Fha Home Loan Insurance

The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) has been a cornerstone of the American housing market for decades, providing millions of individuals and families with opportunities to become homeowners. One of its key offerings is the FHA home loan, which is accompanied by a unique insurance feature. This insurance, often referred to as FHA mortgage insurance, is a critical aspect of the FHA loan program, designed to protect both borrowers and lenders.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of FHA home loan insurance, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and implications for prospective homeowners. By the end of this article, readers should have a thorough understanding of this essential component of the FHA loan process and its role in facilitating homeownership across the United States.
Understanding FHA Home Loan Insurance

The FHA home loan insurance program is a vital component of the Federal Housing Administration’s loan system. It operates as a mutual insurance model, wherein the agency insures mortgages issued by FHA-approved lenders, providing a safety net for both borrowers and lenders.
For borrowers, this insurance offers a pathway to homeownership with more lenient qualification criteria and competitive interest rates. Lenders, on the other hand, benefit from reduced risk associated with providing loans to borrowers who might not otherwise qualify for conventional loans.
The Mechanics of FHA Insurance
The FHA’s insurance mechanism is two-fold, involving both an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) and an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP). The UFMIP is typically paid at closing and is calculated as a percentage of the loan amount. The MIP, on the other hand, is paid annually and is typically included in the monthly mortgage payment.
The specific rates for these premiums can vary based on factors such as the loan term, loan-to-value ratio, and the borrower's credit score. Generally, the higher the loan-to-value ratio, the higher the insurance premiums will be. Additionally, borrowers with lower credit scores may be required to pay higher premiums to compensate for the increased risk associated with their loan.
| Loan Term | UFMIP Rate | Annual MIP Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 15-Year Fixed | 1.75% of the loan amount | 0.45% of the loan amount |
| 30-Year Fixed | 1.75% of the loan amount | 0.85% of the loan amount |
Benefits of FHA Loan Insurance

The FHA’s insurance program offers a range of benefits that contribute to its popularity among prospective homeowners.
Lower Down Payment Requirements
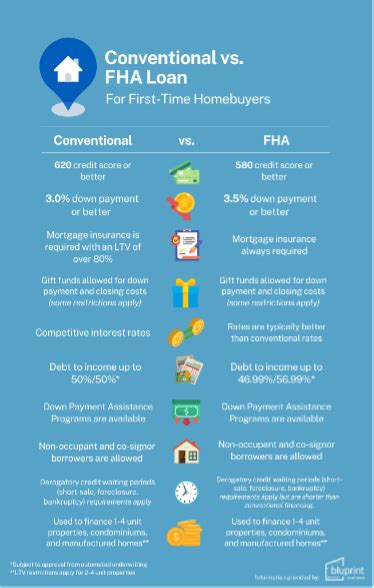
One of the most attractive features of FHA loans is the low down payment requirement. While conventional loans often require a down payment of 20% or more, FHA loans can be approved with as little as 3.5% down. This significantly lowers the barrier to entry for many first-time homebuyers, allowing them to enter the housing market sooner.
Flexible Credit Requirements
FHA loans are known for their flexible credit requirements. While borrowers must meet certain credit score thresholds, the minimum scores are generally lower than those required for conventional loans. Additionally, the FHA considers a broader range of credit factors, including timely payments on rent, utilities, and other bills, which can help borrowers with limited credit histories.
Competitive Interest Rates
FHA loans often come with competitive interest rates, which can save borrowers thousands of dollars over the life of their loan. These rates are typically lower than those offered on conventional loans, making FHA loans an attractive option for those seeking the best possible financing terms.
Reduced Risk for Lenders
For lenders, the FHA’s insurance program significantly reduces the risk associated with providing loans to borrowers who might not meet the stringent requirements of conventional loans. This risk reduction encourages lenders to offer FHA loans, which in turn expands the pool of potential borrowers and fosters a more robust housing market.
Implications and Considerations
While FHA loan insurance offers numerous benefits, there are also some considerations and implications to be aware of.
Mortgage Insurance Premiums
The upfront and annual mortgage insurance premiums can add significant costs to the overall loan. While these premiums can be rolled into the loan amount, they increase the overall cost of borrowing. It’s important for borrowers to understand the total cost of their loan, including these insurance premiums, to make an informed decision.
Limited Loan Limits
FHA loans have loan limits that vary by location. In high-cost areas, these limits may not be sufficient to cover the full cost of a home. Borrowers should be aware of these limits and consider other loan options if they are purchasing a property that exceeds the FHA loan limit in their area.
Property Requirements
Properties purchased with an FHA loan must meet certain standards, known as the FHA Minimum Property Requirements. These standards ensure that the property is safe, secure, and structurally sound. Borrowers should be prepared to make necessary repairs or improvements to the property to meet these requirements.
Future Implications and Industry Insights
The FHA’s home loan insurance program has been a vital part of the housing market for decades, and its role is likely to continue into the future. As the housing market evolves, the FHA will likely adapt its insurance policies and requirements to meet the changing needs of borrowers and lenders.
One potential area of focus for the FHA is the continued refinement of its risk assessment models. By improving its ability to accurately assess risk, the FHA can better protect borrowers and lenders while also ensuring the long-term viability of the FHA loan program. This could involve updating credit scoring models, refining loan-to-value ratios, and improving the overall efficiency of the loan underwriting process.
Additionally, the FHA may explore ways to further streamline the loan process, making it more accessible and user-friendly for borrowers. This could include digitalizing more aspects of the loan application and approval process, reducing paperwork, and providing clearer guidelines for borrowers and lenders alike.
As the housing market continues to evolve, the FHA's role as a facilitator of homeownership for a broad range of borrowers will remain critical. By adapting to changing market conditions and borrower needs, the FHA can continue to provide valuable opportunities for individuals and families to achieve the American dream of homeownership.
How do FHA loan insurance premiums compare to those of conventional loans?
+FHA loan insurance premiums are generally higher than those of conventional loans. This is because FHA loans are designed to provide access to homeownership for a broader range of borrowers, including those with lower credit scores or limited down payment funds. The higher premiums compensate for the increased risk associated with these borrowers.
Can FHA loan insurance premiums be waived or reduced under certain circumstances?
+In some cases, FHA loan insurance premiums can be reduced or waived. For example, if a borrower makes a down payment of 10% or more, the annual mortgage insurance premium may be reduced. Additionally, borrowers who have maintained their FHA loan in good standing for five years may be eligible for the cancellation of their annual MIP.
What happens if I sell my home before the FHA loan insurance is cancelled?
+If you sell your home before the FHA loan insurance is cancelled, you may be able to transfer the insurance to your new FHA loan, assuming you meet certain criteria. Alternatively, if you have built up sufficient equity in your home, you may be able to refinance into a conventional loan, which does not require mortgage insurance.