What Is Medical Insurance

Medical insurance, also known as health insurance, is a vital component of modern healthcare systems, playing a crucial role in providing financial protection and access to medical services for individuals and families. In an era where medical expenses can be exorbitant, understanding the fundamentals of medical insurance is essential for making informed decisions about one's health and well-being.
The Essence of Medical Insurance
At its core, medical insurance is a contractual agreement between an individual (or a group, such as a family or an organization) and an insurance company. This agreement, often referred to as a policy, outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurance provider will compensate the insured for medical expenses. The primary goal is to ensure that individuals have the means to afford necessary medical treatments and services without facing financial ruin.
How Medical Insurance Works
The mechanics of medical insurance involve a series of key components:
Premiums
Policyholders pay regular premiums, typically on a monthly or annual basis, to the insurance company. These premiums are the price one pays to maintain their insurance coverage. The amount of the premium is determined by various factors, including the individual’s age, health status, location, and the type of coverage chosen.
Coverage
Coverage refers to the range of medical services and treatments that are included in the insurance plan. Different plans offer varying levels of coverage, from basic plans that cover essential services like doctor visits and hospitalization to more comprehensive plans that include dental, vision, prescription drugs, and even mental health services. It’s crucial for individuals to carefully review the coverage details to ensure their specific healthcare needs are met.
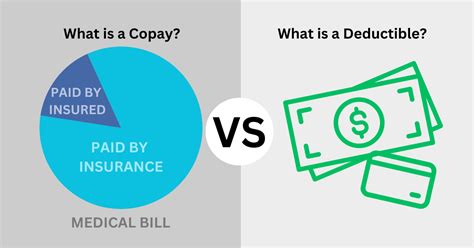
Deductibles and Copays
Most medical insurance plans have a deductible, which is the amount an individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. For instance, if a plan has a 1,000 deductible, the insured must pay the first 1,000 of their medical expenses before the insurance company starts contributing. Some plans also have copays, which are fixed amounts the insured pays for specific services, such as a $20 copay for a doctor’s visit.
Networks and Providers
Insurance companies often have networks of preferred providers, which are doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities that have agreed to provide services at discounted rates. Using in-network providers typically results in lower out-of-pocket costs for the insured. However, out-of-network care can be more expensive and may require additional paperwork and coordination.
Claims and Reimbursement
When an insured individual receives medical services, they (or their provider) must file a claim with the insurance company. This involves submitting detailed information about the services received, along with any supporting documentation. Once the claim is processed and approved, the insurance company reimburses the insured or the provider for the covered expenses, minus any applicable deductibles or copays.
The Benefits of Medical Insurance
Medical insurance offers a myriad of advantages, making it an indispensable tool for navigating the complex world of healthcare:
Financial Protection
Perhaps the most significant benefit is the financial protection it provides. Medical emergencies and chronic conditions can lead to substantial expenses, and insurance helps individuals manage these costs effectively. By spreading the risk across a large group of policyholders, insurance companies can offer affordable coverage, ensuring that individuals can access necessary care without breaking the bank.
Preventive Care
Many insurance plans emphasize preventive care, encouraging individuals to undergo regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations. By catching potential health issues early on, individuals can avoid more serious (and costly) health problems down the line. This proactive approach to healthcare not only benefits individuals but also helps reduce the overall burden on the healthcare system.
Peace of Mind
Knowing that one has medical insurance can provide a sense of security and peace of mind. Individuals no longer have to worry about the financial implications of a sudden illness or injury, allowing them to focus on their recovery and well-being without added stress.
Improved Access to Healthcare
Medical insurance expands access to healthcare services. With insurance, individuals can seek the care they need without worrying about the cost, leading to better overall health outcomes. This is particularly crucial for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those who require specialized treatments.
Types of Medical Insurance Plans
The world of medical insurance is diverse, offering a range of plan types to cater to different needs and preferences:
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
HMOs are characterized by their emphasis on preventive care and coordination of services. Policyholders typically select a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as a gatekeeper, referring them to specialists within the HMO network. HMOs often have lower premiums but may have more limited choice of providers.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPOs offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Policyholders can visit in-network providers without a referral, and they also have the option to see out-of-network providers, albeit at a higher cost. PPOs typically have higher premiums but provide greater freedom in choosing healthcare services.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
EPOs are similar to PPOs in that they offer a network of preferred providers. However, unlike PPOs, EPOs do not cover out-of-network care, except in emergencies. EPOs often have lower premiums compared to PPOs but may have more limited provider choices.
