to safeguard their health and financial well-being.
Understanding Supplementary Insurance
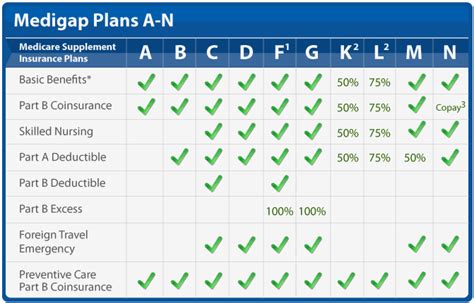
Supplementary insurance, also known as ancillary or supplemental insurance, is a vital component of the broader insurance landscape. It is often sought by individuals who wish to complement their primary health insurance plans with additional coverage tailored to their unique needs.
The primary function of supplementary insurance is to address the limitations or gaps that may exist in a person's primary insurance policy. These limitations could include high deductibles, limited coverage for specific treatments or procedures, or exclusions for pre-existing conditions. By providing an extra layer of protection, supplementary insurance ensures that individuals have access to the healthcare services they require without facing significant financial burdens.
Key Features of Supplementary Insurance
Supplementary insurance offers a range of benefits that cater to diverse healthcare needs. Some of the key features include:
- Gap Coverage: Supplementary insurance fills the gaps in primary insurance plans, covering expenses that are typically not reimbursed, such as co-payments, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Specialized Treatment: It provides coverage for specialized medical procedures, treatments, or therapies that may not be covered by standard health insurance plans. This includes alternative medicine, fertility treatments, or experimental therapies.
- Travel Assistance: Many supplementary insurance policies offer travel assistance benefits, which can be invaluable when seeking medical care while traveling domestically or internationally.
- Pre-existing Condition Coverage: Some supplementary plans specifically address pre-existing conditions, ensuring that individuals with prior health issues can access necessary treatments without facing exclusions.
- Dental and Vision Care: Supplementary insurance often extends to dental and vision care, covering routine check-ups, eyeglasses, contact lenses, and dental procedures.
The specific features of supplementary insurance can vary depending on the provider and the individual's needs. It is essential to carefully review the terms and conditions of any supplementary insurance plan to ensure it aligns with one's healthcare requirements.
How Supplementary Insurance Works

Understanding the mechanics of supplementary insurance is crucial for individuals considering this type of coverage. Here’s a breakdown of how supplementary insurance operates:
Primary vs. Supplementary Insurance
Primary insurance, often referred to as major medical insurance, is the foundational layer of healthcare coverage. It typically provides broad coverage for a range of medical services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications. However, primary insurance plans often come with limitations, such as high deductibles or specific exclusions.
Supplementary insurance, on the other hand, is designed to work in conjunction with primary insurance. It steps in to cover the expenses that primary insurance may not fully reimburse. By doing so, supplementary insurance ensures that individuals have comprehensive coverage for their healthcare needs.
The Claims Process
When an individual receives medical treatment or undergoes a procedure, they typically submit a claim to their primary insurance provider. The primary insurance company then processes the claim, determining the amount that will be reimbursed based on the terms of the policy.
If the primary insurance does not cover the full cost of the treatment or procedure, the individual can then submit a claim to their supplementary insurance provider. The supplementary insurance company will assess the claim and determine the amount to be reimbursed, often taking into account the remaining balance after the primary insurance coverage.
It's important to note that the claims process for supplementary insurance may vary depending on the provider and the specific plan. Some supplementary insurance plans may require the individual to pay out-of-pocket first and then submit a claim for reimbursement, while others may allow for direct billing to the insurance company.
Coordination of Benefits
In cases where an individual has both primary and supplementary insurance coverage, the concept of coordination of benefits comes into play. This process ensures that the individual receives the maximum benefit while avoiding duplicate coverage.
Coordination of benefits involves determining which insurance plan is the primary payer and which is the secondary payer. The primary insurance company will pay its share of the claim first, and then the secondary insurance (usually the supplementary insurance) will pay its share, taking into account the remaining balance after the primary insurance payment.
The Benefits of Supplementary Insurance
Supplementary insurance offers a multitude of advantages that make it an attractive option for individuals seeking comprehensive healthcare coverage. Here are some of the key benefits:
Financial Protection
One of the primary advantages of supplementary insurance is the financial protection it provides. By covering expenses that primary insurance may not fully reimburse, supplementary insurance helps individuals avoid significant out-of-pocket costs. This is especially beneficial for those who require specialized medical treatments or have high healthcare needs.
For instance, suppose an individual has a primary insurance plan with a high deductible. In that case, supplementary insurance can step in to cover the deductible, ensuring that the individual does not have to pay a substantial amount upfront before their insurance coverage kicks in.
Enhanced Coverage
Supplementary insurance allows individuals to customize their coverage to meet their specific healthcare needs. It provides an opportunity to fill in gaps left by primary insurance, ensuring that individuals have access to a broader range of medical services and treatments.
For example, if an individual has a primary insurance plan that does not cover alternative medicine, supplementary insurance can be tailored to include coverage for acupuncture, chiropractic care, or other complementary therapies.
Peace of Mind
Knowing that one has comprehensive insurance coverage can provide a sense of security and peace of mind. Supplementary insurance ensures that individuals can focus on their health and well-being without worrying about the financial implications of their medical needs.
With supplementary insurance, individuals can seek the best possible care without hesitation, knowing that their insurance will support their healthcare journey. This peace of mind is invaluable, especially for those with chronic conditions or complex healthcare requirements.
