Insurance Mortgage

In the world of finance and personal security, the terms "insurance" and "mortgage" are often heard together, yet they serve distinct purposes and have unique implications. This article aims to demystify these concepts, exploring their definitions, functions, and interconnections in the broader context of financial management and protection. By understanding the roles and benefits of insurance and mortgages, individuals can make informed decisions to secure their financial future and mitigate potential risks.
Understanding Insurance: A Financial Safety Net

Insurance is a cornerstone of modern financial planning, offering a crucial layer of protection against various risks and uncertainties. At its core, insurance is a contract between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company, wherein the policyholder pays a premium in exchange for financial protection or compensation in the event of a specific loss or accident.
Types of Insurance
The insurance landscape is diverse, catering to a multitude of potential risks. Here’s a glimpse into some common types of insurance and their roles:
- Health Insurance: This is perhaps one of the most vital forms of insurance, providing coverage for medical expenses, hospitalization, and sometimes even preventive care. Health insurance ensures individuals can access necessary medical treatments without facing financial ruin.
- Life Insurance: Life insurance policies are designed to provide financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder’s death. It offers a safety net for families, ensuring they can maintain their financial stability despite the loss of their loved one.
- Property Insurance: Property insurance, including home and auto insurance, protects individuals against losses arising from damage to their properties due to accidents, natural disasters, or theft. It covers the cost of repairs or replacements, ensuring individuals can quickly restore their homes or vehicles.
- Liability Insurance: Liability insurance protects individuals and businesses from financial loss arising from claims made by third parties for property damage or bodily injury. This type of insurance is particularly crucial for businesses, as it can cover legal fees and settlements in the event of a lawsuit.
The Benefits of Insurance
The advantages of insurance are multifaceted. Firstly, it provides a sense of security and peace of mind, knowing that financial support is available in times of crisis. Secondly, insurance encourages responsible behavior, as individuals are more likely to take precautions to avoid potential risks when they have insurance coverage. Finally, insurance plays a vital role in economic stability, as it helps individuals and businesses recover from unforeseen events, thereby contributing to overall economic growth.
Mortgages: Financing Your Dream Home
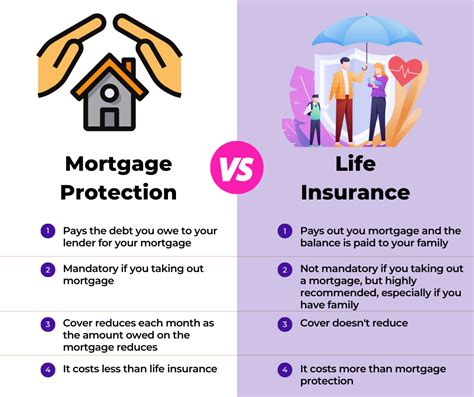
In the realm of real estate, a mortgage is a loan used to purchase a property, typically a home. It allows individuals to access the necessary funds to buy a house, which they may not have the financial means to purchase outright. Mortgages are long-term loans, often spanning decades, and they carry interest, which is how lenders profit from providing this service.
Key Components of a Mortgage
Understanding the components of a mortgage is crucial for anyone considering homeownership. Here are some key elements:
- Down Payment: This is the initial payment made by the borrower towards the purchase price of the home. A larger down payment can result in a lower monthly mortgage payment and may also reduce the interest rate offered by the lender.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate determines the cost of borrowing. It can be fixed, remaining the same throughout the loan term, or adjustable, changing periodically based on market conditions.
- Loan Term: The loan term refers to the length of time over which the mortgage is repaid. Common loan terms include 15, 20, and 30 years, with 30-year mortgages being the most popular due to their lower monthly payments.
- Monthly Payments: Monthly mortgage payments include both the principal (the original loan amount) and interest. The amount allocated to each can vary over the life of the loan, with more of the payment going towards interest in the early years and more towards the principal in later years.
Mortgage Types and Options
The mortgage market offers a variety of loan types to cater to different financial situations and goals. Some common mortgage options include:
- Fixed-Rate Mortgages: As the name suggests, the interest rate remains fixed for the entire loan term. This provides stability and predictability, as borrowers know exactly how much their monthly payments will be over the life of the loan.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARMs): ARMs have interest rates that can change over time. The initial interest rate is typically lower than that of a fixed-rate mortgage, but it can increase or decrease based on market conditions, making monthly payments less predictable.
