Obama Care Health Insurance
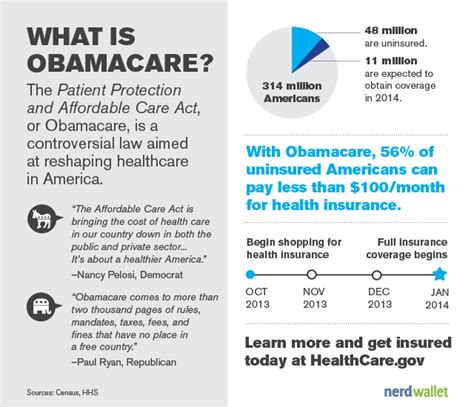
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, commonly known as the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or ObamaCare, is a landmark healthcare reform legislation in the United States. Enacted in 2010, this comprehensive law has significantly transformed the American healthcare system, aiming to increase the affordability, accessibility, and quality of healthcare services for millions of Americans. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of ObamaCare, exploring its key provisions, impact, and the ongoing discussions surrounding its implementation.
Understanding ObamaCare: A Comprehensive Overview

ObamaCare represents a fundamental shift in the US healthcare landscape, introducing a range of measures to address long-standing issues and expand coverage. Here are some of the critical components of this legislation:
Individual Mandate
One of the most controversial aspects of ObamaCare was the individual mandate, which required most Americans to have minimum essential health coverage or face a tax penalty. This mandate aimed to encourage broader participation in the healthcare system, reducing the number of uninsured individuals and spreading the risk among a larger population.
The individual mandate was in effect from 2014 to 2018, but the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 eliminated the penalty for not having coverage starting in 2019. However, some states have since implemented their own individual mandates to maintain a stable insurance market.
Expansion of Medicaid
ObamaCare sought to expand Medicaid, a government-funded healthcare program for low-income individuals and families. The law allowed states to extend Medicaid coverage to adults with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level. This expansion aimed to provide healthcare access to a significant portion of the uninsured population.
While the Supreme Court upheld the constitutionality of the Medicaid expansion, it gave states the option to opt out. As a result, Medicaid coverage varies significantly across states, with some fully embracing the expansion and others choosing not to participate.
Health Insurance Exchanges
The ACA established health insurance exchanges, also known as marketplaces, where individuals and small businesses could compare and purchase qualified health plans. These exchanges, both state-based and federally facilitated, provided a platform for consumers to shop for insurance, with financial assistance available for those meeting certain income criteria.
The exchanges offered a standardized shopping experience, allowing consumers to easily compare plans based on cost, coverage, and quality. Additionally, the ACA introduced essential health benefits that all qualified health plans must cover, ensuring a baseline of coverage across different insurance options.
Pre-Existing Condition Coverage
A significant reform introduced by ObamaCare was the prohibition of pre-existing condition exclusions. Prior to the ACA, individuals with pre-existing health conditions often faced challenges in obtaining affordable health insurance. The law mandated that insurance companies cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based solely on an individual’s health status.
This provision has been particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic illnesses or those who have previously faced health issues. By eliminating pre-existing condition exclusions, ObamaCare aimed to ensure that everyone, regardless of their health history, has access to affordable and comprehensive healthcare coverage.
Insurance Market Reforms
ObamaCare implemented several market reforms to enhance competition and consumer protection in the health insurance industry. These reforms included the prohibition of lifetime and annual limits on coverage, as well as the requirement for insurance companies to spend a minimum percentage of premiums on healthcare services rather than administrative costs.
Additionally, the law introduced a system of community rating, which prohibits insurance companies from varying premiums based on an individual's health status. Instead, premiums are determined by factors such as age, geographic area, and tobacco use. This reform aims to prevent insurance companies from charging higher premiums to individuals with poorer health.
Impact and Implementation of ObamaCare

