Coolant Leak

A coolant leak is a common issue faced by vehicle owners, often causing concern and potential damage to the engine. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of coolant leaks, exploring their causes, detection methods, and effective solutions. By understanding the intricacies of this problem, we can ensure timely action and maintain the health of our vehicles.
Understanding Coolant Leaks: Causes and Symptoms

Coolant, also known as antifreeze, plays a vital role in regulating the temperature of an engine. It prevents freezing in cold climates and overheating in hot conditions. However, when a leak occurs, it can lead to significant engine issues if left unaddressed.
Common Causes of Coolant Leaks
- Worn or Damaged Hoses: Hoses that carry coolant can deteriorate over time, leading to cracks or tears. This is a frequent cause of leaks, especially in older vehicles.
- Failed Gasket or Seals: Gasket failure, often due to age or excessive heat, can result in coolant escaping from the engine block or cylinder head.
- Radiator Issues: A damaged or corroded radiator can develop leaks, allowing coolant to escape. This is a common issue in vehicles exposed to extreme weather conditions.
- Bad Water Pump: A faulty water pump can cause leaks at the pump’s shaft seal or impeller.
- Hose Clamps: Loose or damaged hose clamps can lead to coolant leaks, especially if they are not properly tightened or corroded.
Identifying Coolant Leaks: Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs of a coolant leak is crucial for timely intervention. Here are some indicators to watch out for:
- Low Coolant Level: Regularly check your coolant reservoir. If the level drops consistently, it could indicate a leak.
- Visible Leaks: Keep an eye out for puddles or stains under your vehicle. Coolant often leaves a distinctive green, orange, or yellow trail.
- Sweet Smell: Coolant has a sweet odor, so a strong, sweet scent near the engine could indicate a leak.
- Overheating: A coolant leak can lead to engine overheating, as the cooling system is compromised. If your vehicle’s temperature gauge spikes, it may be a sign of a
A coolant leak is a common issue faced by vehicle owners, but it can often be a source of concern and confusion. Understanding the causes, signs, and potential consequences of a coolant leak is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of your vehicle. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of coolant leaks, offering expert insights and practical advice to help you navigate this automotive challenge effectively.
Understanding Coolant Leaks: Causes and Signs
Coolant, also known as antifreeze, plays a vital role in regulating the temperature of your vehicle’s engine. It prevents the engine from overheating in hot weather and freezing in cold conditions. A coolant leak can occur due to various reasons, and identifying the root cause is essential for an effective repair.
Common Causes of Coolant Leaks
- Hose or Pipe Damage: Over time, coolant hoses and pipes can become brittle, cracked, or worn out due to heat, pressure, or physical damage. This can lead to leaks, especially at the connection points or along the hose’s length.
- Radiator Issues: The radiator is a key component in the cooling system, and any damage or corrosion can result in leaks. Common issues include cracked radiator tanks, damaged fins, or failed radiator hoses.
- Water Pump Failure: The water pump is responsible for circulating coolant through the engine. A failed water pump can cause coolant leaks, often accompanied by other symptoms like a whining noise or overheating.
- Gasket or Seal Failure: Various gaskets and seals are used in the cooling system, including the head gasket, intake manifold gasket, and thermostat housing seal. When these components fail, they can allow coolant to escape.
- Rust or Corrosion: In older vehicles or those exposed to harsh environmental conditions, rust and corrosion can weaken components and cause leaks. This is particularly common in the radiator, heater core, and coolant reservoirs.
Signs of a Coolant Leak
Recognizing the signs of a coolant leak is crucial for early detection and repair. Here are some common indicators:
- Low Coolant Levels: Check your coolant reservoir regularly. If the level is consistently low, it could indicate a leak.
- Visible Fluid Leaks: Pay attention to any puddles or stains under your vehicle, especially after parking. Coolant has a distinct sweet smell and often leaves a greenish or reddish residue.
- Overheating Engine: A coolant leak can lead to insufficient coolant circulation, causing the engine to overheat. This is often accompanied by the temperature gauge rising or the “Check Engine” light illuminating.
