Insurance U.s

The insurance industry in the United States is a complex and vital sector, playing a crucial role in safeguarding individuals, businesses, and communities against various risks and uncertainties. With a long history and a diverse range of products and services, the U.S. insurance market is one of the most advanced and highly regulated in the world. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the U.S. insurance landscape, covering its historical evolution, key players, regulatory environment, and the latest trends and innovations shaping the industry.
A Historical Perspective: The Evolution of Insurance in the U.S.
The roots of insurance in the United States can be traced back to the early colonial era. In the 17th century, the first marine insurance policies were issued, reflecting the importance of maritime trade for the young nation. These early policies provided a foundation for the development of the industry, as insurers gradually expanded their offerings to include fire, life, and property insurance.
The 19th century witnessed significant growth and transformation in the insurance sector. The establishment of the first life insurance company in 1810 marked a pivotal moment, followed by the creation of the first mutual assessment company, which introduced the concept of shared risk among policyholders. This period also saw the emergence of health insurance, as organizations like the Equitable Life Assurance Society began offering disability and medical benefits.
The 20th century brought further advancements and challenges. The Great Depression highlighted the importance of insurance as a safety net, while World War II emphasized the industry's role in protecting assets and providing financial security. The post-war era saw the rise of new insurance products, such as automobile and homeowner's insurance, catering to the changing needs of a growing nation.
Over the years, the U.S. insurance industry has faced numerous regulatory changes and market shifts. The implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010, for instance, significantly impacted the health insurance market, expanding coverage and introducing new regulations. Today, the industry continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and a focus on innovation and sustainability.
Key Players and Market Dynamics

The U.S. insurance market is characterized by a diverse range of players, from large multinational corporations to regional and specialty insurers. Some of the leading insurance companies in the country include:
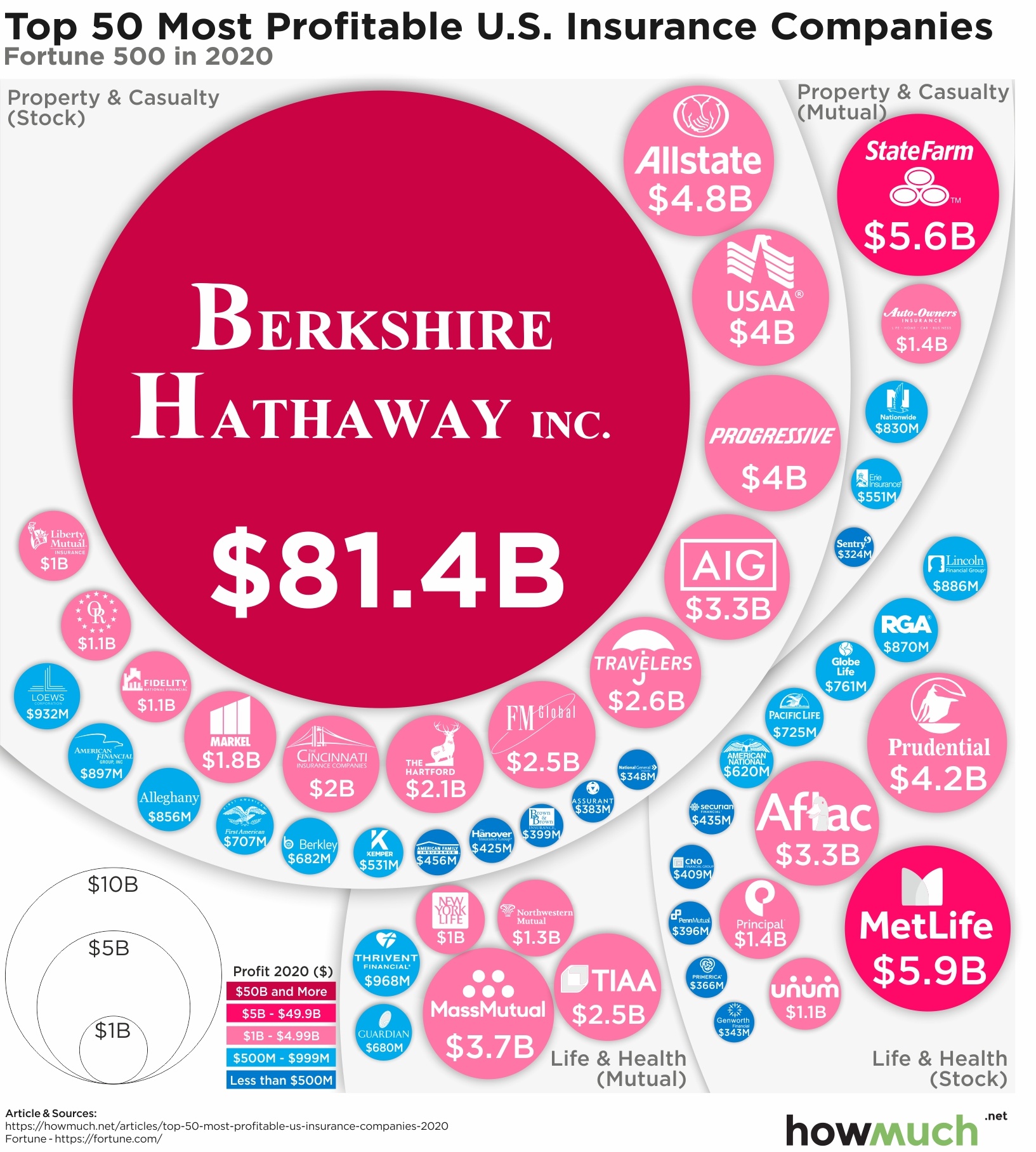
- Berkshire Hathaway: A conglomerate led by legendary investor Warren Buffett, Berkshire Hathaway is one of the largest insurers in the world, offering a wide range of insurance and reinsurance products.
