How Much Does Health Insurance Cost Without A Job
The cost of health insurance when you're not employed can be a daunting concern, especially in countries where healthcare is primarily funded through employment-based plans. In the United States, for instance, a significant portion of the population relies on employer-sponsored health insurance. However, this traditional model leaves many without coverage when they lose their jobs or are unable to find employment. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the costs associated with securing health insurance without a job, offering practical insights and strategies to navigate this challenging situation.
Understanding the Landscape: Health Insurance for the Unemployed

For those who find themselves without employment, the immediate concern often shifts to maintaining health insurance coverage. In the United States, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has played a pivotal role in expanding access to health insurance for the unemployed and underinsured. The ACA introduced the concept of individual market insurance, allowing individuals to purchase health coverage directly from insurance companies or through government-run marketplaces, often with the benefit of premium subsidies.
The costs associated with individual market insurance can vary significantly based on several factors, including:
- Location: Insurance rates can differ substantially from state to state due to variations in healthcare costs and regulations.
- Age: Older individuals often face higher premiums, as the risk of requiring healthcare services increases with age.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or using tobacco products can lead to higher premiums, as it is associated with increased health risks.
- Health Status: Pre-existing conditions or poor health can result in higher premiums or even exclusion from certain plans.
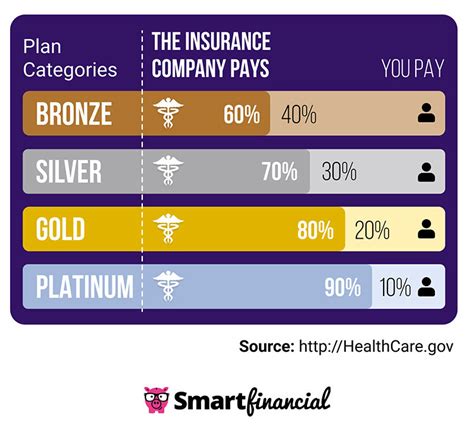
- Plan Type and Coverage: The type of plan chosen, such as HMO, PPO, or EPO, along with the level of coverage and deductibles, influences the cost.
Premium Subsidies: A Lifeline for the Unemployed
A key aspect of the ACA is the provision of premium subsidies for individuals and families with modest incomes. These subsidies, often referred to as Advanced Premium Tax Credits (APTC), can significantly reduce the cost of monthly premiums for eligible individuals. The amount of subsidy is determined by the person’s income and family size, ensuring that healthcare remains accessible even without employment.
| Income Level | Premium Subsidy |
|---|---|
| Up to 138% of Federal Poverty Level | May be eligible for Medicaid |
| 138% - 400% of Federal Poverty Level | Receives Premium Subsidy |
| Above 400% of Federal Poverty Level | No Premium Subsidy |
Navigating the Individual Market: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Determine Eligibility for Subsidies: Before purchasing a plan, check your eligibility for premium subsidies. You can use the Healthcare.gov Premium Calculator to estimate your potential savings.
- Compare Plans and Costs: Explore the available plans on your state’s health insurance marketplace. Compare premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums to find the best fit for your needs and budget.
- Apply for Coverage: During the Open Enrollment Period, typically from November to December, you can apply for individual market insurance. If you qualify for a Special Enrollment Period due to a life event, such as losing your job, you can apply outside of the Open Enrollment.
- Enroll and Manage Your Plan: Once enrolled, familiarize yourself with your plan’s coverage and benefits. Regularly review your coverage to ensure it aligns with your changing health needs and financial situation.
Alternative Options for Health Insurance Coverage

While the individual market is a primary option for the unemployed, other avenues for health insurance coverage exist, each with its own set of benefits and limitations.
Medicaid: Coverage for Low-Income Individuals
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage for low-income individuals and families. Eligibility for Medicaid is primarily based on income, with some states expanding coverage beyond the federal guidelines.
To qualify for Medicaid, your income must be at or below a certain percentage of the Federal Poverty Level (FPL). For example, in 2023, the FPL for a single person is $13,840, while for a family of four, it's $31,800. Some states have adopted the Medicaid expansion under the ACA, which raises the income threshold to 138% of the FPL, ensuring broader coverage for low-income individuals.
Medicare: Health Insurance for Older Americans
Medicare is a federal program that provides health insurance for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as for younger people with certain disabilities or health conditions. Unlike Medicaid, which is primarily income-based, Medicare is available to all Americans who have paid into the Social Security system for a certain period.
Medicare is divided into several parts, each covering different aspects of healthcare:
- Part A (Hospital Insurance): Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, and some home healthcare services.
- Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers doctor's services, outpatient care, and some home healthcare services.
- Part C (Medicare Advantage): Allows you to receive Medicare benefits through private insurance plans, often including additional benefits like vision, dental, and prescription drug coverage.
- Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Provides coverage for prescription medications.
