Dentist Insurance Cost
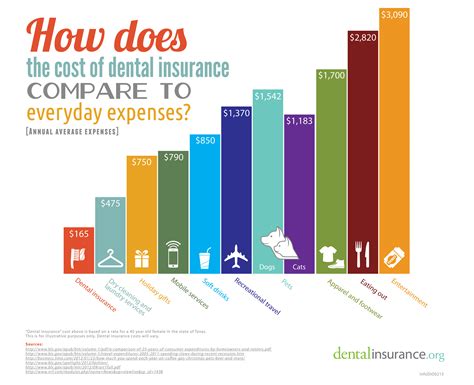
Dental insurance is a vital aspect of the healthcare industry, offering protection and financial support to dentists and their practices. The cost of dentist insurance is a complex topic that encompasses various factors, including the type of coverage, the location of the practice, the number of dentists insured, and the specific risks associated with the dental profession. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of dentist insurance costs, providing an in-depth analysis for an audience seeking expert insights.
Understanding the Factors Influencing Dentist Insurance Costs
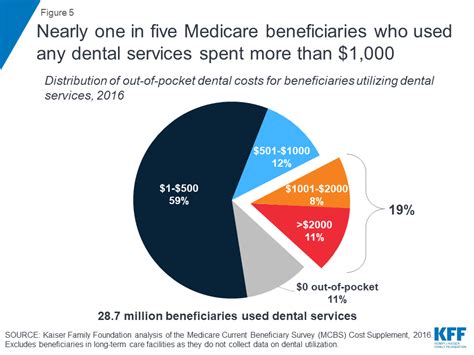
The cost of dentist insurance is influenced by a multitude of factors, each playing a significant role in determining the overall premium. Let’s explore these factors and their impact on insurance expenses for dental professionals.
Type of Coverage and Policy Options
The type of coverage chosen by dentists is a primary determinant of insurance costs. Dentists can opt for different levels of coverage, ranging from basic liability insurance to more comprehensive plans that include malpractice insurance, property coverage, and business interruption insurance. Each type of coverage comes with its own set of premiums, and the level of protection desired by the dentist directly influences the overall cost.
Basic liability insurance, often referred to as professional liability insurance or malpractice insurance, is designed to protect dentists from claims arising from their professional services. This type of insurance provides coverage for legal expenses and potential damages resulting from allegations of negligence or malpractice. While basic liability insurance is essential, it may not be sufficient for all dental practices, especially those with a higher risk profile or complex procedures.
For comprehensive protection, dentists may choose to include additional coverages in their insurance portfolio. Malpractice insurance specifically addresses the risks associated with dental malpractice claims, offering higher limits of liability and broader coverage. Property insurance safeguards the dental practice's physical assets, including equipment, furniture, and the building itself, against damage or loss due to events like fire, theft, or natural disasters. Business interruption insurance provides financial support during periods when the dental practice is unable to operate due to covered events, ensuring a continuous cash flow and helping to mitigate the financial impact of temporary closures.
| Coverage Type | Premium Range |
|---|---|
| Basic Liability Insurance | $1,500 - $3,000 annually |
| Malpractice Insurance | $3,000 - $6,000 annually |
| Property Insurance | $1,000 - $2,500 annually |
| Business Interruption Insurance | $500 - $1,500 annually |

It's important to note that the premiums mentioned above are approximate and can vary significantly based on individual circumstances. Factors such as the size and location of the dental practice, the number of dentists and staff, and the specific coverage limits and deductibles chosen will all influence the final premium amount.
Location and Regional Factors
The geographical location of a dental practice is another critical factor influencing insurance costs. Insurance providers assess the risk associated with different regions, considering factors such as crime rates, natural disaster frequency, and the overall healthcare landscape. Practices located in areas with higher crime rates or a higher propensity for natural disasters may face higher insurance premiums to account for the increased risk of claims.
Furthermore, the cost of living and the general economic climate of a region can impact insurance premiums. Areas with a higher cost of living may have correspondingly higher insurance rates, as the cost of repairs, replacements, and legal expenses tends to be higher in these regions. Additionally, regions with a higher concentration of dental practices may experience competitive pricing, leading to more affordable insurance options.
For example, a dental practice located in a metropolitan area with a dense population and a high cost of living may face insurance premiums that are significantly higher than those for a practice in a rural area with a lower cost of living and fewer potential risks.
Practice Size and Number of Dentists
The size of a dental practice, in terms of the number of dentists and staff employed, is a key factor in determining insurance costs. Larger practices with multiple dentists and a bigger patient base may require more extensive coverage to adequately protect all practitioners and the practice as a whole. As a result, the insurance premiums for larger practices tend to be higher than those for smaller, single-dentist practices.
