Automotive Insurance Rates
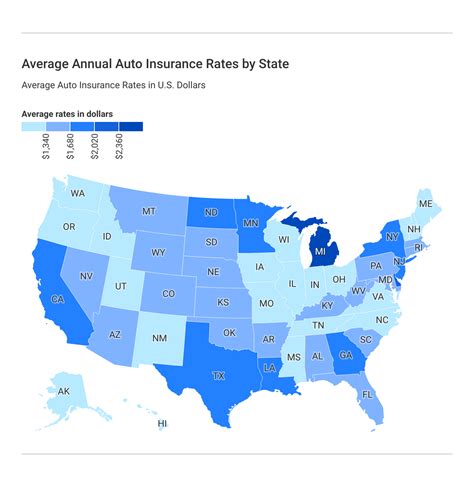
The world of automotive insurance is a complex and ever-evolving landscape, with rates and policies varying significantly across different regions and demographics. Understanding the factors that influence insurance rates is crucial for both insurance providers and consumers. This in-depth analysis delves into the intricacies of automotive insurance rates, exploring the key variables, regional disparities, and the latest trends shaping the industry.
Unraveling the Complexity of Automotive Insurance Rates
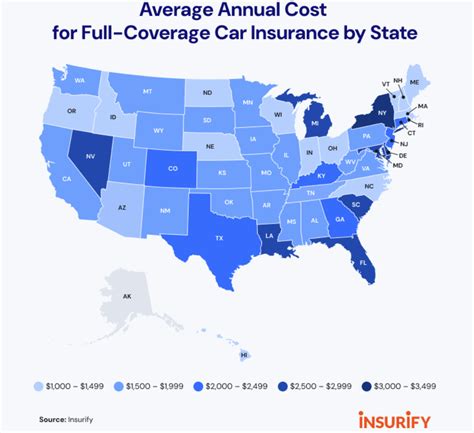
Automotive insurance is a vital aspect of vehicle ownership, providing financial protection against accidents, theft, and other unforeseen events. However, the process of determining insurance rates is far from straightforward. Insurance companies employ intricate methodologies to assess risk and set premiums, considering a myriad of factors that contribute to the overall cost of coverage.
Key Factors Influencing Insurance Rates
Several critical factors play a significant role in determining automotive insurance rates. These include:
- Vehicle Type and Make: Different vehicles have varying risk profiles. High-performance cars, sports cars, and luxury vehicles often attract higher insurance rates due to their potential for higher speeds and increased likelihood of accidents. Additionally, certain makes and models may have a history of higher repair costs or theft rates, further impacting insurance premiums.
- Driver Profile: The characteristics of the driver are a key consideration in insurance rate determination. Younger drivers, particularly those under 25, are generally viewed as higher-risk due to their lack of experience and higher propensity for accidents. Gender, marital status, and driving history (including past accidents and violations) also influence insurance rates.
- Coverage Level: The level of coverage chosen by the policyholder greatly impacts the insurance rate. Comprehensive coverage, which provides protection against a wide range of risks, typically carries a higher premium compared to basic liability coverage.
- Location and Usage: The geographic location where the vehicle is primarily used can significantly affect insurance rates. Urban areas often have higher rates due to increased traffic density, congestion, and a higher risk of accidents and theft. Additionally, the purpose of vehicle usage, such as personal, commercial, or leisure, can impact insurance costs.
- Credit Score: In many regions, insurance companies consider the policyholder’s credit score as an indicator of financial responsibility. Individuals with lower credit scores may face higher insurance rates, as they are statistically more likely to file claims.
Regional Disparities and Market Dynamics
Automotive insurance rates can vary significantly across different regions, even within the same country. These regional disparities are influenced by a combination of factors, including:
- Traffic Density and Accident Rates: Areas with higher traffic density and a higher incidence of accidents often experience elevated insurance rates. This is particularly true for regions with a history of frequent collisions and high-speed accidents.
- Theft and Vandalism Risks: Regions with higher rates of vehicle theft and vandalism typically face higher insurance premiums. Insurance companies factor in the cost of replacing or repairing stolen or vandalized vehicles when setting rates.
- Legal and Regulatory Environment: The legal framework and regulatory requirements in a given region can impact insurance rates. For instance, regions with stricter liability laws or higher minimum coverage requirements may see increased insurance costs.
- Market Competition: The level of competition among insurance providers in a region can influence insurance rates. In highly competitive markets, insurers may offer more affordable rates to attract customers, while less competitive regions may see higher premiums.
Emerging Trends in Automotive Insurance
The automotive insurance industry is undergoing significant transformations driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Here are some key trends shaping the future of automotive insurance rates:
- Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance (UBI): Telematics devices and UBI programs allow insurance companies to track driving behavior and usage patterns in real-time. By analyzing factors such as speed, acceleration, braking, and mileage, insurers can offer personalized insurance rates based on individual driving habits. This trend is expected to gain traction, promoting safer driving and more accurate risk assessment.
- Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms are enabling insurers to process vast amounts of data more efficiently. This includes not only traditional factors like driving history and vehicle type but also emerging variables such as weather patterns, road conditions, and even social media behavior. By leveraging these insights, insurers can refine their risk assessment models and offer more tailored insurance rates.
- Connected Vehicles and Autonomous Driving: The rise of connected vehicles and the development of autonomous driving technologies are set to revolutionize the automotive industry. As vehicles become more interconnected and self-driving capabilities advance, insurance rates may undergo significant changes. Insurers will need to adapt their models to account for the reduced risk of human error and the potential for safer driving environments.
- Digital Transformation and InsurTech: The insurance industry is experiencing a digital transformation, with InsurTech companies leveraging technology to streamline processes and enhance customer experiences. Online insurance platforms, mobile apps, and digital payment options are becoming increasingly popular, offering convenience and potentially lower insurance rates for tech-savvy consumers.
The Future of Automotive Insurance: A Balancing Act
As the automotive insurance landscape continues to evolve, insurers face the challenge of balancing risk assessment and pricing with the need to remain competitive and provide value to customers. The adoption of advanced technologies and data-driven approaches is expected to play a pivotal role in achieving this balance.
By leveraging real-time data and advanced analytics, insurers can refine their risk models, identify new opportunities for cost reduction, and offer more personalized insurance rates. This shift towards a data-centric approach not only benefits insurance providers but also empowers consumers with greater control over their insurance costs.
In conclusion, the world of automotive insurance is a complex ecosystem, influenced by a multitude of factors and constantly evolving with technological advancements and changing market dynamics. Understanding these dynamics and staying informed about the latest trends is essential for both insurance providers and consumers to navigate this intricate landscape effectively.
How often do insurance rates change, and what triggers these changes?
+Insurance rates can change periodically, typically annually or semi-annually. These changes are influenced by various factors, including claim frequency and severity, changes in traffic patterns, and updates in state or local regulations. Additionally, insurers may adjust rates based on their own internal data and risk assessment models.
Are there any ways to lower my automotive insurance rates?
+Yes, there are several strategies to potentially lower your insurance rates. These include maintaining a clean driving record, shopping around for competitive quotes, considering higher deductibles, and taking advantage of available discounts (such as for safe driving, multiple policies, or vehicle safety features). Additionally, embracing usage-based insurance programs can offer personalized rates based on your driving behavior.
What is the impact of autonomous vehicles on automotive insurance rates?
+The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles is expected to significantly impact automotive insurance rates. As self-driving technologies reduce the risk of human error, accidents are anticipated to decrease, leading to lower insurance costs. However, the transition period may be complex, as insurers adapt their models to account for the changing risk landscape.



