Subrogation Meaning In Insurance
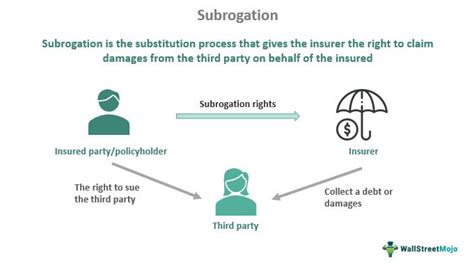
Subrogation is a fundamental concept in the insurance industry, playing a pivotal role in claims settlement and risk management. It is a legal mechanism that allows an insurer, having compensated an insured for a loss, to step into the shoes of the insured and assert the insured's rights against a third party who is legally responsible for that loss. This intricate process ensures that insurers can recover their payments, promoting fairness and efficiency in the insurance ecosystem.
Understanding subrogation is crucial for policyholders, as it can directly impact their rights and responsibilities, particularly when dealing with complex claims involving multiple parties. This article aims to demystify the concept, exploring its intricacies, legal basis, and practical implications, all while shedding light on its significance in the world of insurance.
The Essence of Subrogation

At its core, subrogation is about equity and justice. When an insured party suffers a loss and is compensated by their insurer, the insurer steps in to recover the payment from the party legally responsible for the loss. This process ensures that the burden of the loss is placed on the responsible party rather than being borne solely by the insurer or the insured.
For instance, imagine a scenario where a driver insured by Company X gets into an accident with a driver insured by Company Y. Both drivers have comprehensive insurance policies. The driver from Company X sustains injuries and their vehicle is severely damaged. Company X steps in, paying for the medical expenses and vehicle repairs as per the policy terms. However, the accident was primarily the fault of the driver from Company Y. In this case, Company X, through subrogation, can recover the expenses it paid from Company Y, ensuring that Company Y's policyholder bears the financial responsibility for the accident they caused.
Legal Basis and Principles

Subrogation in insurance is founded on equitable principles, allowing insurers to seek reimbursement from responsible parties. This legal doctrine has its roots in common law, aiming to prevent unjust enrichment and ensure that insurers, having compensated their policyholders, can recover their payments from the liable party.
The process of subrogation typically involves a thorough investigation by the insurer. They examine the circumstances of the loss, identify the responsible party, and assess the liability. Once the liability is established, the insurer can initiate legal proceedings or negotiate a settlement with the responsible party to recover the payments made to the insured. This process ensures that insurers are not left bearing the full financial burden of losses caused by third parties.
The Role of Subrogation in Claims Settlement
Subrogation is an integral part of the claims settlement process, especially in scenarios involving multiple parties and complex liability situations. When an insurer settles a claim, they assess the circumstances of the loss and determine the degree of responsibility of each party involved. If the insurer concludes that a third party is primarily liable, they may pursue subrogation to recover the payments made to the insured.
For example, consider a situation where a building suffers fire damage due to faulty electrical wiring installed by an electrician. The building owner, insured by Company Z, files a claim. Company Z investigates and finds that the electrician's negligence caused the fire. In this case, Company Z can invoke subrogation, recovering the payments made for the fire damage from the electrician's insurance company. This ensures that the electrician's insurance company, rather than Company Z or the building owner, bears the financial burden of the loss caused by their insured's negligence.
Subrogation and Policyholder Rights
While subrogation benefits insurers by providing a mechanism for reimbursement, it also safeguards policyholder rights. By allowing insurers to recover payments from liable third parties, subrogation helps maintain the financial stability of the insurance industry. This, in turn, ensures that insurers can continue providing coverage and compensating policyholders for legitimate claims.
Moreover, subrogation encourages accountability and responsibility among parties. When individuals or entities know that they may be held financially responsible for their actions, they are more likely to exercise caution and adhere to safety standards. This culture of accountability contributes to a safer and more responsible society, ultimately reducing the frequency and severity of losses, which benefits both insurers and policyholders.
The Practical Implications of Subrogation
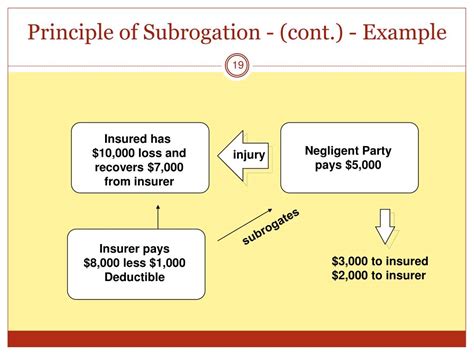
In practice, the subrogation process can be intricate and time-consuming. Insurers must conduct thorough investigations, gather evidence, and establish liability before initiating subrogation proceedings. This process often involves legal expertise, as insurers may need to engage attorneys to navigate the complex legal landscape and pursue recovery effectively.
The success of subrogation efforts can significantly impact an insurer's financial health. Efficient and successful subrogation practices can lead to substantial recoveries, enhancing an insurer's profitability and capacity to provide coverage. Conversely, unsuccessful subrogation attempts can result in financial losses for the insurer, potentially impacting their ability to offer competitive rates and maintain their financial stability.
The Future of Subrogation
As the insurance industry evolves, subrogation practices are likely to adapt and innovate. With advancements in technology and data analytics, insurers are increasingly able to streamline the subrogation process, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Automated systems can expedite investigations, identify responsible parties, and calculate potential recoveries, enabling insurers to make more informed decisions about pursuing subrogation.
Furthermore, the increasing interconnectedness of the digital world presents both challenges and opportunities for subrogation. On the one hand, digital footprints and electronic records can provide valuable evidence in establishing liability. On the other hand, the proliferation of digital data raises privacy concerns and ethical dilemmas, necessitating a delicate balance between efficient subrogation practices and respect for individual privacy rights.
Conclusion
Subrogation is a critical component of the insurance industry, ensuring fairness, accountability, and financial stability. By allowing insurers to recover payments from liable third parties, subrogation promotes a culture of responsibility and safeguards the interests of policyholders. As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, the principles of subrogation will remain integral, guiding the industry toward equitable and sustainable practices.
For policyholders, understanding subrogation is essential, as it directly influences their rights and the claims settlement process. By recognizing the role of subrogation, policyholders can better navigate the complex world of insurance, making informed decisions and advocating for their rights when necessary.
How does subrogation benefit policyholders?
+Subrogation ensures that policyholders receive prompt and fair compensation for their losses while also holding responsible parties accountable. This process helps maintain the financial stability of the insurance industry, which benefits policyholders by ensuring the continued availability and affordability of insurance coverage.
What happens if an insurer cannot recover through subrogation?
+If an insurer is unable to recover payments through subrogation, they may bear the financial burden of the loss. This can impact their financial health and potentially lead to increased premiums for policyholders to maintain the insurer’s stability.
Can policyholders initiate subrogation on their own?
+In most cases, policyholders assign their rights to their insurer as part of the insurance contract. However, in certain situations, policyholders may have the right to pursue subrogation directly, especially if the insurer waives their rights or if the policyholder’s loss is not covered by their insurance policy.