- MetLife: A global provider of life insurance, employee benefits, and asset management services, MetLife is a well-known name in the industry with a strong presence in the U.S. market.
- State Farm: Known for its comprehensive insurance offerings, including auto, home, life, and health insurance, State Farm is a prominent player in the U.S. with a focus on customer service and community involvement.
- Allstate: A leading insurer offering a wide array of products, Allstate is known for its innovative approaches to insurance, including its use of telematics for auto insurance.
- Progressive: Specializing in auto insurance, Progressive has gained a reputation for its customer-centric approach and innovative marketing strategies.
These companies, along with many others, compete in a dynamic market characterized by changing consumer preferences, regulatory pressures, and technological disruptions. The rise of digital technologies and the increasing importance of data analytics have led to a shift towards more personalized and data-driven insurance products and services.
The Role of Technology in the Insurance Industry
Technology has become a game-changer for the U.S. insurance industry. Insurtech, a term used to describe the use of technology to innovate and disrupt traditional insurance practices, has brought about significant changes in how insurance is delivered and experienced.
One of the key areas where technology has had a profound impact is in the area of data analytics. Insurers are now able to leverage vast amounts of data to better understand customer needs, assess risks, and price policies more accurately. Advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, are being used to develop more sophisticated risk models and enhance fraud detection capabilities.
Additionally, the rise of digital channels has transformed the way insurance is sold and serviced. Online platforms and mobile apps have made it easier for consumers to compare policies, purchase coverage, and manage their insurance needs. Insurers are also exploring the use of blockchain technology to enhance security, streamline processes, and improve the efficiency of claims handling.
| Insurance Type | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Life Insurance | 30 |
| Health Insurance | 25 |
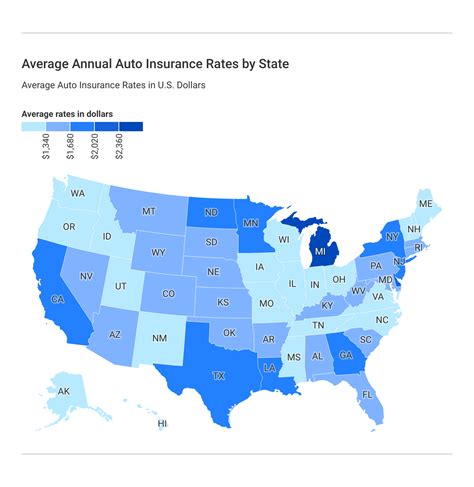
| Property & Casualty | 20 |
| Auto Insurance | 15 |
| Other (Travel, Pet, etc.) | 10 |
Regulatory Landscape: Navigating the Complex Web
The U.S. insurance industry is subject to a complex and multifaceted regulatory environment. At the federal level, the primary regulator is the Federal Insurance Office (FIO), which is responsible for monitoring the insurance industry and ensuring compliance with federal laws and regulations.
