Out Of Pocket Meaning Insurance

In the world of insurance, the term "out-of-pocket" (OOP) is a key concept that plays a significant role in how healthcare costs are managed and paid for. This article will delve into the intricacies of out-of-pocket expenses, explaining what they are, how they work, and why they are an essential consideration for anyone navigating the healthcare system. We will explore real-world examples, delve into the technical aspects, and offer practical insights to help you understand and manage your out-of-pocket costs effectively.
Understanding Out-of-Pocket Expenses

Out-of-pocket expenses, in the context of insurance, refer to the costs of healthcare services that are not covered or fully reimbursed by your insurance provider. These expenses are paid directly by the policyholder, hence the term “out of pocket.”
To put it simply, when you receive medical treatment or purchase prescribed medications, the amount you pay that is not covered by your insurance plan is considered out-of-pocket. These expenses can include co-pays, deductibles, co-insurance, and, in some cases, services that are not covered by your insurance plan at all.
Key Components of Out-of-Pocket Costs
- Deductibles: This is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Deductibles can vary depending on the type of insurance plan you have. For example, in a health insurance plan, you might have a deductible of 1,500 per year. Until you reach this amount, all your medical expenses are paid by you, and only after you exceed the deductible does your insurance start covering a portion or all of the costs.</li> <li><strong>Co-pays:</strong> Co-pays are fixed amounts you pay for specific services or prescriptions. For instance, you might have a 20 co-pay for each doctor’s office visit or a $5 co-pay for each generic prescription medication. Co-pays are typically paid at the time of service.
- Co-insurance: Co-insurance is a percentage of the total cost of a service or medication that you are responsible for paying. For example, your insurance plan might cover 80% of the cost of a procedure, leaving you responsible for the remaining 20%. Co-insurance amounts can vary depending on the service and your specific insurance plan.
Real-World Examples of Out-of-Pocket Expenses
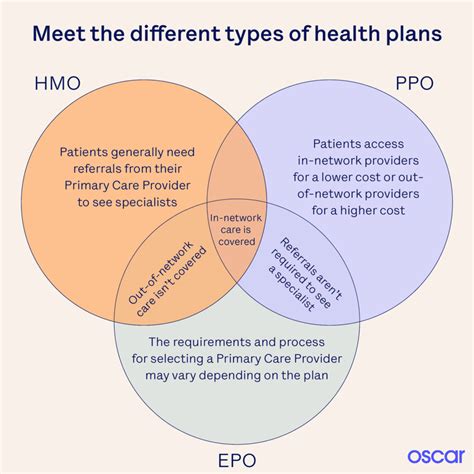
Let’s illustrate these concepts with some practical scenarios:
Scenario 1: Annual Check-up and Prescription Medication
Imagine you have a health insurance plan with a 1,000 annual deductible and a 20 co-pay for each doctor’s visit. You visit your primary care physician for your annual check-up, which costs 250. Since you haven't met your deductible yet, you pay the full 250 out of pocket. Additionally, you receive a prescription for a brand-name medication, which costs 150. Your insurance plan covers 70% of the cost of brand-name medications, so you pay a co-insurance amount of 45 (70% of 150), bringing your total out-of-pocket expense for the visit and medication to 295.
Scenario 2: Emergency Room Visit and Surgery
Now, consider an emergency situation. You’re involved in a car accident and need to visit the emergency room. Your insurance plan has a 500 deductible for emergency services. The ER visit and initial treatment cost 2,000. Since you haven’t met your deductible, you pay the full 500 out of pocket. Later, you undergo surgery related to your injuries, which costs 15,000. Your insurance plan covers 100% of surgical costs after the deductible is met. Therefore, you pay nothing out of pocket for the surgery, as your deductible has already been satisfied.
Managing Out-of-Pocket Costs
Understanding and managing out-of-pocket expenses is crucial for effective healthcare planning and financial well-being. Here are some strategies to help you navigate these costs:
Review Your Insurance Plan
Familiarize yourself with the details of your insurance plan. Know your deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance percentages for different services and medications. This knowledge will help you estimate your out-of-pocket costs for various scenarios.
Utilize Preventive Care
Many insurance plans offer preventive care services at little to no cost to the policyholder. These services can include annual check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings. Taking advantage of these services can help you stay healthy and catch potential issues early, potentially reducing future out-of-pocket costs.
Shop Around for Medications
Prescription medications can be a significant source of out-of-pocket expenses. Explore options for generic medications, which are often much more affordable than brand-name drugs. Additionally, some pharmacies offer discount programs or loyalty cards that can reduce the cost of your prescriptions.
Consider Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
If you have a high-deductible health plan (HDHP), you may be eligible for a Health Savings Account. HSAs allow you to set aside pre-tax dollars to pay for qualified medical expenses. The money in your HSA rolls over year to year and can be used to cover out-of-pocket costs, providing a tax-efficient way to manage your healthcare expenses.
Out-of-Pocket Maximums
Insurance plans often have an out-of-pocket maximum, which is the maximum amount you will pay out of pocket for covered services in a given year. Once you reach this maximum, your insurance plan typically covers 100% of the cost of covered services for the remainder of the year. Out-of-pocket maximums can vary widely between plans, so it’s essential to understand this aspect of your insurance coverage.
| Insurance Plan | Out-of-Pocket Maximum |
|---|---|
| Plan A | $5,000 |
| Plan B | $7,500 |
| Plan C | $10,000 |

Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Healthcare Costs

Out-of-pocket expenses are an inherent part of navigating the healthcare system. By understanding the different components of these costs, reviewing your insurance plan, and implementing strategic approaches to healthcare and financial planning, you can take control of your healthcare costs and make informed decisions about your well-being. Remember, being proactive and knowledgeable about your insurance coverage can lead to significant savings and better overall healthcare outcomes.
How do out-of-pocket expenses affect my overall healthcare costs?
+
Out-of-pocket expenses directly impact your overall healthcare costs. They represent the portion of medical services and medications that you pay for personally. These costs can add up quickly, especially if you have high healthcare needs or require specialized treatments. Understanding and managing your out-of-pocket expenses is crucial for financial planning and ensuring your healthcare needs are met without breaking the bank.
Are there any ways to reduce my out-of-pocket expenses?
+
Yes, there are several strategies to reduce out-of-pocket expenses. First, review your insurance plan to understand your deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance rates. Utilize preventive care services, which are often covered at little to no cost. Shop around for generic medications, as they are typically more affordable than brand-name drugs. Consider opening a Health Savings Account (HSA) if you’re eligible, as it allows you to save pre-tax dollars specifically for medical expenses.
What is the difference between a deductible and a co-pay?
+
A deductible is the amount you must pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage begins. It’s typically an annual amount, and once you meet or exceed it, your insurance plan starts covering a portion or all of your medical costs. On the other hand, a co-pay is a fixed amount you pay for specific services or prescriptions, and it’s typically paid at the time of service. Co-pays are usually smaller amounts compared to deductibles and are designed to encourage cost-sharing between the insurance provider and the policyholder.