The implementation of ObamaCare has had a significant impact on the US healthcare system and the lives of millions of Americans. Here are some key aspects of its impact:
Increased Insurance Coverage
One of the primary goals of ObamaCare was to reduce the number of uninsured Americans. Since its implementation, the uninsured rate has dropped significantly. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the percentage of adults without health insurance decreased from 16.0% in 2010 to 8.5% in 2020. This reduction in the uninsured rate is a testament to the success of ObamaCare in expanding access to healthcare.
| Year | Uninsured Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 16.0 |
| 2014 | 11.4 |
| 2018 | 8.9 |
| 2020 | 8.5 |

Affordable Coverage Options
ObamaCare aimed to make healthcare more affordable for individuals and families. The law introduced premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions to assist those with lower incomes in purchasing insurance through the marketplaces. These subsidies have helped millions of Americans obtain coverage they could not afford previously.
Furthermore, the law's market reforms and the introduction of essential health benefits have contributed to more comprehensive coverage options, ensuring that insurance plans cover a wide range of healthcare services, including preventive care, hospitalization, and prescription drugs.
Enhanced Consumer Protections
ObamaCare implemented several consumer protections to safeguard individuals from unfair insurance practices. The prohibition of pre-existing condition exclusions and the ban on lifetime and annual limits on coverage are key examples. Additionally, the law ensures that insurance companies provide clear and concise summaries of benefits and coverage, empowering consumers to make informed choices.
Furthermore, the law's emphasis on quality improvement and patient safety has led to the development of programs and initiatives aimed at reducing medical errors, improving patient outcomes, and promoting evidence-based medicine.
Challenges and Ongoing Discussions
Despite its successes, ObamaCare has faced challenges and criticisms. One of the major concerns has been the cost of insurance premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, particularly for those who do not qualify for subsidies. The law’s complexity and the administrative burden on both insurers and consumers have also been areas of contention.
The future of ObamaCare remains a subject of debate and political discussion. While the law has withstood legal challenges, efforts to repeal or modify its provisions continue. Some states have taken proactive measures to expand coverage and improve the healthcare system, while others have opted out of certain provisions or implemented alternative reforms.
Conclusion: The Legacy and Future of ObamaCare
ObamaCare has left an indelible mark on the US healthcare system, increasing insurance coverage, expanding access to healthcare services, and introducing consumer protections. Its implementation has reduced the number of uninsured Americans and provided affordable coverage options for many. However, the law’s impact and sustainability continue to be topics of debate and ongoing reform efforts.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, it is essential to evaluate the successes and challenges of ObamaCare. By understanding its provisions and impact, policymakers, healthcare providers, and the public can engage in informed discussions to shape the future of healthcare in the United States. ObamaCare's legacy serves as a foundation for further improvements and innovations in healthcare accessibility and affordability.
What is the current status of the individual mandate in the Affordable Care Act?
+The individual mandate was a key provision of the Affordable Care Act, requiring most individuals to have health insurance coverage or pay a penalty. However, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 eliminated the penalty for not having coverage starting in 2019. While the mandate is no longer enforced at the federal level, some states have implemented their own individual mandates to maintain a stable insurance market.
How has ObamaCare impacted the uninsured rate in the United States?
+ObamaCare has significantly reduced the uninsured rate in the United States. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the percentage of adults without health insurance decreased from 16.0% in 2010 to 8.5% in 2020. This decrease is largely attributed to the expansion of Medicaid and the availability of affordable coverage options through the health insurance exchanges.
What are the essential health benefits mandated by the Affordable Care Act?
+The Affordable Care Act requires all qualified health plans to cover a set of essential health benefits. These benefits include ambulatory patient services, emergency services, hospitalization, maternity and newborn care, mental health and substance use disorder services, prescription drugs, rehabilitative and habilitative services and devices, laboratory services, preventive and wellness services, and chronic disease management. By mandating these benefits, ObamaCare ensures that insurance plans provide comprehensive coverage.