- Government-Backed Loans: These loans are insured or guaranteed by government agencies like the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), or the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). They often have more flexible eligibility criteria and lower down payment requirements than conventional loans.
The Intersection of Insurance and Mortgages
While insurance and mortgages serve different purposes, they are intricately linked, especially in the context of homeownership. When individuals take out a mortgage to purchase a home, lenders often require borrowers to have insurance coverage on the property.
Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage insurance, often referred to as private mortgage insurance (PMI), is a type of insurance that protects the lender in case the borrower defaults on the loan. It is typically required for borrowers who make a down payment of less than 20% of the home’s purchase price. PMI can be canceled once the borrower’s equity in the home reaches 20%, providing a financial incentive for homeowners to pay down their mortgage.
Homeowner’s Insurance
Homeowner’s insurance, on the other hand, protects the borrower (and by extension, the lender) against financial losses arising from damages to the property caused by events like fires, storms, or theft. It also provides liability coverage, protecting the homeowner if someone is injured on their property.
The Role of Insurance in Mortgage Approval
Insurance plays a pivotal role in the mortgage approval process. Lenders want to ensure that the property they’re lending against is adequately protected. They require borrowers to have homeowner’s insurance in place before finalizing the mortgage, and they may even require specific coverage limits to ensure the property is fully protected.
Maximizing Benefits: Combining Insurance and Mortgage Strategies
By understanding the interplay between insurance and mortgages, individuals can develop comprehensive financial strategies. For instance, homeowners can review their insurance policies regularly to ensure they have adequate coverage without paying for unnecessary premiums. Additionally, they can explore different mortgage options to find the best fit for their financial situation and goals.
Financial Planning and Security
A well-rounded financial plan often involves a combination of insurance and mortgage strategies. Insurance provides a safety net against unforeseen events, while a mortgage can be a tool for building wealth through homeownership. By managing these aspects effectively, individuals can work towards financial stability and long-term security.
The Future of Insurance and Mortgages
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, so too do the options and strategies available for insurance and mortgages. Technological advancements, changing market conditions, and shifting consumer preferences are all influencing the way these industries operate. Staying informed and adapting to these changes can help individuals make the most of their insurance and mortgage choices.
Industry Innovations and Trends
| Innovation/Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| Digital Insurance Platforms | These platforms offer convenient, efficient ways to compare and purchase insurance policies, providing consumers with more control over their coverage choices. |
| Flexible Mortgage Options | Lenders are offering more flexible mortgage products, such as interest-only mortgages or adjustable-rate mortgages with lower initial rates, to cater to a wider range of borrowers. |
| Shared Equity Mortgages | Shared equity mortgages, where the lender takes a share of the property’s equity in exchange for a reduced down payment, are gaining popularity as an alternative to traditional mortgages. |
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the main difference between insurance and a mortgage?
+Insurance is a financial contract that provides protection against specific risks, while a mortgage is a loan used to purchase property, typically a home. Insurance offers financial security in the event of unforeseen circumstances, while a mortgage allows individuals to access the funds needed to buy a home, which they may not have the means to purchase outright.
How does insurance affect mortgage approval?
+Lenders require borrowers to have insurance on the property being purchased with a mortgage. This insurance, typically homeowner’s insurance, protects both the borrower and the lender against financial losses due to damages or liabilities related to the property. Without adequate insurance, a lender may deny a mortgage application.
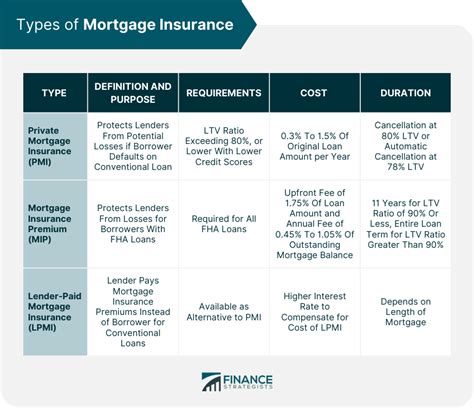
What are the different types of mortgage insurance?
+There are several types of mortgage insurance, including private mortgage insurance (PMI), lender-paid mortgage insurance (LPMI), and government-backed mortgage insurance. PMI is typically required for borrowers with a down payment of less than 20% and protects the lender in case of default. LPMI is paid by the lender but can result in a higher interest rate for the borrower. Government-backed mortgage insurance, such as FHA or VA loans, is often more affordable and accessible for certain borrowers.