- White Smoke from Exhaust: If coolant enters the combustion chamber due to a leak, it can burn and produce white smoke from the exhaust.
- Sweet Odor Inside the Vehicle: A strong, sweet odor inside the car, especially when the engine is running, can indicate a coolant leak into the cabin.
The Impact of Untreated Coolant Leaks
Ignoring a coolant leak can have serious consequences for your vehicle’s performance and longevity. Here’s a closer look at the potential issues:
Engine Overheating
The most immediate and noticeable impact of a coolant leak is engine overheating. Without sufficient coolant, the engine can quickly reach dangerous temperatures. This can lead to:
- Warped or Cracked Engine Components: Excessive heat can cause warping or cracking in various engine parts, including the cylinder head, block, or even the radiator itself.
- Head Gasket Failure: The head gasket seals the combustion chamber and prevents coolant and oil from mixing. Overheating can cause the head gasket to fail, leading to further coolant leaks and engine damage.
- Seized Engine: In severe cases, an overheated engine can seize, rendering it inoperable and requiring a complete overhaul or replacement.
Coolant Contamination
If a coolant leak is left untreated, the coolant can become contaminated with oil, debris, or other foreign substances. This contamination can lead to:
- Cooling System Clogging: Contaminants can accumulate and clog the cooling system, reducing its efficiency and causing further overheating.
- Rust and Corrosion: Contaminated coolant can accelerate rust and corrosion within the cooling system, weakening components and causing more leaks.
- Poor Heat Transfer: Contaminants can interfere with the coolant’s ability to absorb and dissipate heat effectively, further exacerbating overheating issues.
Long-Term Engine Damage
Over time, untreated coolant leaks can have severe consequences for the engine’s overall health. Here are some potential long-term issues:
- Piston Scuffing: Inadequate coolant circulation can cause the engine’s pistons to scuff against the cylinder walls, leading to reduced compression and potential engine failure.
- Cylinder Head Warping: Prolonged overheating can cause the cylinder head to warp, distorting the combustion chamber and affecting engine performance.
- Increased Wear and Tear: The engine’s components, including bearings, seals, and gaskets, can experience increased wear due to inadequate cooling, leading to premature failure.
Expert Tips for Coolant Leak Diagnosis and Repair
Dealing with a coolant leak promptly and effectively is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s health. Here are some expert tips to guide you through the process:
Diagnosing the Leak
When you suspect a coolant leak, start by visually inspecting the engine bay and undercarriage for any visible signs of leakage. Check the hoses, radiator, and other components for cracks, corrosion, or damage. Pay attention to any puddles or stains.
If the leak is not immediately apparent, you can perform a pressure test or use a dye additive to help identify the source. A pressure test involves introducing pressure into the cooling system to locate leaks, while a dye additive can help highlight leaks when viewed under a UV light.
Locating the Source
Once you’ve identified a potential leak, it’s crucial to pinpoint the exact source. This will guide your repair efforts and prevent further issues. Common leak sources include:
- Radiator: Inspect the radiator for cracks, holes, or damaged fins. Replace the radiator if necessary.
- Hoses and Clamps: Check hoses for cracks, splits, or leaks at the connection points. Ensure clamps are secure and replace any damaged hoses.
- Water Pump: A failed water pump can cause coolant leaks. Inspect the pump for leaks and replace it if needed.
- Gaskets and Seals: Leaks can occur at various gaskets and seals, including the head gasket, intake manifold gasket, and thermostat housing seal. Replace these components as necessary.
- Heater Core: The heater core, located behind the dashboard, can also develop leaks. If this is the case, you may need to remove the dashboard to access and repair or replace the heater core.
Repairing the Leak
After locating the source of the leak, the next step is to repair it. Here are some common repair methods:
- Hose Replacement: If a hose is damaged, replace it with a new hose of the correct size and type. Ensure proper routing and secure all clamps.
