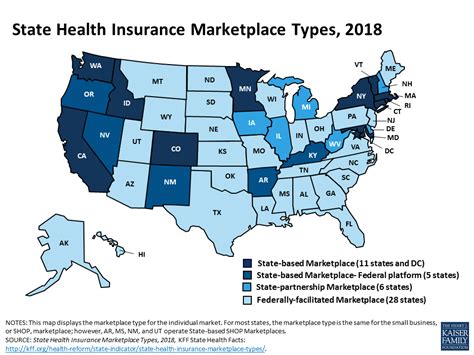
State Health Insurance
In the realm of healthcare, ensuring access to quality and affordable medical services is a fundamental concern for individuals and governments alike. One of the primary mechanisms through which this access is facilitated is through health insurance, a critical component of any robust healthcare system. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the intricacies of State Health Insurance, a specific type of health coverage that holds significant importance in the United States healthcare landscape.
Understanding State Health Insurance

State Health Insurance, as the name suggests, is a type of health coverage offered by individual states within the United States. It is a crucial aspect of the broader healthcare system, designed to provide medical benefits to residents who may not have access to private insurance or federal programs like Medicare or Medicaid. Each state has the autonomy to develop and implement its own health insurance program, leading to a diverse landscape of coverage options across the nation.
The primary goal of State Health Insurance is to fill the gaps in healthcare coverage, ensuring that residents, regardless of their economic status, have access to essential medical services. These programs are typically funded through a combination of state budgets, federal grants, and, in some cases, contributions from enrollees themselves. The specific benefits, eligibility criteria, and cost structures can vary significantly from one state to another, reflecting the unique healthcare needs and priorities of each region.
Key Features and Benefits
State Health Insurance programs offer a range of benefits tailored to the specific healthcare needs of their respective states. Here are some key features that are often included:
- Comprehensive Coverage: Many State Health Insurance plans provide a wide array of medical services, including primary care, specialty care, hospitalization, prescription drugs, and preventive care. Some plans even offer dental and vision benefits.
- Affordable Premiums: These programs are designed with affordability in mind. They often have lower premiums compared to private insurance plans, making healthcare more accessible to individuals and families with limited financial resources.
- Eligibility for Low-Income Residents: State Health Insurance is often geared towards low-income individuals and families who may not qualify for federal programs like Medicaid. This ensures that those most in need have access to essential healthcare services.
- No Pre-Existing Condition Exclusions: Unlike some private insurance plans, State Health Insurance programs typically do not discriminate against individuals with pre-existing medical conditions. This is a critical aspect, ensuring that people with ongoing health issues can access the care they require.
- State-Specific Benefits: Each state may include benefits that are unique to its residents. For example, some states may offer coverage for specific treatments or services that are prevalent in their region, such as allergy treatments in states with high pollen counts.
State Health Insurance in Practice
To illustrate the diversity and impact of State Health Insurance, let’s examine a few real-world examples:
California’s Medi-Cal Program
Medi-Cal, California’s Medicaid program, is one of the largest and most comprehensive State Health Insurance programs in the country. It provides healthcare coverage to low-income adults, children, pregnant women, seniors, and people with disabilities. Medi-Cal offers a wide range of benefits, including primary care, specialty care, dental services, vision care, and mental health services. The program is funded by a combination of state and federal funds, with the federal government contributing a significant portion of the costs.
Massachusetts’ Health Connector
The Health Connector, Massachusetts’ health insurance marketplace, offers a unique State Health Insurance program. It was established as part of the state’s landmark healthcare reform law, which aimed to provide health insurance to all residents. The Health Connector offers a variety of insurance plans, including those designed specifically for low-income individuals and families. The program has been successful in reducing the state’s uninsured rate and improving access to healthcare services.
New York’s Essential Plan
New York’s Essential Plan is a State Health Insurance program that provides coverage to individuals who earn too much to qualify for Medicaid but cannot afford private insurance. The plan offers a comprehensive set of benefits, including primary care, hospital care, prescription drugs, and mental health services. It is funded through a combination of state and federal funds, as well as a small premium contribution from enrollees.
The Future of State Health Insurance
The landscape of State Health Insurance is continually evolving, influenced by various factors such as changes in federal healthcare policies, advancements in medical technology, and shifts in demographic needs. As states strive to provide better access to healthcare, we can expect to see innovations in program design, such as the integration of telemedicine services and the adoption of value-based care models.
Furthermore, the ongoing debate surrounding healthcare reform at the federal level often impacts the trajectory of State Health Insurance programs. States may need to adapt their programs to align with any significant changes in federal policy, ensuring that their residents continue to have access to the healthcare services they need.
As we look ahead, the role of State Health Insurance in the broader healthcare ecosystem is poised to become even more critical. These programs will continue to serve as a safety net for millions of Americans, providing essential healthcare coverage and contributing to the overall health and well-being of the nation.
What is the difference between State Health Insurance and Medicaid?
+
While State Health Insurance and Medicaid are both government-funded healthcare programs, they serve different populations. State Health Insurance is primarily designed for low-income individuals and families who do not qualify for Medicaid. Medicaid, on the other hand, is a federal and state program that provides healthcare coverage to eligible low-income individuals, pregnant women, children, and people with disabilities.
How can I find out if I’m eligible for State Health Insurance in my state?
+
Eligibility criteria for State Health Insurance programs can vary from state to state. You can start by visiting your state’s official health insurance website or contacting your state’s Department of Health. These resources will provide detailed information about the eligibility requirements, application process, and benefits offered by your state’s program.
Are there any income restrictions for State Health Insurance?
+
Yes, most State Health Insurance programs have income restrictions to ensure that the benefits are targeted towards those who need them the most. The specific income limits can vary depending on the state and the program. It’s important to check with your state’s health insurance department to understand the income eligibility criteria.



