How Much Should House Insurance Cost
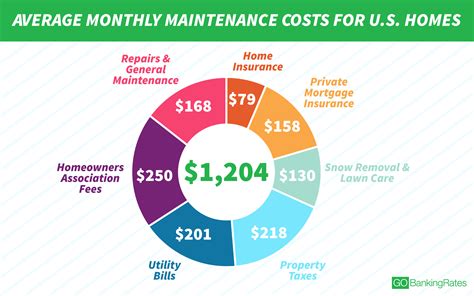
Understanding the cost of home insurance is essential for any homeowner. With a multitude of factors influencing premiums, it can be challenging to pinpoint an exact figure. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of house insurance costs, shedding light on the key elements that impact your policy and providing valuable insights to help you navigate this essential aspect of homeownership.
The Average Cost of House Insurance
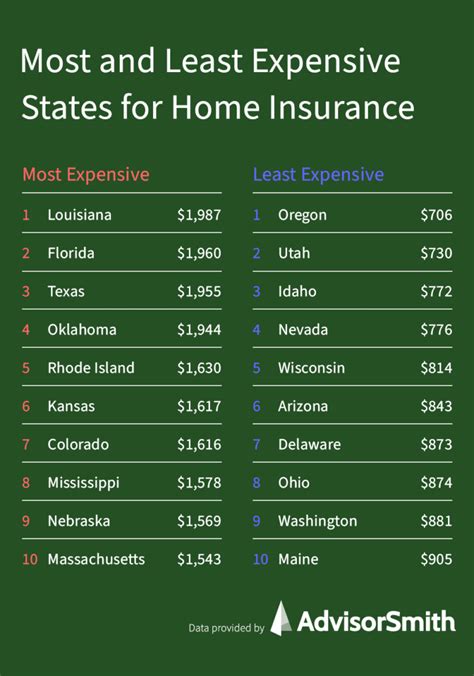
The average cost of house insurance varies significantly across different regions and depends on numerous factors. While it’s challenging to provide an exact figure, we can explore the average costs based on various scenarios to give you a clearer picture.
Regional Variations
House insurance costs can differ considerably from one state to another. Factors such as the cost of living, the prevalence of natural disasters, and the average home value all contribute to these variations. For instance, in California, known for its earthquakes and wildfires, insurance premiums tend to be higher compared to Wisconsin, which experiences fewer severe weather events.
According to recent data, the average annual premium for home insurance in the United States is approximately $1,300. However, this average masks significant disparities between states. In Louisiana, for example, the average premium can reach as high as $2,700 due to the state's vulnerability to hurricanes and floods. On the other hand, states like Ohio and Pennsylvania often have lower average premiums, ranging from $600 to $900 annually.
| State | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| California | $1,800 |
| Texas | $1,500 |
| Florida | $2,000 |
| New York | $1,400 |
| Illinois | $1,200 |

These variations highlight the importance of considering your specific location when estimating house insurance costs.
Coverage Amount and Limits
The amount of coverage you choose is a critical factor in determining the cost of your house insurance. Insurance providers typically offer coverage limits ranging from 100,000</strong> to <strong>500,000 or even higher. The coverage amount should be sufficient to rebuild your home if it’s completely destroyed, and it also influences the cost of your premiums.
For example, a homeowner in Chicago with a coverage limit of $200,000 might pay an annual premium of around $750. However, if the same homeowner increases their coverage limit to $300,000, the premium could rise to $900 or more.
Deductibles and Discounts
Another aspect that affects the cost of your house insurance is the deductible you choose. A deductible is the amount you agree to pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. Opting for a higher deductible can lead to lower premiums, as you’re accepting a larger financial responsibility in the event of a claim.
Additionally, insurance companies often offer discounts to encourage safer practices or to reward loyal customers. Common discounts include:
- Multi-Policy Discount: Combining your home and auto insurance policies with the same insurer can result in significant savings.
- Safety Features Discount: Installing security systems, smoke detectors, and fire sprinklers may qualify you for discounts.
- Loyalty Discount: Staying with the same insurance provider for an extended period can lead to reduced premiums.
- New Home Discount: Insuring a newly constructed home often comes with discounted rates.
Factors Influencing House Insurance Costs
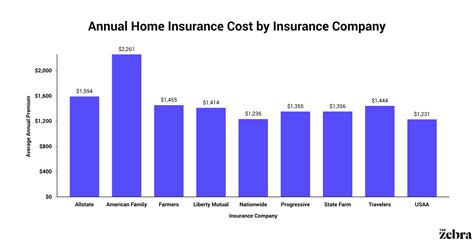
Several factors contribute to the cost of house insurance. Understanding these elements can help you make informed decisions and potentially lower your premiums.
Home Value and Location
The value of your home is a primary factor in determining insurance costs. Higher-value homes typically require more extensive coverage, resulting in higher premiums. Additionally, the location of your home plays a significant role. Areas prone to natural disasters, crime, or high property values tend to have higher insurance costs.
Construction Materials and Age
The materials used to construct your home and its age can impact insurance costs. Homes built with fire-resistant materials or reinforced against earthquakes may qualify for lower premiums. Older homes might require more extensive coverage due to potential issues with outdated wiring or plumbing, leading to higher insurance costs.
