Banks Insured

Understanding the safety and security of one's finances is a crucial aspect of personal finance management. When it comes to banking, one of the primary concerns for individuals is the insurance and protection of their deposits. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) in the United States, and similar organizations in other countries, play a vital role in safeguarding bank customers' money.
This article aims to delve into the world of bank insurance, exploring the ins and outs of how it works, the benefits it provides, and the peace of mind it offers to millions of people worldwide. By examining the mechanisms and limits of deposit insurance, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of this essential financial safeguard.
The Importance of Bank Insurance

In the complex world of finance, bank insurance serves as a critical safety net for individuals and businesses alike. The primary objective of this insurance is to protect depositors from the potential risks associated with banking institutions. Throughout history, bank failures and financial crises have highlighted the need for a robust system to protect the hard-earned money of customers.
The concept of deposit insurance emerged as a response to the Great Depression of the 1930s, a period marked by widespread bank failures and significant economic turmoil. Recognizing the need to restore public confidence in the banking system, the FDIC was established in the United States to insure bank deposits and provide a layer of protection for depositors.
Since its inception, deposit insurance has played a pivotal role in stabilizing the financial system and protecting the interests of consumers. By offering insurance on deposits, it encourages people to keep their money in banks, fostering economic growth and financial stability. Moreover, it ensures that even in the event of a bank's failure, depositors can retrieve their funds, providing a vital safety net for individuals and small businesses.
How Bank Insurance Works

Bank insurance, or deposit insurance, operates as a government-backed program designed to protect bank customers’ deposits. In the United States, the FDIC stands as the primary regulator and insurer of deposits, ensuring the safety and soundness of the nation’s banking system.
FDIC Insurance Coverage
The FDIC insures deposits held in various types of accounts, including checking, savings, money market deposit accounts, and certificates of deposit (CDs). Importantly, the insurance coverage extends to both individual and joint accounts, providing protection for a wide range of depositors.
The standard insurance amount is $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank, for each account ownership category. This means that an individual with multiple accounts at the same bank can have up to $250,000 in each account type insured. For joint accounts, each co-owner is considered a separate depositor, doubling the insurance coverage.
| Account Type | Insurance Coverage |
|---|---|
| Single Accounts | $250,000 per depositor |
| Joint Accounts | $250,000 per co-owner |
| Trust Accounts | Varies based on beneficiary |
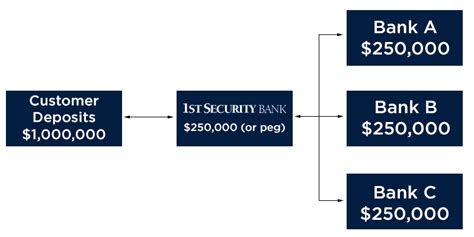
Understanding Insurance Limits
While the FDIC insurance coverage provides a substantial level of protection, it’s essential to understand the limits and exceptions. The insurance coverage applies to the net balance of an account, taking into account any outstanding loans or other obligations the depositor may have with the bank.
Additionally, it's crucial to note that the insurance coverage is per insured bank. If an individual has accounts at multiple banks, each bank's deposits are insured separately up to the $250,000 limit. This means that by spreading deposits across different banks, individuals can maximize their insurance coverage.
Benefits and Peace of Mind
The implementation of bank insurance brings about a multitude of benefits and fosters a sense of peace of mind for depositors. By insuring deposits, the FDIC and similar organizations worldwide provide a vital layer of protection, ensuring that even in the face of bank failures, depositors can retrieve their funds without incurring losses.
Financial Security and Stability
One of the primary advantages of bank insurance is the financial security it affords to individuals and businesses. The knowledge that deposits are insured up to a significant limit instills confidence in the banking system, encouraging people to utilize banks for their financial needs. This, in turn, promotes economic growth and stability, as a robust banking sector is essential for a thriving economy.
Protection Against Bank Failures
Bank failures can occur for various reasons, including mismanagement, economic downturns, or other unforeseen circumstances. When a bank fails, it can leave depositors vulnerable to losses. However, with deposit insurance in place, the likelihood of depositors experiencing significant financial setbacks is greatly reduced.
In the event of a bank failure, the FDIC steps in to resolve the situation, ensuring that depositors receive their insured funds promptly. This resolution process typically involves transferring the accounts of the failed bank to another, healthy institution, allowing depositors to access their funds without interruption. In rare cases where a transfer is not feasible, the FDIC may provide direct payments to depositors.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
The effectiveness of bank insurance can be best illustrated through real-world examples and case studies. Throughout its history, the FDIC has successfully resolved numerous bank failures, safeguarding the interests of depositors and maintaining financial stability.
The Washington Mutual Case
One notable example is the failure of Washington Mutual, the largest bank failure in American history at the time. In 2008, amid the financial crisis, Washington Mutual encountered significant financial difficulties and was seized by the FDIC. The FDIC promptly arranged for the transfer of Washington Mutual’s deposits to JPMorgan Chase, ensuring that depositors’ funds remained secure and accessible.
Despite the scale of the failure, depositors experienced minimal disruption, and their funds were protected thanks to the FDIC's insurance coverage. This case exemplifies the crucial role deposit insurance plays in mitigating the impact of bank failures and maintaining public confidence in the banking system.
Small Business Protection
Bank insurance is not limited to protecting individuals; it also extends its safety net to small businesses. For entrepreneurs and small business owners, the stability and security provided by deposit insurance are invaluable. In the event of a bank failure, small businesses can rest assured that their operating funds, payroll accounts, and other critical deposits are insured, allowing them to continue their operations without financial strain.
Future Implications and Continuous Improvement