Choosing the Right Supplementary Insurance
Selecting the appropriate supplementary insurance plan is a critical decision that requires careful consideration. Here are some factors to keep in mind when choosing the right supplementary insurance:
Assess Your Healthcare Needs
Begin by evaluating your current and potential future healthcare needs. Consider any pre-existing conditions, specialized treatments you may require, or unique circumstances such as travel plans or family planning.
Understanding your healthcare needs will help you identify the specific coverage gaps that supplementary insurance can address. This assessment will guide you in choosing a plan that provides the necessary coverage.
Compare Plans and Providers
Research and compare different supplementary insurance plans and providers. Look for plans that offer comprehensive coverage tailored to your needs. Consider factors such as deductibles, co-payments, and out-of-pocket maximums, ensuring they align with your financial capabilities.
Review the fine print of each plan, including any exclusions or limitations. It's essential to understand what is and isn't covered to avoid any unexpected surprises.
Consider Cost and Budget
While supplementary insurance provides valuable coverage, it’s important to consider the cost and ensure it fits within your budget. Evaluate the premiums, deductibles, and any additional fees associated with the plan.
Look for plans that offer flexible payment options and consider the potential savings you may achieve by having supplementary insurance. Weigh the cost against the peace of mind and financial protection it provides.
Real-World Applications of Supplementary Insurance

To better understand the impact and relevance of supplementary insurance, let’s explore some real-world scenarios where it has made a significant difference:
Chronic Condition Management
Individuals living with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, often require ongoing medical care and specialized treatments. Supplementary insurance can provide coverage for regular check-ups, medications, and any additional therapies needed to manage their condition effectively.
For instance, a person with diabetes may have a primary insurance plan that covers routine doctor visits and basic medications. However, supplementary insurance can step in to cover the cost of specialized diabetes management programs, insulin pumps, or other advanced treatments, ensuring comprehensive care.
Major Medical Procedures
Major medical procedures, such as surgeries or complex treatments, can be costly. Primary insurance plans may not fully cover these expenses, leaving individuals with significant out-of-pocket costs. Supplementary insurance can provide the necessary financial support to cover these expenses, ensuring individuals can access the medical care they need without financial strain.
Imagine a patient requiring heart surgery. While their primary insurance may cover a portion of the procedure, supplementary insurance can fill in the gaps, covering additional costs such as post-operative care, rehabilitation, and any specialized medications required during recovery.
Traveling for Medical Treatment
In some cases, individuals may need to travel for specialized medical treatments that are not available locally. Supplementary insurance plans with travel assistance benefits can provide coverage for these situations, ensuring individuals have access to the necessary care, regardless of their location.
For example, a person with a rare medical condition may need to travel to a specialized medical center for treatment. Supplementary insurance can cover the cost of transportation, accommodation, and any additional medical expenses incurred during the trip.
Future Implications and Innovations
As the healthcare industry evolves, supplementary insurance is also adapting to meet the changing needs of individuals. Here are some future implications and innovations to consider:
Integration with Telehealth
The rise of telehealth services has revolutionized healthcare access. Supplementary insurance providers are increasingly integrating telehealth benefits into their plans, ensuring individuals can access remote medical consultations and treatments.
This integration allows for more convenient and accessible healthcare, especially for individuals in remote areas or those with mobility issues. It also reduces the need for in-person visits, providing a cost-effective solution for both patients and insurance providers.
Personalized Medicine
The field of personalized medicine is rapidly advancing, offering tailored treatment plans based on an individual’s unique genetic makeup and health profile. Supplementary insurance plans are beginning to incorporate coverage for genetic testing and personalized treatment options.
By embracing personalized medicine, supplementary insurance can provide coverage for innovative therapies and treatments that are specifically designed to address an individual's unique healthcare needs.
Wellness and Prevention
There is a growing emphasis on preventive healthcare and wellness initiatives. Supplementary insurance providers are recognizing the importance of these aspects and are offering coverage for preventive services, such as health screenings, vaccinations, and lifestyle coaching.
By promoting wellness and prevention, supplementary insurance can help individuals maintain their health and avoid costly medical issues down the line. This proactive approach aligns with the industry's shift towards value-based care.
Conclusion
Supplementary insurance is an invaluable tool for individuals seeking comprehensive healthcare coverage. It provides financial protection, enhances existing insurance plans, and offers peace of mind during challenging medical situations.
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, supplementary insurance will play a crucial role in ensuring individuals have access to the care they need. By staying informed and selecting the right supplementary insurance plan, individuals can take control of their healthcare journey and safeguard their well-being.
FAQ
Can supplementary insurance be used in conjunction with government-provided healthcare plans?
+
Yes, supplementary insurance can complement government-provided healthcare plans. It fills in the gaps left by public insurance, providing additional coverage for specific treatments or expenses not covered by the government plan.
How does supplementary insurance differ from primary insurance?
+
Primary insurance, or major medical insurance, is the foundational layer of healthcare coverage, providing broad coverage for a range of medical services. Supplementary insurance, on the other hand, works alongside primary insurance to cover expenses not fully reimbursed by the primary plan, such as deductibles and specialized treatments.
Are there any limitations or exclusions in supplementary insurance plans?
+
Yes, like any insurance plan, supplementary insurance may have limitations and exclusions. It’s important to carefully review the terms and conditions of the plan to understand what is and isn’t covered. Some common exclusions may include pre-existing conditions, elective procedures, or specific treatments deemed experimental.



