Comprehensive On Insurance

The Evolution and Impact of Insurance: A Comprehensive Guide
Insurance is a financial tool that has revolutionized the way individuals and businesses manage risk and uncertainty. With its complex history and far-reaching implications, insurance has become an integral part of our modern world. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of insurance, exploring its evolution, various types, and the profound impact it has on our lives and the global economy.
The Historical Roots and Evolution of Insurance

The concept of insurance can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where early forms of risk sharing and protection were practiced. However, it was during the medieval period that insurance as we know it began to take shape. The maritime trade of the 14th century witnessed the birth of marine insurance, as traders sought to protect their cargo and investments against the perils of sea voyages.
The evolution of insurance accelerated during the 17th and 18th centuries. The establishment of Lloyd's of London in 1688 marked a significant milestone, as it became a hub for insurance and reinsurance transactions. This period saw the emergence of various types of insurance, including fire insurance, life insurance, and accident insurance. The Industrial Revolution further propelled the growth of insurance, as businesses sought to mitigate the risks associated with industrial operations and expanding global trade.
Key Milestones in Insurance History:
- 1752: The Equitable Life Assurance Society became the first life insurance company in England, offering policies to protect families against the financial impact of premature deaths.
- 1837: The first workers' compensation law was enacted in Prussia, setting a precedent for social insurance and protecting laborers from work-related injuries and illnesses.
- 1850s: The rise of mutual insurance companies, owned and operated by policyholders, provided an alternative to traditional insurance models.
- 1908: Henry Ford introduced automobile insurance, acknowledging the risks associated with the growing popularity of cars.
- 1935: The Social Security Act in the United States established a comprehensive social insurance program, providing retirement, disability, and survivor benefits.
As societies became more complex and interconnected, insurance evolved to meet the diverse needs of individuals and organizations. Today, insurance has become a multifaceted industry, offering protection against a wide range of risks, from natural disasters to healthcare costs and cyber threats.
Understanding the Types of Insurance
Insurance encompasses a vast array of products and services, each designed to address specific risks and provide tailored protection. Let's explore some of the key types of insurance and their significance:
1. Life Insurance
Life insurance is a cornerstone of financial planning, providing peace of mind and financial security to individuals and their loved ones. It offers a lump-sum payment, known as a death benefit, to beneficiaries upon the insured individual's passing. Life insurance policies can be tailored to meet various needs, including income replacement, debt repayment, and funding for future goals such as education or retirement.
| Life Insurance Types | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Term Life Insurance | Affordable coverage for a specified term, typically 10-30 years. Ideal for covering temporary needs like mortgage payments or providing income for dependents. |
| Whole Life Insurance | Provides lifetime coverage with a fixed premium. Builds cash value over time, offering a savings component and potential tax benefits. |
| Universal Life Insurance | Flexible coverage with adjustable premiums and death benefits. Allows policyholders to control premium payments and provides access to cash value. |
| Group Life Insurance | Often offered as an employee benefit, providing coverage to a group of individuals, such as employees of a company. Typically more affordable than individual policies. |

