What Does Self Insured Mean
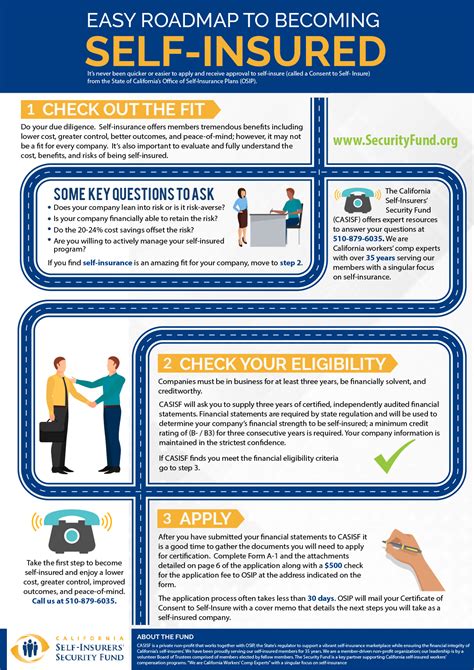
In the realm of insurance and healthcare, the term "self-insured" holds significant importance and carries unique implications for individuals, businesses, and healthcare systems. Understanding the concept of self-insurance is crucial for making informed decisions about healthcare coverage and risk management. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of self-insured entities, exploring their definition, how they operate, and the benefits and considerations they present.
Understanding Self-Insurance: A Comprehensive Overview

Self-insurance is a strategy employed by entities, often businesses or organizations, to assume financial responsibility for their own healthcare or other insurance-related risks rather than outsourcing this responsibility to traditional insurance companies. This approach involves setting aside funds or utilizing other financial mechanisms to cover potential losses or expenses associated with the risks they face.
Key Definitions and Concepts
To grasp the concept of self-insurance fully, it’s essential to understand the following key terms:
- Self-Insured Entity: This refers to an individual, business, or organization that takes on the role of an insurer for specific risks, such as healthcare expenses.
- Risk Retention: Self-insured entities retain the financial risk associated with the insured events or claims, which can include medical costs, property damage, or liability claims.
- Risk Pooling: Self-insured entities often form risk pools, where funds are collected and managed collectively to cover potential losses. This pooling of resources allows for more efficient risk management.
- Claims Handling: Self-insured entities are responsible for managing and paying out claims, which involves evaluating and processing requests for coverage and reimbursements.
How Self-Insurance Works
The process of self-insurance typically involves the following steps:
- Risk Assessment: Self-insured entities carefully evaluate the potential risks they face and determine the likelihood and financial impact of those risks.
- Fund Establishment: Funds are set aside or allocated specifically for self-insurance purposes. This can be done through dedicated accounts, trusts, or other financial arrangements.
- Claims Management: When claims arise, self-insured entities assess their validity and process payments accordingly. This may involve working with third-party administrators or utilizing internal resources.
- Financial Planning: Self-insured entities must carefully manage their funds to ensure they have sufficient resources to cover potential claims and maintain financial stability.
- Risk Mitigation: Self-insurance often goes hand in hand with proactive risk management strategies to minimize the frequency and severity of claims.
Benefits of Self-Insurance
Self-insurance offers several advantages, including:
- Cost Savings: Self-insured entities can potentially save on insurance premiums, as they are not paying traditional insurers. However, this requires careful financial planning and management.
- Flexibility: Self-insurance provides entities with greater control over their healthcare or insurance coverage, allowing them to tailor policies to their specific needs and preferences.
- Customized Coverage: Self-insured entities can design coverage plans that align with their unique circumstances and risk profiles, ensuring a better fit for their operations.
- Cash Flow Management: By setting aside funds for self-insurance, entities can have better control over their cash flow and potentially avoid large, unexpected insurance payments.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Self-insurance encourages entities to implement proactive risk management measures, leading to a safer and more efficient workplace or environment.
Considerations and Challenges
While self-insurance offers benefits, it also comes with certain considerations and challenges, such as:
- Financial Risk: Self-insured entities bear the financial responsibility for claims, which can be substantial. Proper financial planning and risk assessment are crucial to mitigate this risk.
- Expertise and Resources: Effective self-insurance requires specialized knowledge and resources for claims management, risk assessment, and financial planning. Entities may need to invest in these areas or partner with experts.
- Regulatory Compliance: Self-insured entities must navigate complex regulatory landscapes, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations governing self-insurance practices.
- Unpredictable Claims: The nature of self-insurance means that entities must be prepared for unexpected and potentially large claims, which can be challenging to forecast accurately.
Real-World Examples
Self-insurance is utilized by a wide range of entities, including:
- Large Corporations: Many multinational corporations self-insure their employees’ healthcare benefits, allowing them to customize coverage and potentially save on insurance costs.
- Public Entities: Government agencies and public institutions often self-insure their employees’ healthcare and other benefits, leveraging their size and resources to manage risks effectively.
- Professional Associations: Some professional associations, such as bar associations or medical societies, offer self-insured healthcare plans to their members, providing specialized coverage and cost savings.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Non-profit entities may self-insure to manage their risks and maintain financial stability while providing benefits to their employees or beneficiaries.
Performance Analysis and Metrics
Evaluating the performance of self-insured entities involves examining key metrics such as:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Claims Incurred | The total amount of claims paid out by the self-insured entity over a specific period. |
| Claims Ratio | The ratio of claims incurred to the total funds set aside for self-insurance, indicating the entity’s claims management efficiency. |
| Risk Retention Capacity | The maximum amount of risk the entity can retain, based on its financial resources and risk tolerance. |
| Claim Severity | The average cost of claims, helping to assess the financial impact of individual claims on the entity. |

The Future of Self-Insurance

As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, self-insurance is likely to play an increasingly prominent role. Here are some future implications and trends to consider:
- Technology Integration: Advancements in technology, such as digital claims management systems and predictive analytics, will enhance the efficiency and accuracy of self-insurance practices.
- Collaborative Risk Pools: The formation of larger, collaborative risk pools among self-insured entities can lead to more effective risk management and cost savings through shared resources and expertise.
- Customized Coverage Options: Self-insured entities will have greater flexibility to design coverage options that cater to the unique needs of their employees or beneficiaries, promoting better health outcomes and employee satisfaction.
- Regulatory Changes: Governments and regulatory bodies may introduce new guidelines or incentives to encourage or support self-insurance practices, impacting the landscape for self-insured entities.
In conclusion, self-insurance is a strategic approach that empowers entities to take control of their financial risks and healthcare coverage. While it offers significant advantages, it also requires careful planning, expertise, and a proactive approach to risk management. As the healthcare industry evolves, self-insurance is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare coverage and risk mitigation.
What are the key benefits of self-insurance for businesses?
+Self-insurance allows businesses to potentially save on insurance premiums, have greater flexibility in coverage design, and manage cash flow more effectively. It also encourages proactive risk management strategies.
How do self-insured entities handle claims?
+Self-insured entities assess and process claims using internal resources or third-party administrators. They manage claims payments from the funds set aside for self-insurance.
What are the potential challenges of self-insurance?
+Challenges include financial risk, the need for specialized expertise and resources, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Self-insured entities must also manage unpredictable claims and potential large payouts.



