What Is Copay In Health Insurance
In the realm of health insurance, understanding the intricacies of financial responsibilities is paramount for policyholders. One such essential aspect is the concept of copay, also known as copayment, which plays a significant role in the cost-sharing mechanism between insurance providers and policyholders.
This article aims to delve into the world of copays, shedding light on its definition, purpose, and practical implications. By exploring real-world examples and providing an in-depth analysis, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge to navigate their health insurance plans more effectively.
Understanding the Copay Mechanism

At its core, a copay is a predetermined, fixed amount that an insured individual pays out of pocket for a covered healthcare service at the time of receiving that service. It serves as a direct payment to the healthcare provider, distinct from the premiums paid to the insurance company.
The purpose of the copay is multifaceted. Firstly, it acts as a deterrent for unnecessary or excessive healthcare utilization, encouraging policyholders to make informed decisions about their healthcare needs. Secondly, it helps spread the financial burden more equitably, ensuring that insurance providers and policyholders share the costs of healthcare services.
Real-World Copay Examples
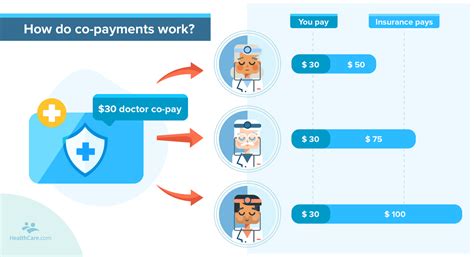
Let’s illustrate the concept with practical scenarios. Consider a health insurance plan with a 30 copay for office visits. When an insured individual visits their primary care physician for a routine check-up, they would be responsible for paying 30 directly to the doctor’s office. This copay remains the same regardless of the actual cost of the visit, providing a predictable financial outlay for the policyholder.
Another common example is prescription medications. Many insurance plans have copays for pharmacy services, ranging from $10 to $50 or more, depending on the tier of the medication. For instance, a plan with a $20 copay for generic drugs and a $50 copay for brand-name drugs ensures that policyholders have a clear understanding of their financial obligations when filling prescriptions.
Factors Influencing Copay Amounts

The determination of copay amounts is influenced by various factors, each shaping the financial landscape of health insurance plans.
Plan Design and Network
Insurance providers design their plans with specific copay structures, considering factors like the desired level of cost-sharing and the expected utilization of services. Plans with lower copays often have higher premiums, reflecting a more equitable distribution of costs.
Additionally, the provider network associated with a plan can impact copays. In-network providers typically have negotiated rates with the insurance company, which may result in lower copays compared to out-of-network services. This incentivizes policyholders to choose providers within the network for more affordable care.
Individual vs. Family Plans
Copay amounts can vary between individual and family plans. Family plans often have higher copays to account for the potential increased utilization of healthcare services by multiple family members. However, these plans may offer family discounts or caps on copays to provide a more manageable financial burden.
| Plan Type | Copay Example |
|---|---|
| Individual Plan | $30 copay for office visits |
| Family Plan | $40 copay for office visits, with a maximum family copay of $120 per visit |

