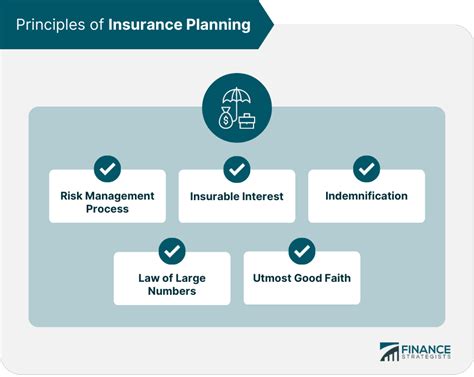
Insurance Liabilities
Insurance liabilities are a crucial aspect of the insurance industry, impacting both policyholders and insurance companies. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of insurance liabilities, exploring their nature, implications, and management strategies. By understanding insurance liabilities, stakeholders can make informed decisions and navigate the complex landscape of risk and responsibility.
Understanding Insurance Liabilities

Insurance liabilities refer to the financial obligations that insurance companies incur when policyholders make valid claims under their insurance policies. These liabilities arise from various types of insurance coverage, including property, casualty, health, and life insurance. The concept of insurance liabilities is foundational to the insurance industry, as it defines the financial commitments insurance companies make to their policyholders in the event of covered losses or damages.
Insurance liabilities are a crucial aspect of risk transfer, a fundamental principle of insurance. When individuals or entities purchase insurance policies, they transfer a portion of their financial risk to the insurance company. In return, the insurance company assumes the responsibility of compensating policyholders for covered losses. This transfer of risk is what makes insurance an indispensable tool for managing financial uncertainties and safeguarding individuals and businesses from potential financial ruin.
The scope of insurance liabilities is broad and varies based on the type of insurance policy and the specific terms and conditions outlined in the policy contract. For instance, in property insurance, liabilities may include compensating policyholders for damage to their homes or businesses caused by natural disasters, fires, or theft. Casualty insurance, on the other hand, covers liabilities arising from accidents, injuries, or legal claims, providing protection for individuals and businesses against potential lawsuits.
Health insurance liabilities involve compensating policyholders for medical expenses, including hospital stays, surgical procedures, and prescription medications. Life insurance, a critical component of financial planning, provides a payout to beneficiaries upon the insured individual's death, helping to secure their financial future.
The Importance of Adequate Reserves
Managing insurance liabilities effectively requires insurance companies to maintain adequate reserves. Reserves are funds set aside to meet future insurance obligations, ensuring that insurance companies have the financial resources to pay out valid claims as they arise. Adequate reserves are crucial for maintaining the financial stability and solvency of insurance companies, as they provide a buffer against unexpected or catastrophic losses.
The calculation and management of reserves are highly regulated by insurance authorities to ensure the financial soundness of the industry. Insurance companies employ actuarial science to estimate future liabilities and determine the appropriate level of reserves. Actuaries use complex mathematical models and statistical techniques to analyze historical data, demographic trends, and economic factors to make accurate predictions about future claims and liabilities.
By maintaining adequate reserves, insurance companies can fulfill their obligations to policyholders, even in the face of unforeseen events or a high volume of claims. This not only protects policyholders but also helps to maintain public trust in the insurance industry. Insufficient reserves can lead to insolvency, compromising the ability of insurance companies to pay out claims and potentially causing widespread financial distress for policyholders.
Types of Insurance Liabilities
Insurance liabilities can be categorized into different types based on their nature and the specific coverage provided by insurance policies. Understanding these different types of liabilities is essential for both insurance companies and policyholders to manage risks effectively and ensure proper compensation in the event of losses.
First-Party Liabilities
First-party liabilities refer to insurance claims made by policyholders themselves. In this case, the insured individual or entity is the direct beneficiary of the insurance coverage. For instance, if a homeowner’s property is damaged by a storm, they can make a claim under their property insurance policy to receive compensation for repairs or replacement of damaged items. Similarly, a person injured in a car accident can make a claim under their auto insurance policy to cover medical expenses and vehicle repairs.
First-party liabilities are a critical aspect of insurance coverage, providing policyholders with financial protection against unforeseen events. By promptly and fairly settling first-party claims, insurance companies uphold their contractual obligations and maintain the trust of their policyholders. Efficient claim management processes, including timely investigations and fair assessments of damages, are essential for ensuring a positive customer experience and fostering long-term relationships with policyholders.