Point of Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine elements of both HMOs and PPOs. Policyholders can choose to either stay within the network or opt for out-of-network care. When staying in-network, they follow HMO-like protocols, requiring referrals from their PCP. POS plans offer flexibility but may have higher premiums.
High Deductible Health Plans (HDHP)
HDHPs are characterized by their high deductibles, often in the range of 1,000 to 6,000 or more. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing individuals to save pre-tax dollars for medical expenses. HDHPs are cost-effective for individuals who rarely need medical care but want the financial protection for more significant health events.
The Future of Medical Insurance

The landscape of medical insurance is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing healthcare needs, and shifts in policy and regulation. Here are some key trends and developments to watch:
Digital Transformation
The digital revolution is transforming the way medical insurance operates. From online enrollment and claims submission to telemedicine and digital health records, technology is streamlining processes and enhancing the overall experience for both insurers and policyholders. Digital tools also enable more personalized and data-driven approaches to healthcare.
Value-Based Care
There is a growing shift towards value-based care models, where payment is tied to the quality and outcomes of healthcare services rather than the volume of services provided. This approach aims to improve patient health while also controlling costs, potentially leading to more efficient and effective healthcare delivery.
Consumer-Directed Health Plans
Consumer-directed health plans, such as HDHPs paired with HSAs, are gaining popularity. These plans put more control in the hands of individuals, allowing them to manage their healthcare expenses and make more informed decisions about their healthcare choices. However, this approach may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with chronic conditions or higher healthcare needs.
Expanding Coverage Options
Efforts to expand access to medical insurance are ongoing, with initiatives aimed at making healthcare more affordable and accessible for all. This includes expanding Medicaid coverage, improving affordability in the individual market, and exploring innovative approaches to coverage, such as public option plans or universal healthcare models.
Telemedicine and Remote Care
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of telemedicine and remote care services. While these technologies were already gaining traction, the pandemic has highlighted their value in providing convenient and safe access to healthcare. Telemedicine is likely to play a significant role in the future of medical insurance, offering cost-effective solutions for routine care and chronic condition management.
Conclusion
Medical insurance is a complex yet essential aspect of modern healthcare. By understanding the fundamentals, individuals can make informed choices about their healthcare coverage, ensuring they have the protection they need to navigate the healthcare system with confidence. As the field continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and developments is crucial for making the best decisions for one’s health and financial well-being.
How do I choose the right medical insurance plan for my needs?
+Selecting the right medical insurance plan involves considering several factors. Evaluate your healthcare needs, including any pre-existing conditions or regular medical services you require. Assess the coverage offered by different plans, comparing deductibles, copays, and the network of providers. Consider your budget and whether you prefer more comprehensive coverage or a plan with lower premiums. It’s also beneficial to read reviews and seek recommendations from trusted sources to ensure you make an informed choice.
What happens if I don’t have medical insurance and need emergency care?
+In emergency situations, hospitals are required by law to provide necessary treatment regardless of an individual’s insurance status. However, the financial burden of emergency care without insurance can be significant. It’s crucial to explore options for obtaining insurance, whether through an employer-sponsored plan, the individual market, or government programs like Medicaid or Medicare. Being uninsured can lead to substantial debt and limited access to ongoing healthcare.
Are there any tax benefits associated with medical insurance?
+Yes, there are potential tax benefits related to medical insurance. In many countries, including the United States, premiums paid for medical insurance may be tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income. Additionally, certain types of insurance plans, such as Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs), offer tax advantages by allowing you to set aside pre-tax dollars for medical expenses. It’s advisable to consult a tax professional to understand the specific tax benefits applicable to your situation.
Can I switch my medical insurance plan if I’m not satisfied with my current coverage?
+Yes, you have the option to switch your medical insurance plan during open enrollment periods or under certain qualifying life events. Open enrollment typically occurs annually, allowing you to review and change your coverage. However, if you experience a significant life event, such as marriage, divorce, birth of a child, or loss of job-based coverage, you may qualify for a Special Enrollment Period, enabling you to change your plan outside of the regular open enrollment timeframe.