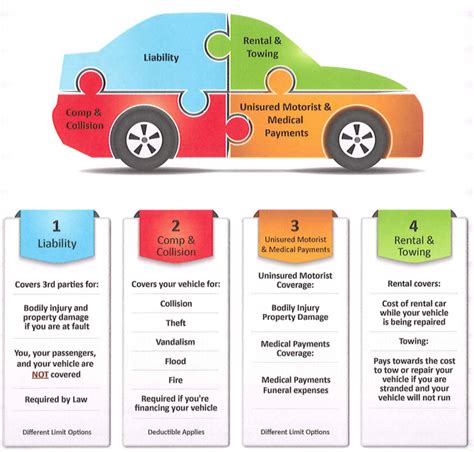
Where Can I Get Medical Insurance

Understanding Medical Insurance and Your Options

When it comes to safeguarding your health and financial well-being, medical insurance plays a crucial role. With the right coverage, you can access essential healthcare services without worrying about overwhelming costs. Whether you're an individual, a family, or an employee seeking benefits, there are various avenues to explore when obtaining medical insurance. Let's delve into the key sources and considerations to help you make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
Exploring the Avenues: Where to Find Medical Insurance
Securing medical insurance involves exploring multiple channels, each with its unique benefits and considerations. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the process and find the right coverage for your needs.
Employer-Sponsored Health Plans
One of the most common ways to obtain medical insurance is through your employer. Many companies offer group health insurance plans as part of their employee benefits package. These plans often provide comprehensive coverage at a reduced cost, as employers may contribute to the premiums. The advantage of employer-sponsored plans is the potential for lower out-of-pocket expenses and access to a network of healthcare providers.
When evaluating employer-sponsored plans, consider the following:
- Coverage Options: Employers may offer a range of plans, including Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), or Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs). Each plan has different provider networks and coverage rules, so choose the one that aligns with your healthcare needs.
- Premium Contributions: Understand the cost-sharing arrangement. Some employers cover a significant portion of the premium, while others may require employees to contribute a percentage.
- Eligibility: Check if you're eligible for the plan. Certain plans may only be accessible to full-time employees or those who have worked for the company for a specific duration.
- Open Enrollment: Mark your calendar for the open enrollment period, as this is typically the only time you can make changes to your coverage without a qualifying life event.
Individual and Family Plans
If you're self-employed, unemployed, or your employer doesn't offer health insurance, you can explore individual and family plans. These plans are designed for individuals, couples, or families who need coverage outside of an employer-sponsored program.
Key considerations for individual and family plans include:
- Marketplace vs. Private Insurers: You can purchase individual plans through the Health Insurance Marketplace (created by the Affordable Care Act) or directly from private insurance companies. The Marketplace offers cost-assistance programs, while private insurers may have more flexibility in plan design.
- Plan Networks: Similar to employer-sponsored plans, individual plans come with various network options. Evaluate the providers within the network to ensure they align with your healthcare preferences.
- Premium Costs: Individual plans can be more expensive than group plans, but they offer the flexibility to choose the coverage that suits your needs.
- Subsidies and Tax Credits: If you purchase a plan through the Marketplace, you may be eligible for subsidies or tax credits to reduce your premium costs.
Government-Sponsored Programs
Certain government programs provide medical insurance to specific populations. Understanding your eligibility for these programs is essential, as they can offer comprehensive coverage at little to no cost.
- Medicaid: This program is available to low-income individuals and families. Eligibility criteria vary by state, but it typically covers a wide range of healthcare services.
- Medicare: Medicare is primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, but it also covers younger people with certain disabilities. It consists of different parts, each covering specific healthcare aspects.
- Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP): CHIP provides low-cost healthcare coverage for children in families that earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance.
Short-Term and Limited-Duration Plans
Short-term and limited-duration plans offer temporary coverage for individuals between jobs, waiting for other coverage to start, or those who missed the open enrollment period. These plans typically have lower premiums but often come with restrictions and limited coverage.
Consider the following when evaluating short-term plans:
- Duration: These plans are intended for short-term coverage, usually lasting up to a year. They may not renew, so plan accordingly.
- Coverage Limitations: Short-term plans often exclude pre-existing conditions and may have limited benefits. Carefully review the policy to understand what's covered.
- Underwriting: Unlike many other plans, short-term plans may require medical underwriting, meaning your health history could impact your eligibility and premium costs.
Special Enrollment Periods
In certain situations, you may qualify for a Special Enrollment Period (SEP) outside of the standard open enrollment window. SEPs allow you to enroll in or change your health plan due to specific life events, such as marriage, divorce, birth or adoption of a child, loss of other coverage, or a move to a new service area.
Keep in mind that SEPs are time-sensitive, so act promptly when a qualifying event occurs.
Comparing Plans and Making Informed Choices
With a wide range of medical insurance options available, it's essential to compare plans to find the best fit for your needs. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Premium Costs: Evaluate the monthly premiums, deductibles, copays, and out-of-pocket maximums to understand the financial implications of each plan.
- Coverage Benefits: Review the specific services covered, including prescription drugs, mental health services, maternity care, and preventive care. Ensure the plan aligns with your healthcare requirements.
- Provider Networks: Verify that your preferred healthcare providers are included in the plan's network. Out-of-network care can be costly.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Consider the plan's flexibility in choosing providers and accessing services. Some plans may offer more convenience through digital tools and a broader network.
- Cost-Sharing Arrangements: Understand how costs are shared between you and the insurer. Higher premiums may result in lower out-of-pocket expenses during healthcare utilization.
The Importance of Staying Informed
Navigating the world of medical insurance requires staying informed about your options, eligibility, and the latest healthcare regulations. Regularly review your coverage, especially during open enrollment periods, to ensure it continues to meet your needs. Additionally, keep an eye on industry trends and changes that may impact your coverage.
Conclusion: Your Path to Affordable Healthcare

Obtaining medical insurance is a critical step towards safeguarding your health and financial stability. By exploring the various avenues, from employer-sponsored plans to government programs and individual options, you can find the coverage that best suits your unique circumstances. Remember to thoroughly evaluate your needs, compare plans, and stay informed about the ever-evolving healthcare landscape. With the right medical insurance, you can access the care you need without the worry of overwhelming costs.
Can I have multiple medical insurance plans at once?
+Yes, it’s possible to have multiple medical insurance plans, but coordination of benefits is essential to avoid duplicating coverage. Each plan will have its own rules and coverage limits, so ensure you understand how they work together.
What if I have a pre-existing condition? Will I be able to get insurance?
+Thanks to the Affordable Care Act, insurance companies cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions. However, short-term plans may have different rules, so it’s crucial to review the policy carefully.
How can I reduce my insurance costs without sacrificing coverage?
+Consider a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA). HDHPs often have lower premiums, and HSAs allow you to save pre-tax dollars for medical expenses, providing a cost-effective way to manage healthcare costs.