Federal Deposit Insurance Limit
In the realm of finance and banking, understanding the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) and its deposit insurance limit is crucial for safeguarding your hard-earned money. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of the FDIC deposit insurance limit, its history, how it works, and its significance in ensuring the stability and security of the American banking system.
A Brief History of FDIC Deposit Insurance

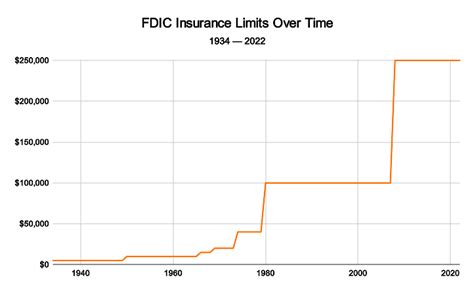
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation was established in the aftermath of the Great Depression, a period marked by widespread bank failures and economic turmoil. The primary objective of the FDIC was to restore confidence in the banking system and protect depositors’ funds. Since its inception in 1933, the FDIC has played a pivotal role in maintaining financial stability and preventing bank runs.
The initial deposit insurance limit was set at $2,500 per depositor, a substantial increase from the previous limit of $2,500 per bank. This move aimed to provide greater security to depositors and encourage them to keep their funds in insured banks. Over the years, the FDIC deposit insurance limit has been periodically adjusted to keep pace with inflation and changing economic conditions.
How Does FDIC Deposit Insurance Work?

The FDIC insures deposits held at member banks, which are institutions that have chosen to participate in the insurance program. It’s important to note that not all banks are FDIC-insured, so it’s crucial to verify the insurance status of your bank before opening an account.
FDIC insurance covers various types of deposits, including checking accounts, savings accounts, money market accounts, and certificates of deposit (CDs). The coverage extends to both interest and principal amounts, providing comprehensive protection for depositors.
One key aspect of FDIC insurance is the concept of ownership categories. Deposits are insured separately for each ownership category, ensuring that individuals with multiple accounts or different ownership structures can maximize their coverage. Some common ownership categories include:
- Single Accounts: Deposits held in an individual's name, such as a personal checking or savings account.
- Joint Accounts: Accounts owned by two or more individuals, where each owner's share is insured separately.
- Revocable Trusts: Accounts held in trust for beneficiaries, with the trustee having control over the funds.
- Corporations and Partnerships: Business accounts are insured separately from personal accounts, providing protection for business funds.
- Employee Benefit Plans: Retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, are insured separately to safeguard retirement savings.
The FDIC deposit insurance limit currently stands at $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, and per ownership category. This means that an individual with deposits in different ownership categories or at multiple FDIC-insured banks can potentially have millions of dollars insured.
It's worth mentioning that the FDIC insurance coverage extends to both domestic and foreign-related banks operating in the United States. However, it's important to note that the insurance limit applies separately for each country's banking system. For example, if an individual has deposits in both a U.S. bank and a Canadian bank, the $250,000 limit would apply to each institution separately.
The Significance of FDIC Deposit Insurance
The FDIC deposit insurance limit serves as a crucial safeguard for depositors, providing peace of mind and ensuring that their funds are protected in the event of a bank failure. Here’s a closer look at the significance of FDIC insurance:
Financial Stability and Confidence
The existence of FDIC insurance has been instrumental in maintaining financial stability and fostering confidence in the banking system. By providing a safety net for depositors, the FDIC has prevented bank runs and mitigated the impact of economic downturns on the banking industry.
The knowledge that their deposits are insured encourages individuals and businesses to keep their funds in FDIC-insured banks, promoting a stable and secure financial environment. This, in turn, benefits the overall economy by facilitating lending and investment activities.
Protection for Depositors
FDIC insurance offers invaluable protection to depositors, ensuring that their savings are secure. In the unlikely event of a bank failure, the FDIC steps in to guarantee the repayment of insured deposits up to the specified limit. This protection provides depositors with the assurance that their hard-earned money is safe, even in the face of financial turmoil.
Risk Mitigation for Banks
The FDIC deposit insurance program also benefits banks by mitigating the risk of depositor runs. By providing insurance coverage, the FDIC reduces the likelihood of widespread panic and mass withdrawals, allowing banks to focus on their core operations and maintain financial stability.
Coverage for Various Deposit Types
FDIC insurance covers a wide range of deposit types, ensuring that individuals and businesses can protect their funds regardless of the account type. Whether it’s a basic checking account or a long-term certificate of deposit, the FDIC provides comprehensive coverage, giving depositors the flexibility to choose the financial products that best suit their needs.
FDIC Deposit Insurance Limit: Key Considerations
While the FDIC deposit insurance limit offers significant protection, there are a few key considerations to keep in mind:
Excess Deposits
Deposits that exceed the insurance limit are not covered by the FDIC. It’s important for depositors to be aware of their total deposit amounts and ensure that they stay within the insured limit. Banks are required to notify customers when their deposits exceed the insurance limit, helping individuals manage their accounts accordingly.
Multiple Banks and Ownership Categories
As mentioned earlier, the FDIC insurance limit applies separately for each insured bank and ownership category. By spreading deposits across multiple banks or utilizing different ownership structures, individuals can maximize their insurance coverage. This strategy ensures that depositors can protect their funds effectively and mitigate the risk of losses.
Uninsured Deposit Products
It’s essential to understand that certain deposit products, such as investments in stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, are not insured by the FDIC. These products carry inherent risks and are not covered by deposit insurance. Depositors should carefully evaluate their investment options and consider the level of risk they are comfortable with.
FDIC’s Financial Stability
The FDIC maintains a robust financial reserve to ensure it can meet its insurance obligations. The Deposit Insurance Fund (DIF) is funded by premiums paid by member banks and is designed to provide a cushion in the event of widespread bank failures. The FDIC’s financial stability is a key factor in maintaining confidence in the deposit insurance program.
The Future of FDIC Deposit Insurance