Copayment and Deductibles: A Comparative Analysis
While copays and deductibles are both cost-sharing mechanisms in health insurance, they differ in their application and impact on policyholders.
Deductibles: An Annual Threshold
A deductible is the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. It applies to the overall healthcare expenses incurred during a policy period, typically a year. Once the deductible is met, the insurance provider starts covering a percentage of the costs.
For example, a plan with a $1,500 deductible means the policyholder must pay the first $1,500 of their medical expenses before the insurance coverage becomes effective. After meeting the deductible, the insurance company may cover 80% of eligible expenses, while the policyholder is responsible for the remaining 20% (known as coinsurance) until they reach their out-of-pocket maximum.
Copays: Specific Service Charges
In contrast, copays are specific charges for individual healthcare services, irrespective of the deductible. Policyholders pay copays regardless of whether they have met their deductible or not. Copays are designed to be lower than the actual cost of the service, making healthcare more accessible and predictable for policyholders.
For instance, an insured individual with a $1,500 deductible may still be responsible for a $30 copay for a doctor's visit, even if they have not yet met their deductible. This ensures that routine care remains affordable and encourages policyholders to seek necessary medical attention without financial barriers.
The Impact of Copays on Healthcare Utilization
Copays have a direct influence on how policyholders utilize healthcare services, shaping their decision-making process.
Encouraging Preventive Care
Lower copays for preventive services, such as annual physical exams or immunizations, incentivize policyholders to prioritize their health. By making these services more affordable, insurance providers promote a proactive approach to healthcare, potentially reducing the need for more costly interventions in the future.
Managing Chronic Conditions
For individuals with chronic conditions, consistent healthcare management is crucial. Copays for prescription medications and specialty care can significantly impact their ability to manage their health effectively. Insurance plans often offer discounted copays for medications and services related to chronic conditions, ensuring that policyholders have the necessary resources to maintain their well-being.
Navigating the Copay Landscape: Tips for Policyholders
Understanding the copay structure of your health insurance plan is crucial for effective financial planning and healthcare utilization.
Review Your Plan Details
Familiarize yourself with the copay amounts and services covered by your plan. Pay attention to any variations in copays for in-network vs. out-of-network providers, as well as differences between generic and brand-name medications. Knowing these details can help you make informed choices about your healthcare providers and prescriptions.
Utilize In-Network Providers
Choosing in-network providers can result in lower copays and overall healthcare costs. Insurance companies negotiate rates with these providers, often leading to more affordable services. Additionally, out-of-network providers may not be contractually obligated to accept the copay as full payment, potentially resulting in higher out-of-pocket expenses.
Compare Prescription Options
When filling prescriptions, consider the copay differences between brand-name and generic medications. While brand-name drugs may have a higher copay, they are not always necessary. Discuss with your healthcare provider whether a generic alternative is suitable for your condition, as it can significantly reduce your out-of-pocket expenses.
Explore Copay Assistance Programs
Some insurance providers or pharmaceutical companies offer copay assistance programs to help policyholders manage their healthcare costs. These programs may provide discounts or even cover the entire copay amount for specific medications or services. Researching and enrolling in such programs can provide significant financial relief, especially for those with chronic conditions.
The Future of Copays: Trends and Innovations
As the healthcare industry evolves, so do the strategies employed by insurance providers to manage costs and encourage responsible healthcare utilization. Here are some emerging trends and innovations in the copay landscape.
Value-Based Copays
Some insurance companies are experimenting with value-based copays, where the copay amount is tied to the effectiveness of the treatment or service received. For example, if a prescription medication successfully treats a condition, the copay for that medication may decrease over time. This approach incentivizes both providers and policyholders to seek the most effective treatments, potentially reducing overall healthcare costs.
Dynamic Copay Adjustments
Insurance providers are exploring dynamic copay adjustments based on various factors, such as the policyholder’s health status, the severity of the condition being treated, and the expected utilization of services. This approach aims to personalize copays, making them more equitable and reflective of individual healthcare needs.
Integrating Copays with Digital Health Solutions
The integration of copays with digital health solutions, such as telemedicine platforms and health tracking apps, is gaining traction. By incorporating copays into these digital tools, policyholders can easily access and manage their healthcare needs remotely, while still benefiting from the cost-sharing mechanism.
Enhanced Copay Transparency
Insurance providers are recognizing the importance of copay transparency in building trust with policyholders. Enhanced transparency initiatives include providing real-time copay estimates during the healthcare utilization process and offering clear explanations of copay structures and variations. This empowers policyholders to make informed decisions about their healthcare choices.
Conclusion
The copayment system in health insurance is a fundamental component of the cost-sharing equation, influencing how policyholders engage with the healthcare system. By understanding the intricacies of copays, policyholders can navigate their health insurance plans more effectively, making informed decisions about their healthcare needs and financial responsibilities.
As the healthcare industry continues to innovate, the role of copays will likely evolve to align with the changing dynamics of healthcare delivery and cost management. Policyholders can stay ahead of these changes by staying informed, leveraging available resources, and advocating for their healthcare needs.
How do copays differ from coinsurance?
+
Copays and coinsurance are both cost-sharing mechanisms, but they differ in their application. Copays are predetermined, fixed amounts paid for specific healthcare services, while coinsurance is a percentage of the allowed amount for a service, typically applied after meeting the deductible. Coinsurance continues until the out-of-pocket maximum is reached, whereas copays are typically one-time payments for each service.
Can copays change during the policy period?
+
Yes, insurance providers may adjust copay amounts annually or as part of plan revisions. It’s important for policyholders to review their plan details regularly to stay informed about any changes to copays and other cost-sharing structures.
Are there any exceptions to copay requirements?
+
Some insurance plans offer waivers or reductions in copays for certain services or circumstances. For example, preventive care services like annual physicals or immunizations may have lower or no copays. Additionally, some plans may waive copays for emergency services or for individuals with specific health conditions.