Third-Party Liabilities
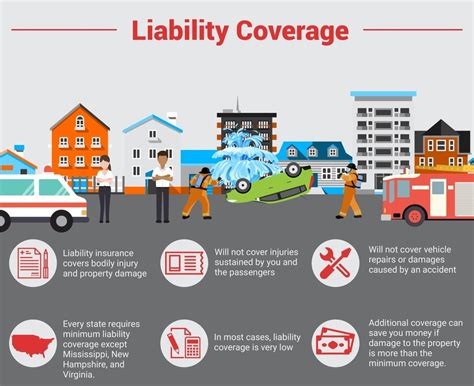
Third-party liabilities arise when an insured individual or entity is held legally responsible for damages or injuries caused to a third party. In such cases, the insurance company steps in to provide coverage and defend the insured against legal claims. For example, if a driver insured under a liability auto insurance policy causes an accident that injures another person, the insurance company would be responsible for compensating the injured party for medical expenses, property damage, and potentially other losses.
Third-party liabilities are a crucial component of liability insurance, which protects individuals and businesses from the financial consequences of legal claims. By providing coverage for damages and legal defense, liability insurance helps policyholders manage the risks associated with their activities, whether it's driving a car, operating a business, or engaging in other potentially hazardous pursuits. Effective management of third-party liabilities requires insurance companies to have robust claims handling processes, including prompt investigations, thorough assessments of liability, and skilled legal representation when necessary.
Uninsured and Underinsured Motorist Liabilities
Uninsured and underinsured motorist liabilities are unique to auto insurance and address situations where an insured individual is involved in an accident with a driver who does not have adequate insurance coverage. In these cases, the insured’s own auto insurance policy may provide coverage for damages and injuries sustained in the accident.
Uninsured motorist coverage protects policyholders when they are involved in an accident with a driver who has no insurance. This coverage ensures that the insured receives compensation for their losses, even when the at-fault driver cannot be held financially responsible. Underinsured motorist coverage, on the other hand, comes into play when the at-fault driver's insurance coverage is insufficient to fully compensate the insured for their damages and injuries.
Managing uninsured and underinsured motorist liabilities is essential for ensuring that policyholders are adequately protected in the event of an accident. Insurance companies must have comprehensive claims handling procedures in place to promptly investigate and assess these types of claims, ensuring that policyholders receive the compensation they are entitled to under their insurance policies. By effectively managing these liabilities, insurance companies can provide a valuable safety net for policyholders, helping them to navigate the complexities of the legal and insurance systems following an accident.
Managing Insurance Liabilities
Effective management of insurance liabilities is a complex and critical task for insurance companies. It involves a combination of strategic planning, risk assessment, and claims handling processes to ensure that policyholders receive timely and fair compensation while also safeguarding the financial stability of the insurance company.
Risk Assessment and Underwriting
Risk assessment and underwriting are fundamental processes in managing insurance liabilities. Underwriters play a crucial role in evaluating the risks associated with each insurance policy, considering factors such as the insured’s age, health status, driving record, or the nature of the business being insured. By carefully assessing these risks, underwriters can determine the appropriate level of premiums and the terms of coverage, ensuring that the insurance company can adequately cover potential liabilities.
Risk assessment also involves the use of advanced analytics and data-driven techniques. Insurance companies leverage predictive modeling and machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, including historical claims data, demographic information, and external factors such as weather patterns or economic trends. This enables them to identify potential risk factors and make informed decisions about policy terms and premiums, ultimately enhancing the accuracy of their liability estimates.
Claims Handling and Settlement
Claims handling and settlement are critical aspects of managing insurance liabilities. When a policyholder makes a claim, the insurance company’s claims department steps in to investigate the claim, assess the extent of the damages or injuries, and determine the validity of the claim based on the terms and conditions of the insurance policy. This process requires thoroughness, fairness, and efficiency to ensure that policyholders receive the compensation they are entitled to while also protecting the insurance company’s financial interests.
