Does Insurance Cover Covid Testing
In the wake of the global COVID-19 pandemic, one of the most frequently asked questions regarding healthcare and financial implications has been, "Does insurance cover COVID-19 testing?" This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on this important topic, providing an in-depth analysis of insurance coverage for COVID-19 testing and related services. With the ongoing nature of the pandemic, staying informed about insurance coverage is crucial for individuals and families.
Understanding Insurance Coverage for COVID-19 Testing
The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted many healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies to take unprecedented steps to ensure widespread access to testing and treatment. Understanding the nuances of insurance coverage for COVID-19 testing is essential for navigating the healthcare system effectively.
Health Insurance and COVID-19 Testing
Most major health insurance plans in the United States now cover COVID-19 testing at no cost to the patient. This includes both diagnostic tests, which detect an active infection, and antibody tests, which detect past infection. The coverage extends to various testing scenarios, such as drive-through testing sites, doctor’s offices, and emergency rooms.
Insurance companies have adopted this approach in response to the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act, which was signed into law in March 2020. The CARES Act mandates that health plans cover COVID-19 testing without cost-sharing, meaning patients do not have to pay any deductibles, copayments, or coinsurance for the tests.
| Insurance Provider | COVID-19 Testing Coverage |
|---|---|
| Aetna | Covers diagnostic and antibody tests with no cost-sharing |
| Blue Cross Blue Shield | Offers coverage for FDA-approved tests with no out-of-pocket expenses |
| Cigna | Provides coverage for COVID-19 tests as preventive care, waiving any patient responsibility |
| UnitedHealthcare | Covers testing for members with symptoms or potential exposure, including home testing kits |

It's important to note that insurance coverage for COVID-19 testing may vary based on the specific plan and state regulations. Some plans may require a doctor's referral or have certain criteria for coverage, such as symptoms or potential exposure.
Medicare and Medicaid Coverage
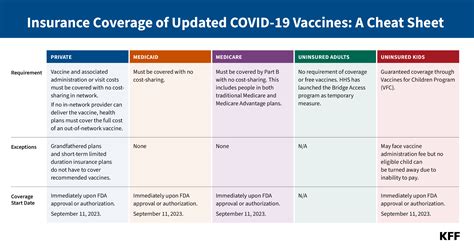
Both Medicare and Medicaid also provide coverage for COVID-19 testing. Medicare, the federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, and certain younger people with disabilities, covers diagnostic tests and antibody tests without any cost to the beneficiary. This coverage includes tests administered in a variety of settings, from doctor’s offices to drive-through testing sites.
Medicaid, a joint federal and state program that provides health coverage to eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people with disabilities, also covers COVID-19 testing. Each state's Medicaid program may have its own specific guidelines and requirements, but generally, the coverage includes diagnostic and antibody tests without cost-sharing.
Uninsured Individuals and COVID-19 Testing
For individuals without health insurance, COVID-19 testing is still accessible and, in many cases, provided at no cost. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has implemented the COVID-19 Testing Program, which ensures that uninsured individuals receive free testing for COVID-19. This program is funded through the Provider Relief Fund and is administered by various state and local public health departments.
Uninsured individuals can locate free testing sites by visiting HHS.gov, where they can find information on testing locations, eligibility criteria, and any necessary appointments or registrations.
COVID-19 Testing and Treatment: What’s Covered

While insurance coverage for COVID-19 testing is now fairly standard, the specifics of coverage for related services and treatments can be more complex. Here’s a breakdown of what’s typically covered:
Diagnostic Testing
Diagnostic tests for COVID-19, which include PCR tests and rapid antigen tests, are generally covered by insurance plans without cost-sharing. These tests are used to detect an active infection and are often recommended for individuals with symptoms or potential exposure.
Antibody Testing
Antibody tests, also known as serology tests, are used to detect past infection with COVID-19. These tests are typically covered by insurance plans, but there may be some limitations or requirements. For instance, some plans may only cover antibody testing if it’s ordered by a healthcare provider for medical necessity.
