Insurance Premium Meaning

In the world of finance and risk management, the term "insurance premium" holds significant importance, as it forms the foundation of the insurance industry. Understanding what an insurance premium is, how it works, and its implications is crucial for anyone looking to protect themselves, their assets, or their businesses. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the concept of insurance premiums, exploring its definition, the factors influencing it, and its broader impact on the insurance landscape.
Unraveling the Insurance Premium: Definition and Key Concepts

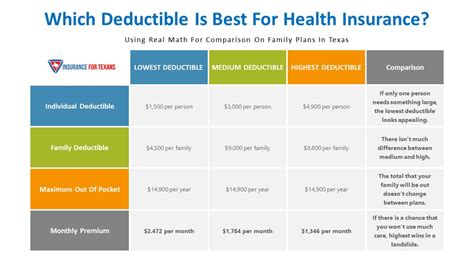
At its core, an insurance premium represents the cost of insurance coverage, the price paid by the policyholder to the insurance company for the promise of financial protection against specified risks. It is the contractual agreement between the insurer and the insured, where the insurer agrees to indemnify the insured against potential losses in exchange for regular premium payments.
The insurance premium is typically paid in regular installments, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, and it varies based on the type of insurance policy, the coverage limits, and the individual or entity's risk profile. This risk profile takes into account various factors, including age, health status, location, occupation, and the type of assets or activities being insured.
For instance, consider a homeowner's insurance policy. The insurance premium in this case would be the amount the homeowner pays to the insurance company to secure coverage against potential risks like fire, theft, or natural disasters. The premium is calculated based on factors such as the value of the home, its location (e.g., in a flood-prone area or not), the age and condition of the property, and the desired coverage limits.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
Risk Assessment and Underwriting
Insurance companies employ sophisticated risk assessment and underwriting processes to determine the appropriate insurance premium for each policyholder. Underwriters analyze a range of factors to assess the level of risk associated with the insured individual or entity.
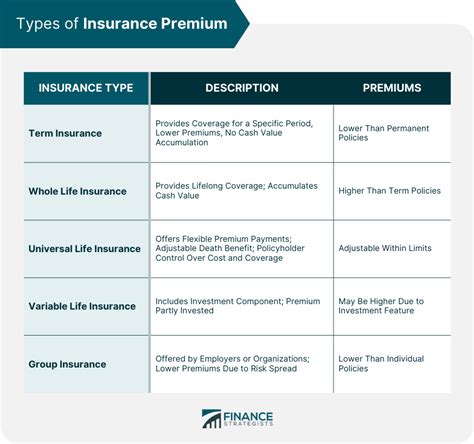
For instance, in life insurance, factors like age, health conditions, and lifestyle choices (e.g., smoking) play a significant role in determining the premium. Younger individuals, for example, typically pay lower premiums due to their lower risk of immediate health issues.
Similarly, in auto insurance, the premium is influenced by factors such as the driver's age, driving record, the make and model of the vehicle, and the geographic location. High-risk drivers or those living in areas with a history of frequent accidents or thefts may incur higher premiums.
Policy Coverage and Limits
The scope and extent of coverage under an insurance policy have a direct impact on the insurance premium. Policies with broader coverage and higher limits generally carry a higher premium.
Take health insurance as an example. Policies that offer comprehensive coverage, including hospitalization, prescription drugs, and specialist care, will likely have a higher premium compared to basic plans that only cover emergency care.
Historical Loss Data and Claims Experience
Insurance companies rely on extensive historical loss data and claims experience to set insurance premiums. By analyzing past claims and losses, insurers can predict future risks and set premiums accordingly.
For instance, in property insurance, areas with a history of frequent natural disasters like hurricanes or earthquakes may have higher premiums to account for the increased likelihood of claims. Similarly, in liability insurance, businesses with a higher propensity for claims, such as those in high-risk industries, may face higher premiums.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
Insurance premiums are also influenced by regulatory frameworks and legal requirements. Governments often impose regulations on insurance companies to ensure fair practices and protect consumers. These regulations can impact the premiums insurers can charge and the coverage they offer.
For example, in certain countries, there are laws mandating that insurers provide certain minimum levels of coverage for specific types of insurance, which can affect the premiums charged.
The Impact of Insurance Premiums on Consumers and the Industry
Affordability and Accessibility
Insurance premiums play a crucial role in determining the affordability and accessibility of insurance coverage for consumers. Higher premiums can make insurance policies less accessible to those with limited financial means, while lower premiums can encourage wider adoption of insurance.
For instance, in developing countries, where the majority of the population may have lower disposable incomes, insurance companies often design policies with lower premiums to make insurance more affordable and accessible.
Consumer Behavior and Choice
Insurance premiums influence consumer behavior and their choice of insurance policies. Individuals and businesses often compare premiums across different insurers and policy options to find the best value for their needs.
Some consumers may opt for higher deductibles or lower coverage limits to reduce their insurance premiums, while others may prioritize comprehensive coverage and be willing to pay a higher premium for peace of mind.
Market Competition and Innovation
Insurance premiums are a key factor in the competitive landscape of the insurance industry. Insurers strive to offer competitive premiums while maintaining profitability, which drives innovation and the development of new insurance products.
The rise of insurtech (insurance technology) companies, for instance, has disrupted the traditional insurance model by offering digital-first, data-driven insurance solutions with potentially lower premiums. These companies leverage technology to streamline processes, reduce costs, and offer more personalized insurance products.
Economic and Social Impact
Insurance premiums and the insurance industry as a whole have significant economic and social implications. Insurance provides a safety net for individuals and businesses, helping them manage financial risks and plan for the future.
For instance, in the event of a natural disaster or a health emergency, insurance coverage can provide the necessary financial support to individuals and communities, aiding in their recovery and reducing the economic burden on society as a whole.
Conclusion: The Complex World of Insurance Premiums
The insurance premium is a complex concept that lies at the heart of the insurance industry. It is a critical factor in determining the accessibility, affordability, and scope of insurance coverage for individuals and businesses. Understanding the factors that influence insurance premiums, from risk assessment to regulatory frameworks, is essential for making informed decisions about insurance coverage.
As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer needs, insurance premiums will remain a key consideration for insurers, policyholders, and regulators alike. The balance between providing adequate coverage and setting fair premiums will continue to shape the industry's future and its impact on society.
How are insurance premiums calculated?
+Insurance premiums are calculated through a complex process involving risk assessment, underwriting, and actuarial science. Insurers consider factors such as the type of insurance, coverage limits, risk profile of the insured, historical loss data, and regulatory requirements. Each insurance type has its unique formula for premium calculation.
Can insurance premiums change over time?
+Yes, insurance premiums can change. Insurers regularly review and adjust premiums based on various factors, including changes in risk profiles, claims experience, market conditions, and regulatory changes. Policyholders may also request changes to their coverage, which can impact their premiums.
Are there ways to reduce insurance premiums?
+There are several strategies to potentially reduce insurance premiums. These include maintaining a good claims history, opting for higher deductibles, bundling multiple policies with the same insurer, installing safety devices (e.g., home security systems), and taking advantage of discounts for safe practices (e.g., safe driving discounts in auto insurance). However, it’s essential to balance cost savings with adequate coverage.