Moreover, the specialization and expertise of the dentists within a practice can also influence insurance costs. Practices with highly specialized dentists, such as those focusing on oral surgery or orthodontics, may face higher premiums due to the increased risks and potential for more complex procedures and associated claims.
For instance, a large dental practice with multiple dentists specializing in various fields, such as general dentistry, orthodontics, and periodontics, may require a more comprehensive insurance policy to cover the diverse range of services offered. This could result in higher insurance premiums compared to a smaller practice with a single general dentist.
Risk Assessment and Claims History
Insurance providers conduct thorough risk assessments when determining insurance costs for dental practices. They analyze various factors, including the practice’s claims history, the age and experience of the dentists, and the types of procedures commonly performed. Practices with a history of frequent claims or those that perform high-risk procedures may be considered higher-risk and, consequently, face higher insurance premiums.
Additionally, insurance companies may take into account the age and experience of the dentists within a practice. Younger dentists with less experience may be seen as higher-risk, as they may have a higher propensity for errors or may not have established a consistent track record of safe and successful procedures. As a result, practices with younger dentists may incur higher insurance premiums.
For example, a dental practice with a dentist who has a history of multiple malpractice claims and a record of performing complex procedures with a higher risk of complications may be assessed as a higher-risk entity, leading to increased insurance premiums.
The Impact of Insurance Costs on Dental Practices
The cost of dentist insurance can significantly impact the financial health and operational decisions of dental practices. Let’s explore how insurance costs affect dental practices and the strategies they employ to manage these expenses.
Financial Considerations and Budgeting
Insurance costs represent a substantial expense for dental practices, and they must be carefully considered when budgeting and planning for the financial health of the practice. Dentists must allocate a significant portion of their revenue towards insurance premiums to ensure adequate protection for their practice and patients.
To manage insurance costs effectively, dental practices often engage in strategic financial planning. This may involve setting aside a specific budget for insurance premiums and regularly reviewing insurance policies to ensure they are aligned with the practice's needs and financial capabilities. Practices may also explore different insurance providers and coverage options to find the most cost-effective solution without compromising on necessary protections.
For instance, a dental practice may decide to increase its insurance coverage limits to better protect itself against potential claims. However, this decision must be balanced with the practice's financial capacity, as higher coverage limits typically result in increased insurance premiums. Careful financial analysis and budgeting are essential to ensure the practice can afford the necessary insurance coverage without compromising its overall financial stability.
Strategies for Managing Insurance Costs
Dental practices employ various strategies to manage insurance costs and ensure they remain competitive and financially viable. One common approach is to negotiate with insurance providers to obtain the best possible rates and coverage options. Dentists may leverage their professional networks, industry associations, or insurance brokers to secure group rates or customized insurance plans that align with their specific needs and risks.
Additionally, dental practices may adopt risk management strategies to reduce the likelihood of claims and, consequently, lower insurance costs. This can include implementing rigorous infection control protocols, investing in advanced training and education for staff, and regularly reviewing and updating safety procedures. By reducing the risk of accidents, errors, and patient harm, practices can lower their insurance premiums and improve their overall risk profile.
For example, a dental practice may decide to implement a comprehensive infection control program, including regular staff training, advanced sterilization techniques, and the use of single-use instruments. By reducing the risk of infections and potential cross-contamination, the practice not only enhances patient safety but also lowers its insurance premiums, as the risk of malpractice claims related to infections is significantly reduced.
The Role of Insurance Brokers and Advisors
Insurance brokers and advisors play a crucial role in helping dental practices navigate the complex world of insurance. These professionals have extensive knowledge of the insurance industry and can provide valuable guidance to dentists when selecting insurance coverage and managing insurance costs.
Insurance brokers work closely with dental practices to understand their unique needs and risks. They can assist in comparing different insurance policies, negotiating with insurance providers, and customizing coverage options to ensure the practice receives the protection it requires at a competitive price. Brokers may also provide ongoing support, helping practices review and update their insurance policies as their needs and circumstances evolve.
Additionally, insurance advisors can offer strategic advice to dental practices beyond insurance coverage. They may assist practices in implementing risk management strategies, developing emergency response plans, and creating business continuity protocols. By taking a holistic approach to risk management and insurance, advisors can help practices not only reduce insurance costs but also improve their overall operational efficiency and patient safety.
For instance, an insurance advisor may work with a dental practice to develop a comprehensive risk management plan. This plan may include regular staff training on infection control, implementing a robust patient consent and documentation process, and establishing protocols for managing medical emergencies. By addressing these key risk areas, the practice not only reduces its insurance costs but also enhances its reputation for safety and quality of care.
Future Trends and Implications for Dentist Insurance Costs
The landscape of dentist insurance is continually evolving, influenced by advancements in healthcare, changes in regulatory environments, and shifting consumer expectations. Let’s explore some of the key trends and their potential impact on insurance costs for dental practices in the future.
