Is Health Insurance Premium Tax Deductible
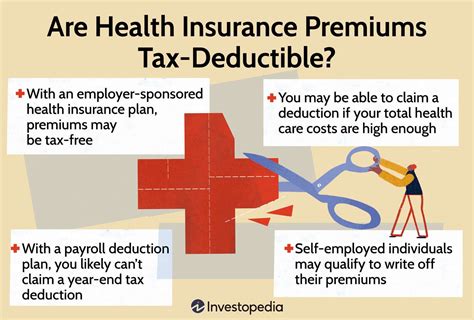
The tax-deductibility of health insurance premiums is a topic that often sparks curiosity among individuals seeking to optimize their financial strategies, especially when it comes to managing healthcare expenses. Understanding the nuances of tax laws and their implications on health insurance premiums can provide valuable insights for taxpayers.
Navigating the Landscape of Tax-Deductible Health Insurance Premiums
In the intricate world of taxation, the deductibility of health insurance premiums is a key consideration for many individuals and families. This section aims to demystify the concept, providing a comprehensive understanding of the circumstances under which these premiums may be eligible for tax deductions.
Understanding Tax-Deductible Health Insurance Premiums
Tax-deductible health insurance premiums are a crucial aspect of financial planning, offering individuals the opportunity to reduce their taxable income by including certain healthcare-related expenses. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) outlines specific criteria that determine whether health insurance premiums can be claimed as deductions.
Generally, individuals who are self-employed or whose employers do not provide health insurance coverage may be eligible to deduct the cost of their premiums on their federal income tax returns. This deduction is applicable to premiums paid for medical, dental, and vision insurance plans, as well as for long-term care insurance.
However, it's important to note that the deductibility of health insurance premiums is subject to certain limitations and qualifications. For instance, the premium amounts must be substantiated with proper documentation, such as receipts or statements from the insurance provider. Additionally, the deductibility may vary based on the taxpayer's filing status and the type of insurance plan they have.
One key consideration is whether the individual or their spouse is eligible for health insurance coverage through their employer. If either of them has access to an employer-sponsored health plan, the deductibility of their premiums may be impacted. In such cases, it's crucial to review the specific guidelines provided by the IRS to ensure compliance.
Moreover, the tax treatment of health insurance premiums can vary depending on whether the individual is enrolled in a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) paired with a health savings account (HSA). HDHPs generally have higher deductibles and lower premiums compared to traditional health plans. When combined with an HSA, individuals can contribute pre-tax dollars to the account, further enhancing the tax advantages associated with healthcare expenses.
It's worth mentioning that the tax landscape is subject to change, and taxpayers should stay informed about any updates or amendments to the tax codes pertaining to health insurance premiums. Regular consultation with tax professionals or staying abreast of IRS publications can ensure individuals make well-informed decisions regarding the deductibility of their health insurance expenses.
Eligible Health Insurance Plans for Tax Deductions
Not all health insurance plans are created equal when it comes to tax deductions. The IRS has specific criteria for which types of health insurance plans qualify for tax-deductible premiums. Here’s a breakdown of the eligible plans:
- Medical Insurance Plans: These include traditional health insurance plans offered by employers or purchased individually. The premiums for such plans are generally tax-deductible, provided they meet the IRS's requirements.
- Dental and Vision Insurance Plans: In addition to medical insurance, premiums for separate dental and vision insurance plans are also eligible for tax deductions. These plans often cover a range of dental and eye care services, from routine check-ups to more extensive procedures.
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Premiums for long-term care insurance plans are also tax-deductible under certain conditions. This type of insurance provides coverage for individuals who require assistance with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and eating, over an extended period of time.
It's important to note that while these plans are eligible for tax deductions, the specific deductibility of premiums can vary based on individual circumstances. Factors such as income level, filing status, and the type of insurance plan can all impact the deductibility of premiums. Taxpayers should consult with tax professionals or refer to IRS guidelines for a comprehensive understanding of their eligibility.
Claiming Health Insurance Premium Deductions: A Step-by-Step Guide
Claiming deductions for health insurance premiums can provide significant tax benefits. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help individuals navigate the process successfully:
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Start by collecting all relevant documentation related to your health insurance premiums. This includes receipts, statements, or other proof of payment from your insurance provider. Ensure that the documentation clearly states the premium amounts and the coverage period.
- Determine Eligibility: Review your eligibility for tax deductions based on your filing status and insurance coverage. If you're self-employed or your employer doesn't provide health insurance, you may be eligible for deductions. Additionally, if you or your spouse have access to an employer-sponsored health plan, the deductibility of your premiums may be impacted.