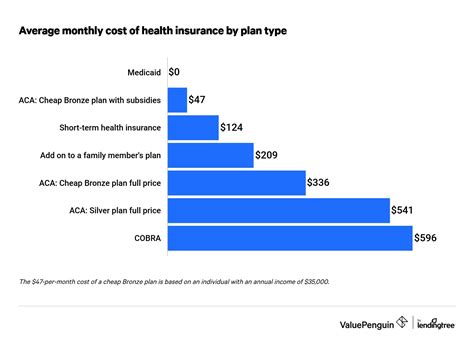
Short-Term Health Insurance: A Temporary Solution
Short-term health insurance plans offer coverage for a limited period, typically ranging from one month to a year. These plans are designed to bridge gaps in coverage and are often more affordable than comprehensive health insurance plans. However, they come with significant limitations and may not be suitable for individuals with pre-existing conditions or those seeking long-term coverage.
State High-Risk Pools: A Safety Net for High-Risk Individuals
State high-risk pools are insurance programs designed to provide coverage for individuals with pre-existing conditions who may be denied coverage by private insurers. These pools offer comprehensive health insurance coverage at a cost comparable to standard plans. While not all states have high-risk pools, they can be a valuable option for those with health conditions that make traditional insurance challenging to obtain.
Catastrophic Health Insurance Plans: Minimal Coverage for Low Premiums
Catastrophic health insurance plans are designed for individuals under the age of 30 or those who qualify for a hardship exemption. These plans offer minimal coverage, primarily for emergency and catastrophic medical events, but come with low monthly premiums. While they may not cover all healthcare needs, they can provide a safety net for unexpected medical emergencies.
Strategies for Affording Health Insurance without a Job
Securing health insurance when unemployed can be a financial challenge. Here are some strategies to help make insurance more affordable:
- Maximize Premium Subsidies: If you're eligible for premium subsidies, ensure you're receiving the maximum benefit. The Premium Tax Credit can significantly reduce your monthly premiums.
- Explore Cost-Sharing Reduction Plans: Some plans offer cost-sharing reduction (CSR) benefits, which can lower your out-of-pocket costs for deductibles, copays, and coinsurance. These plans are often a more affordable option for those with lower incomes.
- Consider Dental and Vision Coverage: Many health insurance plans do not include dental and vision coverage. If these are important to you, look for plans that offer these benefits or consider purchasing separate dental and vision insurance.
- Choose a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): HDHPs typically have lower premiums but higher deductibles. If you're in good health and have limited healthcare needs, an HDHP can be a cost-effective option.
- Utilize Healthcare Sharing Ministries: Healthcare sharing ministries are faith-based alternatives to traditional insurance. Members contribute to a pool that helps cover each other's medical expenses. These ministries often have lower costs but may have restrictions on coverage.
Conclusion: Navigating the Uncertain Waters of Unemployed Healthcare
Finding affordable health insurance without a job is a complex and often stressful endeavor. However, with the right information and strategies, it is possible to navigate the individual market and explore alternative options to secure the coverage you need. From understanding the impact of the Affordable Care Act to exploring state-specific programs like Medicaid and high-risk pools, there are numerous avenues to explore.
Remember, staying informed and proactive about your health insurance options is crucial, especially during periods of unemployment. By comparing plans, understanding your eligibility for subsidies, and making informed choices, you can ensure you have the coverage you need to stay healthy and financially secure.
What is the average cost of individual health insurance without a job in the United States?
+
The average cost of individual health insurance in the U.S. varies widely based on factors like location, age, and plan type. According to the Kaiser Family Foundation, the average monthly premium for an individual in 2023 is around 539. However, this can range from as low as 350 to over $1,000 per month. Premium subsidies under the Affordable Care Act can significantly reduce these costs for eligible individuals.
Can I get health insurance without a job through the Affordable Care Act (ACA)?
+
Absolutely! The ACA provides an individual market where you can purchase health insurance directly from insurance companies or through government-run marketplaces. You may also be eligible for premium subsidies if your income is below a certain threshold, making insurance more affordable.
Are there any free or low-cost health insurance options for the unemployed?
+
Yes, several options are available. Medicaid provides free or low-cost health coverage for low-income individuals and families. Additionally, states may offer high-risk pools or other programs to provide coverage for those with pre-existing conditions. Short-term health insurance plans and catastrophic health insurance plans can also offer minimal coverage at a lower cost.
What is the best type of health insurance for someone without a job?
+
The best type of health insurance depends on your individual needs and financial situation. If you’re eligible for premium subsidies, an individual market plan through the ACA can be a great option. Medicaid is also a valuable option for low-income individuals. For those with limited healthcare needs, a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP) or short-term health insurance plan can be more affordable. It’s essential to compare plans and understand your specific coverage needs.
How can I save money on health insurance without a job?
+
There are several strategies to save money on health insurance. First, maximize any premium subsidies you’re eligible for. Explore cost-sharing reduction plans, which can lower your out-of-pocket costs. Consider a High Deductible Health Plan if you’re in good health and have limited healthcare needs. Additionally, look into dental and vision insurance separately if these are important to you. Finally, utilize healthcare sharing ministries, which can provide coverage at a lower cost but may have restrictions.



