What Is The Average Car Insurance Payment

Understanding the average car insurance payment is essential for any vehicle owner, as it provides insight into the financial obligations associated with maintaining a vehicle. The cost of car insurance can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including the make and model of the car, the driver's age and driving history, and the location where the vehicle is registered. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of car insurance payments, offering a comprehensive analysis of the average costs and the factors that influence them.
Average Car Insurance Payment: A National Perspective

On a national level, the average cost of car insurance in the United States is approximately 1,674 per year</strong> or roughly <strong>139.50 per month. However, this figure is merely an average, and the actual cost can deviate significantly based on individual circumstances.
To provide a more detailed overview, let's break down the average car insurance payment into specific categories:
| Insurance Type | Average Annual Cost |
|---|---|
| Liability Only | $500 - $1,500 |
| Full Coverage | $1,000 - $2,500 |
| High-Risk Policies | $3,000 - $10,000 |
Factors Influencing Car Insurance Costs
The average car insurance payment is influenced by a multitude of factors, each playing a unique role in determining the final cost. These factors include:
- Vehicle Type and Usage: The make, model, and year of the vehicle can significantly impact insurance costs. Luxury vehicles or those prone to theft often attract higher premiums. Additionally, the primary usage of the vehicle, whether for personal or commercial purposes, can affect the insurance rate.
- Driver's Profile: Age, gender, and driving history are crucial determinants. Younger drivers, particularly males, often face higher premiums due to their perceived risk level. A clean driving record with no accidents or traffic violations can lead to lower insurance costs.
- Location: The geographical location where the vehicle is registered and primarily used plays a significant role. Urban areas often have higher insurance rates due to increased traffic and the higher likelihood of accidents or theft. Additionally, certain states have specific laws and regulations that can influence insurance costs.
- Coverage Level: The level of coverage chosen by the policyholder directly impacts the insurance premium. Full coverage, which includes liability, collision, and comprehensive coverage, generally costs more than liability-only coverage.
- Credit History: In many states, insurance companies are allowed to consider a person's credit score when determining insurance rates. A good credit history can lead to lower premiums, while a poor credit score may result in higher costs.
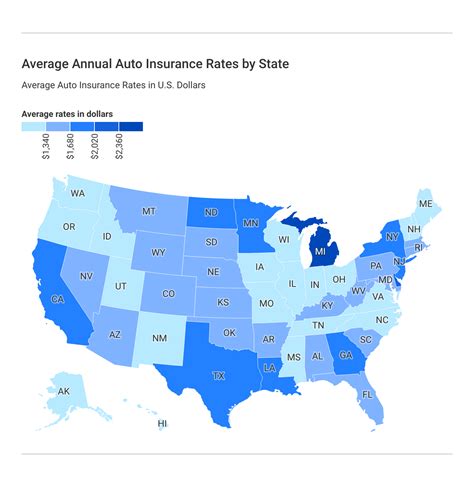
Regional Variations in Car Insurance Costs
Car insurance costs can vary significantly across different regions in the United States. To illustrate this, let’s examine the average annual car insurance premiums in some of the most populous states:
| State | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| California | $1,435 |
| Texas | $1,325 |
| New York | $1,860 |
| Florida | $1,490 |
| Illinois | $1,030 |
Analyzing the Average Car Insurance Payment by Age Group

Age is a significant factor in determining car insurance costs. Let’s delve into how the average car insurance payment varies with age:
Young Drivers (Ages 16-25)
Young drivers, particularly those under 25, often face the highest insurance premiums. This is due to their lack of driving experience and the higher risk associated with this age group. The average annual insurance cost for this age group is approximately $2,200. However, it’s worth noting that this can vary significantly based on the driver’s gender and driving history.
Middle-Aged Drivers (Ages 26-50)
As drivers enter their late 20s and early 30s, insurance costs generally start to decrease. This is because drivers in this age group typically have more experience and a better understanding of road safety. The average insurance cost for this age group is around $1,500 per year, with rates gradually decreasing as the driver ages.
Senior Drivers (Ages 51+)
For drivers aged 51 and above, insurance costs can vary significantly. While some senior drivers may experience an increase in insurance premiums due to age-related health issues or a decline in driving abilities, others may enjoy lower rates due to their long-standing clean driving records. On average, senior drivers pay around $1,300 per year for car insurance.
Tips for Reducing Car Insurance Costs
While the average car insurance payment can be a useful benchmark, it’s important to remember that individual circumstances can greatly influence the final cost. Here are some tips to potentially reduce your car insurance expenses:
- Compare Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the best rates for your specific situation.
- Bundle Policies: Consider bundling your car insurance with other policies, such as home or renters' insurance, to potentially save money.
- Maintain a Clean Driving Record: Avoid accidents and traffic violations, as these can significantly increase your insurance premiums.
- Choose a Higher Deductible: Opting for a higher deductible can lower your monthly premiums, but ensure you can afford the deductible in the event of a claim.
- Take Advantage of Discounts: Many insurance companies offer discounts for a variety of reasons, including safe driving, loyalty, and even certain professions.
The Future of Car Insurance Payments
The car insurance industry is continually evolving, and advancements in technology and changing regulations are likely to influence the average car insurance payment in the future. Here are some potential developments to consider:
- Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance: The use of telematics devices and usage-based insurance policies may become more prevalent. These policies track driving behavior and offer personalized premiums based on actual driving habits.
- Autonomous Vehicles: As autonomous vehicles become more common, insurance costs may shift to cover different types of risks, potentially impacting the average insurance payment.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in state regulations, such as those related to no-fault insurance or minimum coverage requirements, can significantly impact insurance costs.
- Digital Transformation: The insurance industry's digital transformation may lead to more efficient processes, potentially reducing administrative costs and, consequently, insurance premiums.
Conclusion

Understanding the average car insurance payment is just the first step in navigating the complex world of vehicle insurance. By considering the various factors that influence insurance costs and adopting strategies to reduce premiums, vehicle owners can make more informed decisions when selecting an insurance policy. As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable will be key to managing car insurance expenses effectively.
How often should I review my car insurance policy to ensure I’m getting the best rate?
+It’s recommended to review your car insurance policy annually, or whenever your circumstances change significantly (e.g., a new vehicle, a move to a different location, or a life event like marriage or retirement). Regular reviews ensure you’re not overpaying and allow you to take advantage of any new discounts or policy changes.
Are there any ways to save on car insurance if I have a less-than-perfect driving record?
+Yes, even with a less-than-perfect driving record, there are strategies to reduce your insurance costs. These include opting for a higher deductible, maintaining a long-term relationship with your insurance provider, and taking defensive driving courses to improve your driving skills and potentially earn a discount.
What is the difference between liability-only and full coverage car insurance, and which is better for me?
+Liability-only insurance covers the cost of damage or injuries you cause to others in an accident, while full coverage insurance also includes coverage for your own vehicle, whether due to an accident, theft, or other incidents. The best option for you depends on your vehicle’s value, your personal financial situation, and your risk tolerance.