- Calculate the Deductible Amount: The IRS allows for the deduction of the amount you paid for your health insurance premiums, provided it meets the eligibility criteria. Calculate the total amount you paid during the tax year and ensure it aligns with the guidelines set by the IRS.
- Report on Your Tax Return: When filing your tax return, include the deductible amount on the appropriate form. For most taxpayers, this will be Form 1040, Schedule 1, Line 29 for Medical and Dental Expenses. Ensure you accurately report the amount to avoid any discrepancies.
- Consider Additional Tax Benefits: Depending on your specific circumstances, you may be eligible for additional tax benefits related to healthcare expenses. These could include deductions for out-of-pocket medical expenses or tax credits for qualifying health insurance plans. Consult with a tax professional to explore all potential tax advantages.
Remember, claiming deductions for health insurance premiums is a complex process, and it's essential to stay updated with the latest tax laws and guidelines. Consulting with a tax advisor or utilizing reliable tax preparation software can ensure you maximize your deductions while remaining compliant with IRS regulations.
The Impact of Tax-Deductible Health Insurance Premiums on Taxpayers

The availability of tax deductions for health insurance premiums can significantly influence taxpayers’ financial strategies and overall tax liability. This section explores the practical implications and benefits of claiming these deductions.
Reducing Taxable Income and Maximizing Refunds
One of the primary advantages of claiming tax-deductible health insurance premiums is the potential to reduce taxable income. By including these premiums as deductions, taxpayers can effectively lower their overall income subject to taxation. This reduction can result in a substantial decrease in tax liability, leading to larger refunds or reduced tax payments.
For instance, consider a self-employed individual who pays $6,000 in health insurance premiums during the tax year. By claiming this amount as a deduction, they can reduce their taxable income by $6,000. Depending on their income level and tax bracket, this deduction could result in significant tax savings.
Additionally, claiming tax-deductible health insurance premiums can be especially beneficial for individuals with higher incomes. As the tax rate increases with income, the value of each dollar deducted from taxable income becomes more substantial. Therefore, these deductions can provide a greater tax benefit for individuals in higher tax brackets.
Enhancing Financial Planning and Budgeting
Understanding the tax-deductibility of health insurance premiums can empower taxpayers to make more informed financial decisions. By incorporating these deductions into their tax planning, individuals can better forecast their tax liability and optimize their financial strategies.
For instance, taxpayers can strategically plan their insurance coverage and premium payments to maximize deductions. They can explore different insurance plans and coverage options to identify those that offer the best value in terms of tax advantages. This proactive approach to financial planning can lead to more efficient budgeting and better management of healthcare expenses.
Addressing Disparities in Healthcare Access
The tax-deductibility of health insurance premiums also plays a role in addressing disparities in healthcare access. By offering tax incentives for healthcare expenses, the government aims to encourage individuals, especially those who are self-employed or without employer-sponsored coverage, to invest in their health and well-being.
This incentive structure can help bridge the gap in healthcare access, ensuring that more individuals have the financial means to secure adequate health insurance coverage. By reducing the financial burden of premiums, the tax-deductibility provision can contribute to a more equitable healthcare system, where individuals can access the care they need without facing significant financial barriers.
| Tax Deduction Scenario | Impact on Taxpayer |
|---|---|
| Self-employed individual with $6,000 in health insurance premiums | Potential reduction in taxable income by $6,000, leading to substantial tax savings |
| Higher-income taxpayer with tax-deductible premiums | Greater tax benefit due to higher tax bracket, maximizing the value of deductions |
| Taxpayer strategically planning insurance coverage | Enhanced financial planning and budgeting, optimizing healthcare expenses |
Can I deduct health insurance premiums if I’m covered by my employer’s plan?
+
Generally, if you have access to an employer-sponsored health plan, you may not be eligible to deduct your health insurance premiums. However, there are exceptions, such as if you or your spouse are self-employed and meet certain criteria. Consult with a tax professional for a comprehensive understanding of your eligibility.
What if I have a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) and a health savings account (HSA)?
+
If you have an HDHP and contribute to an HSA, you may be eligible for additional tax benefits. The contributions to your HSA can be made pre-tax, further reducing your taxable income. Consult the IRS guidelines or a tax advisor for detailed information on the tax advantages of HDHPs and HSAs.
Are there any limits to the amount of health insurance premiums I can deduct?
+
Yes, there are limits to the deductibility of health insurance premiums. The IRS sets specific thresholds based on your income and filing status. It’s essential to stay informed about these limits and consult with a tax professional to ensure you’re maximizing your deductions while remaining compliant with IRS regulations.