However, the majority of insurance regulation in the U.S. is conducted at the state level. Each state has its own insurance department or regulatory authority, which is responsible for licensing insurers, setting standards for policy terms and conditions, and overseeing market conduct. This state-based regulatory system adds a layer of complexity, as insurers must navigate different rules and requirements in each state they operate in.
Key federal regulations impacting the insurance industry include the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, which established the FIO and introduced new consumer protection measures, and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, which addressed privacy and data security concerns. Additionally, the implementation of the ACA has had a significant impact on the health insurance market, introducing new requirements for insurers and expanding coverage options.
Challenges and Opportunities in Regulation
The regulatory environment in the U.S. insurance industry presents both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, the complex and fragmented regulatory system can make it difficult for insurers to operate across state lines and adapt to changing regulations. It also adds to the administrative burden and compliance costs for insurers.
However, regulation also plays a crucial role in protecting consumers, ensuring fair practices, and maintaining the stability of the insurance market. Regulatory bodies work to prevent fraud, enforce consumer protection laws, and address market conduct issues. The introduction of new regulations, such as those related to data privacy and cybersecurity, also helps insurers stay ahead of emerging risks and adapt to changing consumer expectations.
Future Trends and Innovations: Shaping the Insurance Landscape
The U.S. insurance industry is poised for significant changes in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and a focus on sustainability and social responsibility.
Digital Transformation and Insurtech
The continued adoption of digital technologies will be a key driver of change in the insurance industry. Insurers are investing in digital transformation initiatives to enhance their operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Insurtech startups and established insurers are collaborating to develop innovative solutions, such as parametric insurance products, which provide coverage based on predefined parameters rather than traditional claims processes. These products are particularly relevant in the context of climate change and the increasing frequency of natural disasters.
Additionally, the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning is expected to grow, enabling insurers to offer more personalized and targeted products. Chatbots and virtual assistants are also likely to become more prevalent, providing customers with 24/7 assistance and streamlining the insurance journey.
Sustainability and Social Responsibility
Sustainability and social responsibility are becoming increasingly important considerations for the insurance industry. Insurers are recognizing the need to address environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their business strategies and operations.
This includes initiatives such as promoting sustainable practices in the underwriting process, offering incentives for eco-friendly behaviors, and investing in green technologies. Insurers are also exploring ways to support social causes and address societal challenges, such as providing coverage for underserved communities or supporting initiatives to address income inequality.
The Rise of Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance
Telematics, the use of technology to track and analyze vehicle data, is gaining traction in the insurance industry, particularly in the auto insurance sector. Usage-based insurance (UBI) policies, which use telematics data to calculate premiums based on actual driving behavior, are becoming more popular.
UBI policies reward safe driving behaviors, providing discounts to drivers who exhibit responsible habits. This approach not only benefits consumers by offering more personalized pricing but also encourages safer driving practices, leading to reduced accident rates and improved road safety.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Resilient Industry
The U.S. insurance industry is a dynamic and resilient sector, continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of individuals, businesses, and communities. From its early beginnings in the colonial era to the digital revolution of today, the industry has adapted and innovated to provide protection and financial security.
As the industry navigates the challenges and opportunities presented by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and a focus on sustainability, it is poised to continue its vital role in society. By embracing innovation, prioritizing customer needs, and addressing emerging risks, the U.S. insurance industry will remain a cornerstone of financial stability and a source of security for millions of Americans.
What are the key types of insurance offered in the U.S. market?
+The U.S. insurance market offers a wide range of insurance types, including life insurance, health insurance, property and casualty insurance, auto insurance, and specialty insurance such as travel, pet, and disability insurance.
How does the regulatory environment impact the insurance industry in the U.S.?
+The regulatory environment in the U.S. insurance industry is complex, with both federal and state-level regulations. While it adds complexity and compliance costs, regulation also plays a crucial role in protecting consumers, ensuring fair practices, and maintaining market stability.
What are some of the latest trends and innovations shaping the U.S. insurance industry?
+The U.S. insurance industry is seeing trends such as digital transformation, the rise of insurtech, and a focus on sustainability and social responsibility. Telematics and usage-based insurance are also gaining traction, particularly in the auto insurance sector.