- Radiator Repair: Depending on the extent of the damage, you may be able to repair a cracked radiator with a radiator repair kit. However, for more severe issues, a complete radiator replacement may be necessary.
- Water Pump Replacement: A failed water pump should be replaced with a new, compatible unit. Ensure proper installation and bleeding of the cooling system.
- Gasket and Seal Replacement: Replace faulty gaskets and seals with new ones, ensuring a proper fit and seal. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for gasket replacement.
- Heater Core Repair: Heater core repairs can be complex and may require professional assistance. In some cases, a complete heater core replacement may be necessary.
Maintaining the Cooling System
Regular maintenance is key to preventing future coolant leaks and ensuring the longevity of your vehicle’s cooling system. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Coolant Flush and Replacement: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for coolant flush intervals. Flushing the cooling system helps remove contaminants and prevent corrosion.
- Hose Inspection: Inspect coolant hoses regularly for signs of wear, cracks, or leaks. Replace hoses that show signs of damage or aging.
- Radiator and Water Pump Maintenance: Keep the radiator and water pump clean and free of debris. Ensure proper belt tension and water pump operation.
- Use of Quality Coolant: Use high-quality coolant that is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Follow the recommended mix ratio for optimal performance.
- Monitor Coolant Levels: Regularly check your coolant reservoir levels and top off as needed. If the level drops significantly, investigate for leaks.
The Future of Coolant Leak Prevention
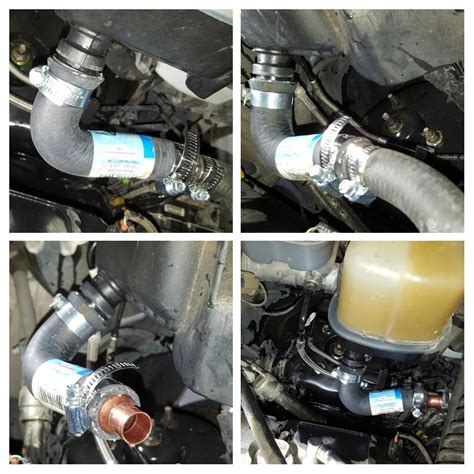

Advancements in automotive technology are constantly shaping the way we approach coolant leak prevention and repair. Here’s a glimpse into the future:
Smart Monitoring Systems
Modern vehicles are equipped with advanced monitoring systems that can detect coolant leaks and alert drivers. These systems use sensors and algorithms to continuously monitor the cooling system, providing real-time data and early leak detection.
For example, some vehicles now have coolant level sensors that can detect even small leaks and trigger a warning on the dashboard. This allows drivers to address the issue promptly, preventing further damage.
Improved Coolant Formulations
Research and development in coolant formulations are focused on creating more durable and leak-resistant coolants. These new coolants are designed to provide better corrosion protection, reduce the risk of leaks, and extend the lifespan of cooling system components.
Additionally, manufacturers are exploring the use of advanced materials and coatings to enhance the durability of hoses, radiators, and other cooling system components, further reducing the likelihood of leaks.
Autonomous Repair Systems
The concept of autonomous repair systems is gaining traction in the automotive industry. These systems aim to identify and repair minor coolant leaks automatically, without the need for human intervention.
Imagine a vehicle equipped with a self-repairing cooling system that can detect a leak, locate the source, and apply a sealant or repair patch to the affected area. While this technology is still in its early stages, it holds great promise for the future of coolant leak prevention and repair.
How often should I check my coolant levels?
+It’s recommended to check your coolant levels at least once a month, or whenever you notice the coolant reservoir level dropping. Regular checks can help you identify potential leaks early on.
Can I drive with a coolant leak?
+It’s not advisable to drive with a coolant leak, as it can lead to engine overheating and potential damage. If you suspect a leak, have it inspected and repaired as soon as possible.
What is the average cost of repairing a coolant leak?
+The cost of repairing a coolant leak can vary widely depending on the source and extent of the leak. Simple hose replacements may cost a few hundred dollars, while more complex repairs like radiator or water pump replacements can range from 500 to 1,500 or more.