Effective claims handling involves timely communication with policyholders, clear and transparent explanations of the claims process, and regular updates on the progress of the claim. Insurance companies may employ a range of technologies and tools, such as online claims portals, mobile apps, and automated claim processing systems, to streamline the claims process and enhance customer satisfaction. Additionally, claims adjusters play a vital role in evaluating claims, conducting thorough investigations, and negotiating settlements with policyholders or their representatives.
Loss Prevention and Mitigation
Loss prevention and mitigation strategies are essential components of insurance liability management. Insurance companies actively work to prevent losses and mitigate the severity of claims by providing risk management advice and resources to policyholders. This may include offering guidance on safety measures, providing educational materials on risk reduction, or recommending specific precautions based on the insured’s circumstances.
For example, insurance companies may offer discounts or incentives to policyholders who take proactive steps to reduce risks, such as installing security systems, implementing fire safety measures, or maintaining regular vehicle maintenance. By encouraging policyholders to adopt safer practices, insurance companies can help prevent losses and reduce the frequency and severity of claims, ultimately benefiting both the policyholders and the insurance company.
Insurance Liabilities and the Future
As the insurance industry continues to evolve, insurance liabilities will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping the future of risk management and financial protection. The dynamic nature of the industry, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer expectations, and emerging risks, necessitates a forward-thinking approach to liability management.
Emerging Risks and Coverage Innovations
The insurance industry is constantly evolving to address emerging risks and provide innovative coverage solutions. With the rapid advancement of technology, new risks such as cyber threats, data breaches, and autonomous vehicles have emerged, requiring insurance companies to adapt their liability coverage to keep pace with these changing landscapes. Insurance companies are developing new products and coverage options to address these emerging risks, ensuring that policyholders have the protection they need in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.
The Impact of Climate Change
Climate change presents a significant challenge to the insurance industry, as it increases the frequency and severity of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires. These events can result in massive insurance liabilities, particularly in regions vulnerable to climate-related disasters. Insurance companies are actively engaging in climate risk assessment and developing strategies to manage these increasing liabilities, including reevaluating coverage limits, adjusting premiums, and partnering with government entities and communities to enhance resilience and mitigation efforts.
Technological Advancements and Digital Transformation
The digital transformation of the insurance industry is revolutionizing the way insurance liabilities are managed. Advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are being leveraged to enhance risk assessment, streamline claims handling, and improve overall operational efficiency. Insurance companies are investing in digital technologies to automate routine tasks, improve data accuracy, and provide policyholders with convenient and accessible digital platforms for managing their insurance needs.
Furthermore, digital transformation is enabling insurance companies to offer personalized insurance products and coverage tailored to individual policyholders' needs. By leveraging data-driven insights, insurance companies can develop dynamic pricing models and innovative coverage options that reflect the unique risks and circumstances of each policyholder. This shift towards personalized insurance not only enhances customer satisfaction but also helps insurance companies better manage their liabilities by aligning coverage with individual risk profiles.
What happens if an insurance company is unable to meet its insurance liabilities?
+If an insurance company is unable to meet its insurance liabilities, it can lead to insolvency and the potential collapse of the company. To prevent this, insurance companies are closely regulated and required to maintain adequate reserves to cover their liabilities. In extreme cases, insurance companies may face legal action or be placed under supervision by regulatory authorities.
How do insurance companies determine the level of reserves needed to cover insurance liabilities?
+Insurance companies employ actuarial science to estimate future liabilities and determine reserve requirements. Actuaries use complex mathematical models, historical data, and demographic trends to predict the likelihood and magnitude of future claims. This information is crucial for setting appropriate reserve levels and ensuring the financial stability of the insurance company.
Can insurance companies be held liable for claims beyond the policy limits?
+Insurance companies are generally not held liable for claims beyond the policy limits outlined in the insurance contract. Policy limits define the maximum amount the insurance company is obligated to pay for covered losses. However, in cases of bad faith or negligent claims handling, insurance companies may face additional legal liabilities.
How do insurance companies manage the risk of uninsured and underinsured motorist liabilities?
+Insurance companies offer uninsured and underinsured motorist coverage as part of auto insurance policies. This coverage provides protection for policyholders when they are involved in accidents with drivers who have no insurance or insufficient insurance coverage. By offering this coverage, insurance companies manage the risk of uninsured and underinsured motorist liabilities and ensure that policyholders are adequately protected.