Medicare And Supplemental Health Insurance
In the complex landscape of healthcare, understanding your insurance coverage is crucial, especially when it comes to Medicare and its supplemental options. This article aims to delve into the world of Medicare and its supplemental health insurance plans, providing you with a comprehensive guide to navigate the often-confusing world of healthcare benefits.
Understanding Medicare: A Brief Overview

Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States, primarily designed for individuals aged 65 and older. However, it also caters to younger individuals with certain disabilities or specific medical conditions. This program is divided into several parts, each covering different aspects of healthcare.
Parts of Medicare
- Part A - Hospital Insurance: Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, and some home healthcare services.
- Part B - Medical Insurance: Provides coverage for outpatient medical services, including doctor visits, lab tests, and some preventive care.
- Part C - Medicare Advantage Plans: These are private insurance plans that offer an alternative to Original Medicare (Parts A and B). They must cover all the services provided by Original Medicare, but may also include additional benefits like vision, dental, or prescription drug coverage.
- Part D - Prescription Drug Coverage: This part of Medicare helps cover the cost of prescription medications. It is available through private insurance companies approved by Medicare.
The Role of Supplemental Health Insurance

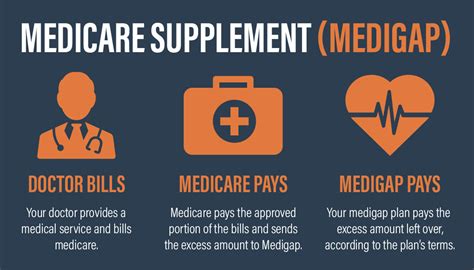
While Medicare offers a wide range of benefits, it may not cover all healthcare expenses, leaving individuals with potential out-of-pocket costs. This is where supplemental health insurance, also known as Medicare Supplement or Medigap insurance, comes into play. These plans are designed to fill the gaps in Original Medicare coverage, helping to reduce or eliminate these additional costs.
Key Features of Supplemental Health Insurance
- Supplemental health insurance plans are standardized, meaning the benefits offered by each plan type are consistent across different insurance companies. However, the premiums can vary.
- These plans are designed to cover costs not typically covered by Original Medicare, such as copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. Some plans may also provide coverage for emergency medical care outside the U.S.
- Medigap policies are sold by private insurance companies, but they must be approved by Medicare and follow federal and state laws. This ensures a certain level of consistency and reliability.
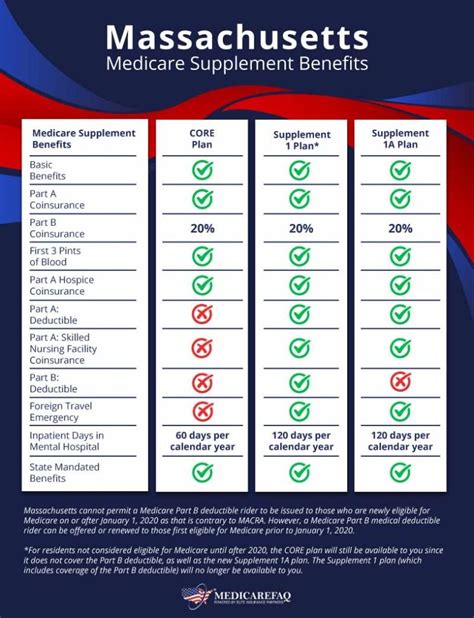
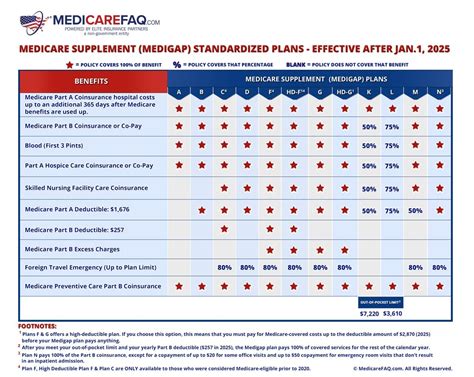
| Medicare Supplement Plan | Covered Services |
|---|---|
| Plan A | Basic coverage for Part A and Part B deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments. |
| Plan B | Same as Plan A, plus coverage for Part A hospice care coinsurance. |
| Plan C | Comprehensive coverage, including all of the above and foreign travel emergency care. |
| Plan D | Similar to Plan A, but with the addition of coverage for blood transfusions. |
| ... | ... |
| Plan N | Covers Part A and Part B coinsurance and copayments, except for a small amount for some office visits and up to 3 pints of blood per year. |
Choosing the Right Supplemental Plan
Selecting the appropriate supplemental health insurance plan involves considering several factors, including your specific healthcare needs, your budget, and the providers you typically visit.