The FDIC deposit insurance limit has proven to be a resilient and effective tool for protecting depositors and maintaining financial stability. As the economic landscape evolves, the FDIC remains vigilant in adapting its policies and procedures to address emerging challenges.
In recent years, the FDIC has taken steps to enhance its risk management capabilities and strengthen its oversight of the banking industry. By closely monitoring bank activities and implementing robust regulatory measures, the FDIC aims to prevent systemic risks and ensure the continued stability of the financial system.
Looking ahead, the FDIC is likely to continue its proactive approach, adapting its policies to meet the changing needs of depositors and the banking industry. As the economic environment evolves, the FDIC will play a vital role in safeguarding the interests of depositors and promoting a resilient banking system.
Conclusion
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and its deposit insurance limit have been instrumental in fostering confidence and stability in the American banking system. By understanding the FDIC’s role and the protection it provides, depositors can make informed decisions about their financial well-being.
As we navigate the complexities of the financial world, the FDIC stands as a trusted guardian, ensuring that depositors' funds are secure and accessible. With its robust insurance program and commitment to financial stability, the FDIC remains a cornerstone of the U.S. banking system, providing peace of mind to millions of Americans.
How often is the FDIC deposit insurance limit adjusted?
+The FDIC deposit insurance limit is periodically reviewed and adjusted based on economic conditions and inflation. The FDIC Board of Directors has the authority to make these adjustments to ensure the limit remains adequate for protecting depositors’ funds.
Are all banks FDIC-insured?
+No, not all banks are FDIC-insured. Banks must choose to participate in the FDIC insurance program and meet the requirements set by the FDIC. It’s important to verify the insurance status of your bank before opening an account.
Can I maximize my FDIC insurance coverage by spreading my deposits across multiple banks?
+Yes, you can maximize your FDIC insurance coverage by spreading your deposits across different FDIC-insured banks. The insurance limit applies separately for each insured bank, allowing you to protect your funds effectively.
Are there any deposit products that are not insured by the FDIC?
+Yes, certain deposit products, such as investments in stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, are not insured by the FDIC. These products carry market risks and are not covered by deposit insurance. It’s important to understand the risks associated with these investments.
How does the FDIC handle bank failures and guarantee insured deposits?
+When a bank fails, the FDIC steps in to resolve the situation and protect insured depositors. The FDIC may arrange for another bank to assume the failed bank’s deposits, or it may directly pay insured depositors their insured funds. The process is designed to minimize disruption and ensure depositors receive their insured amounts promptly.



