Irs Health Insurance
Health insurance is a crucial aspect of life in the United States, providing individuals and families with financial protection and access to essential healthcare services. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) plays a significant role in the health insurance landscape, especially when it comes to tax-related matters and the implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Understanding the IRS' involvement in health insurance is vital for taxpayers to ensure compliance and maximize any available tax benefits.
The IRS and Health Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide

In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate relationship between the IRS and health insurance, exploring the various aspects that affect taxpayers. From tax implications to penalty exemptions and beyond, we aim to provide a detailed analysis of this complex topic.
Understanding the IRS' Role in Health Insurance

The IRS serves as the primary federal agency responsible for administering and enforcing tax laws in the United States. While its primary function is to collect taxes and ensure compliance, the IRS also plays a critical role in the implementation and oversight of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which significantly impacts the health insurance landscape.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA)
The ACA, often referred to as Obamacare, is a comprehensive healthcare reform law enacted in 2010. It aims to expand access to affordable healthcare coverage and reduce the number of uninsured Americans. The IRS is tasked with enforcing certain provisions of the ACA, including the individual mandate, premium tax credits, and the Shared Responsibility Payment.
Under the ACA, most individuals are required to have minimum essential coverage or face a penalty. The IRS enforces this mandate by including a line on tax returns where individuals report their coverage status. If an individual or household fails to maintain minimum essential coverage, they may be subject to a Shared Responsibility Payment, which is calculated as a percentage of household income.
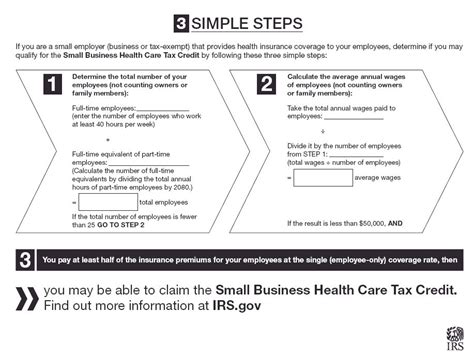
Additionally, the IRS administers premium tax credits to help eligible individuals and families offset the cost of their health insurance premiums. These tax credits are claimed on federal tax returns and can significantly reduce the financial burden of healthcare coverage.
Health Insurance Tax Benefits
Health insurance offers various tax benefits that can help reduce the overall cost of coverage. The IRS provides several tax incentives to encourage individuals to obtain and maintain health insurance. These benefits primarily fall into two categories: deductions and tax credits.
Deductions
Certain medical expenses, including health insurance premiums, can be deducted from taxable income. This deduction is particularly beneficial for individuals who are self-employed or whose insurance premiums are not covered by an employer. By deducting these expenses, taxpayers can lower their taxable income, resulting in potential tax savings.
Tax Credits
Tax credits are a more direct form of financial assistance, as they reduce the amount of tax owed dollar-for-dollar. The ACA introduced the Premium Tax Credit, which is designed to help low- and middle-income individuals and families afford health insurance coverage. This credit is based on income and family size and can be claimed in advance to lower monthly insurance premiums or claimed as a refund on tax returns.
| Type of Tax Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Deductions | Reduce taxable income, benefiting individuals with high medical expenses or self-employed individuals. |
| Tax Credits | Directly reduce tax liability, helping low- and middle-income individuals afford health insurance coverage. |
Reporting Health Insurance on Tax Returns
When filing federal tax returns, taxpayers must report their health insurance coverage status. This information is essential for the IRS to enforce the individual mandate and administer tax benefits accurately.
Taxpayers who have minimum essential coverage throughout the year will indicate their coverage type and provider on their tax return. Those who do not have coverage for part or all of the year may need to pay a penalty, which is calculated based on household income and the number of uninsured months.
Exemptions and Special Circumstances
The IRS recognizes that certain individuals and households may face unique circumstances that prevent them from obtaining health insurance. As such, it offers exemptions from the individual mandate and the Shared Responsibility Payment for specific situations.
- Financial Hardship Exemption: Individuals who cannot afford health insurance due to financial hardship may qualify for this exemption. This could include situations like unemployment, high medical expenses, or a sudden decrease in income.
- Short Coverage Gap Exemption: If an individual has a short gap in coverage, typically less than three months, they may be exempt from the individual mandate penalty.
- Religious Belief Exemption: Members of certain religious groups that object to insurance on religious grounds may be exempt from the individual mandate.
- Other Exemptions: The IRS provides additional exemptions for individuals experiencing homelessness, incarcerated individuals, and those who are not lawfully present in the United States.