Claim History and Credit Score
Your claim history with the insurance company is a critical factor. Frequent claims can lead to higher premiums or even policy cancellations. Maintaining a clean claim history demonstrates stability and can result in more favorable rates. Additionally, your credit score can impact insurance costs, as insurance providers often use credit-based insurance scores to assess risk.
Homeowner’s Associations and Local Laws
If you live in a community with a homeowner’s association (HOA), your insurance costs may be influenced by the association’s rules and regulations. Some HOAs require specific coverage levels or have restrictions on certain home features. Additionally, local laws and ordinances can impact insurance costs, especially if they mandate certain coverage levels or require specific types of insurance.
Tips for Lowering House Insurance Costs
While house insurance costs can vary, there are strategies you can employ to potentially lower your premiums. Here are some effective tips:
Shop Around and Compare
Don’t settle for the first insurance quote you receive. Compare rates from multiple providers to find the best deal. Online insurance marketplaces can be a convenient way to gather quotes from various insurers in one place.
Bundle Your Policies
If you have multiple insurance needs, such as home and auto insurance, consider bundling your policies with the same provider. Many insurers offer significant discounts for customers who bundle their coverage.
Increase Your Deductible
Opting for a higher deductible can lead to lower premiums. However, ensure that you choose a deductible amount that you can comfortably afford in the event of a claim.
Maintain a Good Credit Score
A strong credit score can help you secure lower insurance rates. Insurance providers often use credit-based insurance scores to assess risk, so maintaining a good credit history is crucial.
Improve Your Home’s Security
Installing security features like burglar alarms, fire sprinklers, and smoke detectors can qualify you for discounts on your insurance premiums. These measures not only protect your home but also reduce the risk of claims, making you a more attractive insurance candidate.
The Future of House Insurance Costs
The cost of house insurance is influenced by various factors, and predicting future trends can be challenging. However, we can identify some potential developments that may impact insurance costs in the coming years.
Advancements in Technology
Technological advancements are likely to play a significant role in shaping the insurance industry. The increasing use of smart home technology, such as connected devices and sensors, could lead to more accurate risk assessments and potentially lower insurance costs for homeowners. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning could enhance the efficiency of insurance processes, reducing overhead costs for providers and potentially passing on savings to customers.
Changing Weather Patterns and Climate Risks
The impact of climate change and its effect on weather patterns cannot be ignored. As extreme weather events become more frequent and severe, insurance companies may need to adjust their rates to account for increased risk. Homeowners in areas vulnerable to hurricanes, wildfires, or floods may experience higher insurance costs as providers seek to mitigate their exposure to these risks.
Regulatory Changes and Industry Competition
Government regulations and industry competition can also influence insurance costs. Regulatory changes aimed at protecting consumers or promoting competition within the insurance market could impact the pricing strategies of providers. Increased competition among insurers may lead to more affordable rates as companies strive to attract and retain customers.
Changing Consumer Expectations
The expectations and preferences of consumers are evolving, and insurance providers are adapting to meet these demands. As more homeowners seek personalized and flexible insurance options, providers may respond by offering a wider range of coverage choices and more tailored policies. This shift towards personalized insurance could result in a more nuanced pricing structure, with premiums reflecting the specific needs and risks of individual homeowners.
Conclusion
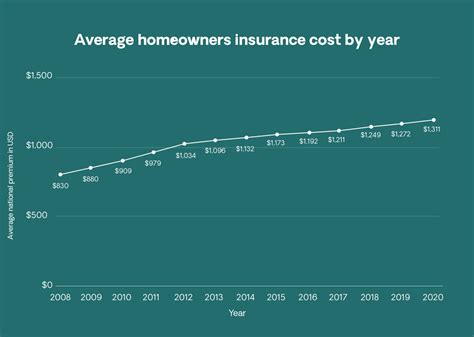
Understanding the cost of house insurance is a critical aspect of homeownership. By considering the average costs, the factors that influence premiums, and the strategies to lower insurance expenses, homeowners can make informed decisions to protect their assets effectively. As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive can help ensure you’re getting the best value for your insurance coverage.
How often should I review my house insurance policy?
+It’s a good practice to review your insurance policy annually, especially after significant life changes or home improvements. This ensures that your coverage remains adequate and that you’re not overpaying for unnecessary coverage.
Can I negotiate my house insurance premiums?
+While insurance premiums are typically set based on standardized rates, you can negotiate with your insurer to explore potential discounts or adjust your coverage limits to lower your premiums. However, be cautious about reducing coverage to an inadequate level.
What should I do if I can’t afford my house insurance premiums?
+If you’re struggling to afford your insurance premiums, consider increasing your deductible or reviewing your coverage limits to see if there are areas where you can reduce costs. Additionally, shop around for quotes from different providers to find more affordable options.
How does my credit score impact my house insurance premiums?
+Insurance providers often use credit-based insurance scores to assess risk. A higher credit score can indicate a lower risk profile, potentially leading to lower insurance premiums. Improving your credit score can be a strategy to reduce insurance costs.