Treatment and Medical Services
Insurance coverage for COVID-19 treatment and related medical services can vary widely depending on the specific plan and the individual’s health status. Here are some general guidelines:
- Inpatient Care: If an individual requires hospitalization for COVID-19, their insurance plan will typically cover the cost of inpatient care, including hospital stays, medications, and other necessary treatments.
- Outpatient Care: Insurance plans generally cover outpatient care for COVID-19, which may include doctor visits, laboratory tests, and other services. However, the specific coverage and cost-sharing requirements can vary.
- Vaccination: COVID-19 vaccines are widely available and covered by most insurance plans without cost-sharing. Uninsured individuals can access free vaccines through various public health programs.
- Post-COVID Care: For individuals experiencing long-term effects of COVID-19, also known as long COVID, insurance coverage can vary. Some plans may cover post-COVID care as part of their standard benefits, while others may require additional documentation or have specific criteria for coverage.
Navigating Insurance Coverage for COVID-19
Understanding your insurance coverage for COVID-19 testing and related services is crucial for making informed healthcare decisions. Here are some tips to help you navigate the process:
- Check Your Plan's Coverage: Review your insurance plan's coverage details for COVID-19 testing and treatment. Most insurance providers have dedicated sections on their websites explaining their coverage policies during the pandemic.
- Contact Your Insurance Provider: If you have questions or need clarification, reach out to your insurance company's customer service department. They can provide specific information about your plan's coverage and any necessary steps for accessing testing or treatment.
- Use In-Network Providers: Whenever possible, use healthcare providers that are in your insurance plan's network. This can help minimize out-of-pocket expenses and ensure smoother claims processing.
- Understand Preauthorization: Some insurance plans may require preauthorization for certain COVID-19-related services, such as advanced treatments or specialized care. Familiarize yourself with your plan's preauthorization requirements to avoid delays in receiving necessary care.
- Keep Records: Maintain a record of all COVID-19-related tests, treatments, and services you receive. This can help with any future insurance claims or if you need to verify your coverage.
Future Implications and Access to Care
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of accessible and comprehensive healthcare coverage. As we continue to navigate the pandemic and its long-term effects, ensuring equitable access to testing, treatment, and vaccines remains a critical public health goal.
Insurance coverage for COVID-19 testing and related services has played a crucial role in facilitating widespread access to healthcare during the pandemic. While significant progress has been made, ongoing efforts are needed to address gaps in coverage and ensure that all individuals, regardless of their insurance status, can access the care they need.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, staying informed about insurance coverage and advocating for accessible healthcare will be key to overcoming the challenges presented by COVID-19 and future public health crises.
What if my insurance plan doesn’t cover COVID-19 testing or treatment?
+If your insurance plan does not cover COVID-19 testing or treatment, you may still have options. Contact your insurance provider to understand the specific reasons for the lack of coverage. In some cases, you may be able to appeal the decision or explore alternative coverage options. Additionally, check with your state’s public health department for information on free testing and treatment programs.
How can I find free COVID-19 testing if I don’t have insurance?
+If you’re uninsured, you can access free COVID-19 testing through various public health programs. Visit the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) website at HHS.gov to find testing locations near you. These sites often offer free testing to uninsured individuals, ensuring that cost is not a barrier to accessing necessary healthcare.
Are there any additional costs associated with COVID-19 testing or treatment?
+While insurance plans typically cover COVID-19 testing without cost-sharing, there may be additional costs associated with treatment, especially if you require hospitalization or specialized care. These costs can vary based on your insurance plan and the specific services received. It’s important to understand your plan’s coverage limits and any potential out-of-pocket expenses.
Can I get a COVID-19 test without a doctor’s referral or prescription?
+Yes, you can typically access COVID-19 testing without a doctor’s referral or prescription. Many testing sites, including drive-through locations and community health centers, offer testing to individuals with symptoms or potential exposure. However, some insurance plans may require a doctor’s referral for coverage, so it’s always a good idea to check with your insurance provider beforehand.