Factors to Consider
- Healthcare Needs: Evaluate your current and potential future healthcare needs. If you anticipate frequent medical visits or have a chronic condition, a plan with more comprehensive coverage might be beneficial.
- Budget: Supplemental insurance plans come with varying premiums and out-of-pocket costs. Assess your financial situation and choose a plan that fits within your budget while providing adequate coverage.
- Provider Network: If you have a preferred healthcare provider or hospital, ensure that they accept the supplemental plan you’re considering. Some plans may have a limited network, while others offer more flexibility.
- Plan Benefits: Carefully review the benefits and exclusions of each plan. Consider the types of services you may require and choose a plan that aligns with your needs. For instance, if you frequently travel abroad, a plan that covers emergency medical services outside the U.S. could be valuable.
Enrolling in Medicare and Supplemental Plans
The enrollment process for Medicare and its supplemental plans is straightforward, but it’s essential to understand the timelines and requirements to ensure you don’t miss out on important benefits.
Enrollment Periods
- Initial Enrollment Period - When you first become eligible for Medicare, you have a 7-month period to enroll. This includes the 3 months before you turn 65, the month of your 65th birthday, and the 3 months after.
- Annual Enrollment Period - This period runs from October 15 to December 7 each year. It’s a chance to review your coverage and make changes for the upcoming year.
- Open Enrollment Period for Medigap - If you enroll in Medicare Part B during your Initial Enrollment Period, you also have a 6-month Open Enrollment Period for Medigap. This starts the month you turn 65 and are enrolled in Part B.
The Enrollment Process
- Visit the official Medicare website or contact your local Social Security office to enroll in Original Medicare (Parts A and B).
- If you’re interested in a Medicare Advantage plan, you can enroll directly through the insurance company offering the plan.
- For Medigap plans, you can purchase them from private insurance companies. Ensure the plan is approved by Medicare and meets your specific needs.
Navigating the Complexities
Understanding Medicare and its supplemental insurance options can be a daunting task, especially with the myriad of plans and enrollment periods. However, with careful research and a clear understanding of your healthcare needs, you can make informed decisions to ensure you have the coverage you need.
Key Takeaways
- Medicare is divided into Parts A, B, C, and D, each covering different aspects of healthcare.
- Supplemental health insurance, or Medigap, fills the gaps in Original Medicare coverage, reducing out-of-pocket expenses.
- When choosing a Medigap plan, consider your healthcare needs, budget, and the providers you typically visit.
- Enroll in Medicare during your Initial Enrollment Period to avoid potential penalties and delays in coverage.
- Review your coverage annually during the Annual Enrollment Period to ensure your plans still meet your needs.
Can I have both a Medicare Advantage plan and a Medigap plan simultaneously?
+No, you cannot have both plans simultaneously. Medicare Advantage plans and Medigap plans are designed to work with Original Medicare (Parts A and B). Choosing one plan type excludes you from the other.
What happens if I miss my Initial Enrollment Period for Medicare?
+If you miss your Initial Enrollment Period, you may still enroll in Medicare, but you might face late enrollment penalties. It’s crucial to understand the reasons for missing the deadline and act accordingly to minimize potential penalties.
Are there any age restrictions for purchasing Medigap plans?
+Medigap plans have no age restrictions, but it’s important to note that premiums can be higher for individuals who enroll at a later age. Enrolling during your Open Enrollment Period can ensure you get the best rates.