The landscape of banking and finance is constantly evolving, and deposit insurance must adapt to meet the changing needs and challenges of the industry. While the FDIC and other similar organizations have proven effective in safeguarding deposits, ongoing efforts are dedicated to enhancing the system and addressing emerging risks.
Enhancing Protection and Transparency
To ensure the continued effectiveness of deposit insurance, regulatory bodies continuously evaluate and update their policies and practices. This includes regular stress tests and assessments of banks’ financial health to identify potential risks early on. By staying vigilant and proactive, deposit insurance organizations can better protect depositors and maintain public trust.
Addressing Cyber Threats
In the digital age, the rise of cyber threats poses a significant challenge to the banking industry. As financial transactions increasingly move online, the potential for cyberattacks and fraud becomes more pronounced. To counter these threats, deposit insurance organizations are investing in advanced cybersecurity measures and collaborating with banks to enhance their digital defenses.
By staying ahead of the curve and implementing robust cybersecurity practices, deposit insurance can continue to provide a reliable safety net for depositors, even in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Promoting Financial Inclusion
Deposit insurance also plays a crucial role in promoting financial inclusion and access to banking services. By providing a layer of protection, it encourages individuals and small businesses, particularly those in underserved communities, to participate in the formal banking system. This, in turn, fosters economic growth and empowers individuals to manage their finances effectively.
Are all banks insured by the FDIC?
+No, not all banks are insured by the FDIC. The FDIC insures deposits at banks that are members of the FDIC, which includes most commercial banks, savings banks, and savings associations. Credit unions are insured by a separate entity, the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA). It’s important to check if your bank is FDIC-insured to ensure the protection of your deposits.
How can I verify if my bank is FDIC-insured?
+You can easily verify if your bank is FDIC-insured by checking for the official FDIC logo on their website, marketing materials, or at their physical branches. Additionally, you can search for your bank’s name on the FDIC’s BankFind tool, which provides information on insured institutions.
What happens if my bank fails, and I have deposits exceeding the insurance limit?
+In the unfortunate event of a bank failure, the FDIC works to ensure that depositors receive their insured funds. However, if your deposits exceed the insurance limit, you may experience losses on the amount that exceeds the limit. It’s crucial to spread your deposits across multiple insured banks to maximize protection and minimize the risk of losses.