Advancements in Dental Technology and Procedures
The dental industry is witnessing rapid advancements in technology and procedures, which can have a significant impact on insurance costs. New technologies, such as digital imaging, 3D printing, and laser dentistry, offer enhanced precision and efficiency, but they also come with increased costs and potential risks. Insurance providers will need to adapt their policies to address the unique risks associated with these advanced technologies, which may result in higher insurance premiums for practices that adopt these innovations.
Additionally, the development of new dental procedures, such as implant dentistry and regenerative therapies, presents both opportunities and challenges for insurance providers. While these procedures offer significant benefits to patients, they also carry higher risks and potential complications. Insurance companies will need to carefully assess the risks associated with these procedures and adjust their coverage and premiums accordingly.
For example, a dental practice that adopts advanced laser dentistry technology may face higher insurance premiums due to the increased cost of the equipment and the potential for more complex procedures. Additionally, practices offering implant dentistry may require specialized insurance coverage to address the unique risks and potential complications associated with this procedure.
Changing Regulatory Environment and Legal Considerations
Changes in regulatory environments and legal considerations can have a profound impact on insurance costs for dental practices. New regulations and laws governing the dental profession, such as those related to patient safety, infection control, and informed consent, may result in increased compliance costs for practices. Insurance providers may need to adjust their policies to address these changing legal requirements, potentially leading to higher insurance premiums.
Furthermore, the legal landscape surrounding dental malpractice claims is constantly evolving. Changes in case law and precedent can influence the frequency and severity of malpractice claims, which, in turn, can impact insurance premiums. Dental practices must stay abreast of these legal developments to ensure they are adequately protected and to mitigate the risk of claims.
For instance, a change in state legislation regarding informed consent requirements for dental procedures may lead to an increase in malpractice claims related to consent issues. Insurance providers would need to adapt their policies to address this heightened risk, potentially resulting in higher insurance premiums for dental practices.
Consumer Expectations and Changing Market Dynamics
Consumer expectations and changing market dynamics are shaping the future of dentist insurance. Patients are increasingly demanding higher standards of care, transparency, and convenience. Practices that embrace these expectations and adopt patient-centric approaches may be rewarded with increased loyalty and market share. However, meeting these expectations often requires significant investments in technology, staff training, and infrastructure, which can impact insurance costs.
Additionally, the rise of digital health and telemedicine is transforming the way dental services are delivered and accessed. Practices that embrace digital solutions, such as teledentistry and online patient portals, may experience increased efficiency and patient engagement. However, these technologies also introduce new risks and potential liabilities, which insurance providers will need to consider when setting insurance premiums.
For example, a dental practice that implements a comprehensive patient portal system, allowing patients to schedule appointments, access their medical records, and receive digital consultation, may face higher insurance premiums due to the increased risk of data breaches and cybersecurity threats associated with these digital platforms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cost of dentist insurance is a multifaceted topic influenced by a range of factors, including coverage type, location, practice size, risk assessment, and evolving industry trends. Dental practices must carefully consider these factors when budgeting for insurance costs and selecting appropriate coverage. By working closely with insurance brokers and advisors, practices can navigate the complex world of insurance, ensuring they receive the protection they need at a competitive price.
As the dental industry continues to evolve, with advancements in technology, changes in regulations, and shifting consumer expectations, insurance providers will need to adapt their policies to address these emerging risks and opportunities. Dental practices, in turn, must stay informed and proactive in managing their insurance costs to remain competitive and financially viable while delivering the highest standards of care to their patients.
How often should dental practices review their insurance coverage and premiums?
+Dental practices should review their insurance coverage and premiums at least annually to ensure they remain adequately protected and to identify opportunities for cost savings. Regular reviews allow practices to stay abreast of changes in their risk profile, industry trends, and insurance options, enabling them to make informed decisions about their insurance coverage.
What are some common exclusions or limitations in dentist insurance policies?
+Common exclusions or limitations in dentist insurance policies may include coverage for certain high-risk procedures, intentional acts or misconduct, nuclear hazards, and war or terrorism. It’s essential for dental practices to carefully review their insurance policies to understand any exclusions or limitations that may apply to their specific circumstances.
How can dental practices reduce their insurance costs while maintaining adequate coverage?
+Dental practices can reduce their insurance costs by implementing effective risk management strategies, such as rigorous infection control protocols, regular staff training, and strict adherence to safety procedures. Additionally, practices can explore group insurance plans, negotiate with insurance providers, and consider self-insuring certain risks to lower their overall insurance premiums.
What are the potential consequences of underinsuring a dental practice?
+Underinsuring a dental practice can have severe consequences, including financial strain, damage to the practice’s reputation, and potential legal liabilities. If a practice is underinsured and faces a significant claim, it may not have sufficient coverage to cover the costs of the claim, leading to financial difficulties and potentially impacting the practice’s ability to continue operating.