The Impact of the Affordable Care Act (ACA)
The ACA has had a significant impact on the health insurance landscape in the United States. While it has expanded access to coverage and provided tax benefits to many, it has also introduced complexities and challenges for taxpayers and the IRS.
Expanding Access to Coverage
One of the primary goals of the ACA was to reduce the number of uninsured Americans. By implementing the individual mandate and offering premium tax credits, the ACA encouraged more individuals to obtain health insurance. As a result, the uninsured rate has decreased significantly since the law's implementation.
The ACA also introduced Health Insurance Marketplaces, also known as Exchanges, where individuals and small businesses can shop for and compare health insurance plans. These Marketplaces offer a range of coverage options and provide a platform for eligible individuals to claim premium tax credits.
Premium Tax Credits and Subsidies
Premium tax credits are a crucial component of the ACA, helping to make health insurance more affordable for low- and middle-income individuals. These credits are available to individuals who purchase coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplaces and meet certain income requirements.
The IRS calculates the premium tax credit based on estimated income and family size. Taxpayers can choose to receive this credit in advance, which lowers their monthly insurance premiums, or claim it as a refund on their tax return.
Shared Responsibility Payment
For individuals who do not maintain minimum essential coverage, the ACA imposes a Shared Responsibility Payment. This payment is calculated as a percentage of household income and is reported on federal tax returns. The amount of the payment depends on the number of months an individual or household goes without coverage.
Complexities and Compliance
While the ACA has brought about significant changes, it has also introduced complexities for taxpayers and the IRS. Reporting health insurance coverage and claiming tax benefits accurately can be challenging, especially for those who are unfamiliar with the intricacies of the law.
The IRS provides extensive guidance and resources to help taxpayers navigate the ACA-related tax provisions. However, it's essential for individuals to stay informed and seek professional advice when needed to ensure compliance and maximize available tax benefits.
Future Implications and Potential Reforms
The future of the IRS' involvement in health insurance is subject to ongoing debates and potential reforms. While the ACA remains in effect, there are ongoing discussions and proposals to modify or repeal certain provisions of the law.
Potential Reforms
Proposed reforms to the ACA often focus on addressing perceived issues with the law, such as rising healthcare costs, limited insurance options in certain areas, and the complexity of the tax provisions. Some potential reforms include:
- Expanding access to short-term health insurance plans.
- Allowing the purchase of insurance across state lines.
- Modifying or eliminating the individual mandate and the associated penalty.
- Simplifying the premium tax credit calculation and administration.
- Introducing new tax incentives to encourage healthy behaviors.
Impact on Taxpayers
Any reforms to the ACA would likely have a significant impact on taxpayers. Changes to the individual mandate, premium tax credits, or other tax provisions could affect the cost and availability of health insurance coverage. Taxpayers would need to stay informed about these potential reforms and their implications to make informed decisions about their healthcare and tax obligations.
FAQs

How do I claim the Premium Tax Credit on my tax return?
+To claim the Premium Tax Credit, you must complete Form 8962, Premium Tax Credit, and attach it to your federal tax return. This form allows you to calculate the credit based on your income and family size. You can choose to receive the credit in advance, which lowers your monthly insurance premiums, or claim it as a refund on your tax return.
What happens if I don't have health insurance and don't qualify for an exemption?
+If you do not have health insurance and do not qualify for an exemption, you may be subject to the Shared Responsibility Payment. This payment is calculated as a percentage of your household income and is reported on your federal tax return. It's important to note that certain exemptions, such as the financial hardship exemption, may require documentation to prove eligibility.
Can I deduct my health insurance premiums if I'm self-employed?
+Yes, if you are self-employed, you can deduct your health insurance premiums as a business expense. This deduction is available for both yourself and your dependents. However, there are certain rules and limitations, so it's recommended to consult a tax professional to ensure you meet all the requirements.
How do I know if I qualify for an exemption from the individual mandate penalty?
+The IRS provides a list of exemptions from the individual mandate penalty. To determine if you qualify, you can review the exemption categories and provide the necessary documentation to support your claim. It's important to note that certain exemptions, like the financial hardship exemption, may require additional forms and proof of eligibility.