2. Health Insurance
Health insurance is essential for protecting individuals and families from the potentially devastating financial consequences of medical expenses. It covers a wide range of healthcare services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and preventive care. Health insurance plans vary in terms of coverage, cost-sharing mechanisms, and provider networks.
The rise of healthcare costs and the complexity of medical treatments have made health insurance an increasingly critical component of financial planning. Many countries have implemented universal healthcare systems, ensuring access to essential medical services for all citizens. In the United States, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) has expanded access to health insurance and introduced reforms to improve affordability and coverage.
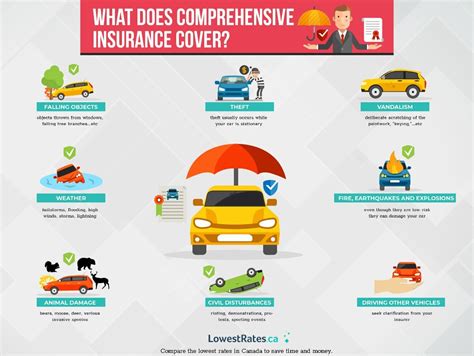
3. Property and Casualty Insurance
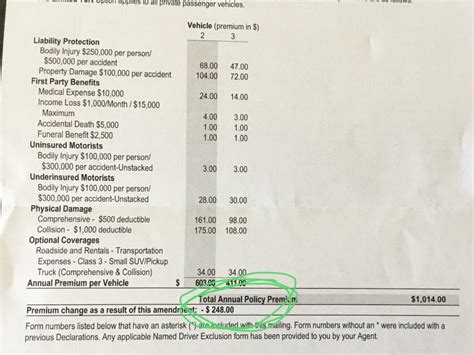
Property and casualty insurance, also known as general insurance, protects individuals and businesses against various risks associated with property damage, liability, and personal injuries. This category includes auto insurance, homeowners' insurance, renters' insurance, and commercial property insurance.
| Property and Casualty Insurance Types | Key Coverage |
|---|---|
| Auto Insurance | Covers damage to vehicles, liability for injuries or property damage caused by the insured, and optional coverage for medical expenses and uninsured/underinsured motorists. |
| Homeowners' Insurance | Provides protection for the structure of a home, personal belongings, and liability coverage for injuries that occur on the insured property. Coverage extends to additional living expenses if the home becomes uninhabitable. |
| Renters' Insurance | Covers personal belongings and liability for renters, protecting against losses due to theft, fire, or other covered perils. |
| Commercial Property Insurance | Protects businesses against property damage, business interruption, and liability claims. Coverage is tailored to the specific needs of the business. |
4. Business Insurance
Business insurance is vital for entrepreneurs and companies of all sizes. It provides protection against a wide range of risks, including property damage, liability claims, worker injuries, and business interruption. Business insurance policies can be customized to meet the unique needs of different industries and businesses.
| Business Insurance Types | Key Coverage |
|---|---|
| General Liability Insurance | Covers bodily injury, property damage, and personal and advertising injury claims arising from business operations. |
| Professional Liability Insurance (Errors and Omissions) | Protects professionals, such as consultants, accountants, and lawyers, against claims of negligence or errors in their work. |
| Workers' Compensation Insurance | Provides coverage for work-related injuries and illnesses, ensuring medical care and wage replacement for injured employees. |
| Cyber Insurance | Protects businesses against the financial impact of cyberattacks, data breaches, and privacy violations. |
The Impact of Insurance on Society and the Economy
Insurance plays a pivotal role in shaping society and driving economic growth. Its influence extends far beyond the protection it provides to individuals and businesses. Here are some key ways in which insurance impacts our world:
1. Economic Stability and Growth
Insurance acts as a stabilizing force in the economy by mitigating risks and providing a safety net for individuals and businesses. It encourages investment and entrepreneurship by reducing the fear of financial ruin. For example, business owners can take calculated risks, knowing that insurance will protect them from potential losses.
Insurance also plays a crucial role in fostering economic growth by promoting investment and innovation. It provides access to capital for businesses, enabling them to expand, hire more employees, and drive economic development. Additionally, insurance companies invest in various sectors, contributing to the overall financial health of the economy.
2. Social Welfare and Safety Nets
Insurance has become an essential component of social welfare systems worldwide. Health insurance, for instance, ensures that individuals have access to necessary medical care, regardless of their financial circumstances. This promotes a healthier population and reduces the societal burden of untreated illnesses.
Social insurance programs, such as those covering retirement, disability, and unemployment, provide a safety net for individuals during challenging times. These programs offer financial support and peace of mind, allowing individuals to plan for their future with confidence.
3. Risk Management and Mitigation
Insurance is a powerful tool for managing and mitigating risks. By transferring the financial burden of potential losses to insurance companies, individuals and businesses can focus on their core activities and avoid catastrophic financial consequences. This risk management approach enables organizations to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
For example, in the construction industry, contractors can secure builders' risk insurance to protect against losses due to property damage, theft, or natural disasters during the construction process. This insurance allows them to manage risks and complete projects with confidence.
4. Disaster Recovery and Resilience
Insurance plays a vital role in disaster recovery and building community resilience. When natural disasters strike, insurance provides a financial safety net for individuals and businesses, helping them rebuild and recover. Property insurance, for instance, covers damages caused by hurricanes, floods, earthquakes, and other catastrophic events.
Insurance companies also contribute to disaster response efforts by quickly assessing and processing claims, providing much-needed financial support to affected communities. This timely assistance enables individuals and businesses to get back on their feet and resume their normal lives and operations.
The Future of Insurance: Trends and Innovations

The insurance industry is continuously evolving to meet the changing needs and risks of society. Here are some key trends and innovations shaping the future of insurance:
1. Digital Transformation
The digital revolution has transformed the insurance industry, making it more efficient, accessible, and customer-centric. Insurtech, a combination of insurance and technology, has emerged as a driving force, leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics to enhance the customer experience and streamline operations.
Digital platforms and mobile apps now allow individuals to compare insurance policies, purchase coverage, and manage their policies seamlessly. Insurance companies are also using data-driven insights to personalize coverage and pricing, offering tailored solutions to meet the unique needs of policyholders.
2. Parametric Insurance
Parametric insurance is an innovative approach that provides rapid payouts based on predefined parameters, such as weather conditions or earthquake intensity. This type of insurance offers a faster and more efficient claims process, particularly in the wake of natural disasters. By leveraging advanced technology and data, parametric insurance can quickly assess losses and provide financial support to policyholders.
3. Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance
Telematics and usage-based insurance are transforming the auto insurance industry. These technologies use sensors and GPS data to monitor driving behavior and assess risk more accurately. By rewarding safe driving habits, usage-based insurance offers policyholders the opportunity to reduce their premiums.
4. Microinsurance
Microinsurance is gaining traction as a way to provide affordable insurance coverage to low-income individuals and communities. This approach offers small, targeted insurance policies that are accessible and tailored to the specific needs of vulnerable populations. Microinsurance can help bridge the insurance gap and protect those who may not have access to traditional insurance products.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Insurance
Insurance is a complex and ever-evolving industry, offering a myriad of products and services to protect individuals, businesses, and communities. From its ancient origins to the digital age, insurance has adapted to meet the changing needs of society. By understanding the types of insurance, their impact, and the latest trends, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions to safeguard their financial well-being.
As we navigate the complexities of modern life, insurance provides a crucial layer of protection, allowing us to embrace opportunities with confidence and peace of mind. Whether it's protecting our health, our homes, or our businesses, insurance is an indispensable tool for managing risk and building a secure future.
What is the purpose of insurance?
+Insurance serves the purpose of providing financial protection and peace of mind by transferring the risk of potential losses to insurance companies. It allows individuals and businesses to manage and mitigate risks, ensuring they can recover from unforeseen events and continue their normal lives or operations.
How does insurance benefit the economy?
+Insurance plays a vital role in economic stability and growth. It encourages investment, entrepreneurship, and innovation by mitigating risks. Additionally, insurance companies contribute to the economy through investments and the provision of financial safety nets for individuals and businesses.
What are some emerging trends in the insurance industry?
+Emerging trends in insurance include digital transformation, with insurtech companies leveraging technology to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. Parametric insurance, telematics, and usage-based insurance are also gaining traction, offering innovative approaches to risk assessment and claims processing.