Medicare Secondary Insurance
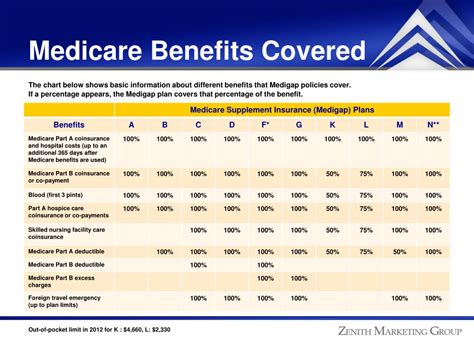
Medicare, the United States' federal health insurance program, plays a vital role in ensuring healthcare coverage for millions of Americans aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities or medical conditions. However, the complexities of the Medicare system often lead to confusion, particularly when it comes to understanding the concept of Medicare Secondary Insurance (MSI) and its implications.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Medicare Secondary Insurance, exploring its definitions, eligibility criteria, enrollment processes, and the impact it has on beneficiaries' healthcare coverage. By unraveling the nuances of MSI, we aim to provide clarity and empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their Medicare coverage.
Understanding Medicare Secondary Insurance (MSI)

Medicare Secondary Insurance refers to situations where Medicare's coverage is supplemented by another insurance plan, effectively making the other insurance the primary payer. This arrangement is designed to help individuals manage their healthcare costs more efficiently, as it leverages the benefits of multiple insurance plans.
MSI is particularly relevant for individuals who have access to other forms of health insurance through their employer, a spouse's employer, or a union. It ensures that these individuals can maximize their coverage and minimize out-of-pocket expenses by strategically utilizing their various insurance plans.
How MSI Works
When an individual has both Medicare and another health insurance plan, the order in which these plans pay for healthcare services is determined by a set of rules known as coordination of benefits. These rules dictate which insurance plan is considered the primary payer and which acts as the secondary payer.
In the context of MSI, the other insurance plan takes on the primary role, meaning it pays first for covered healthcare services. Medicare, acting as the secondary payer, steps in to cover any remaining costs that the primary insurance does not cover. This coordination of benefits ensures that individuals have comprehensive coverage without excessive gaps or overlaps.
| Primary Insurance | Secondary Insurance (Medicare) |
|---|---|
| Pays first for covered services | Pays after the primary insurance, covering remaining costs |
| Handles copayments and deductibles | May cover copayments or deductibles not met by the primary insurance |
| Handles coordination of benefits with Medicare | Adheres to the primary insurance's coordination of benefits rules |
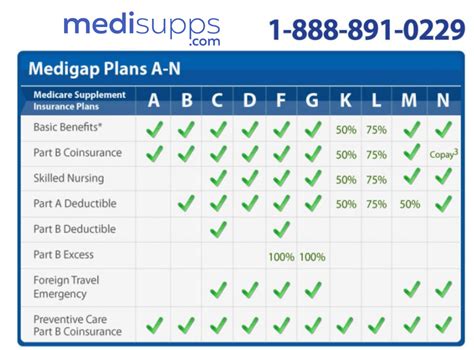
Eligibility for Medicare Secondary Insurance
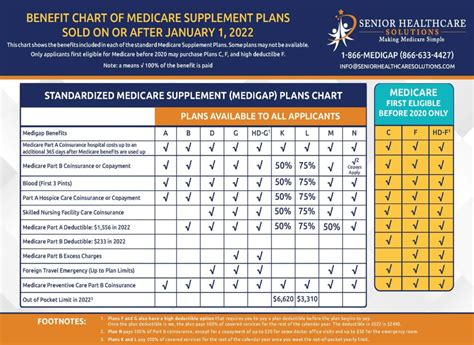
Not everyone is eligible for Medicare Secondary Insurance. The following criteria must be met to qualify for MSI:
- The individual must be enrolled in Part A and Part B of Medicare. Part A covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, and some home health care, while Part B covers medical services and supplies.
- The individual must have other credible health insurance coverage, such as employer-sponsored insurance, retiree insurance, or insurance through a spouse's employer.
- The other insurance plan must be primary to Medicare, meaning it pays first for covered services. This is typically the case for employer-sponsored insurance plans.
- The individual must not be entitled to Medicare Part A solely due to their end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or disability status. If an individual's eligibility for Part A is based on these conditions, MSI may not apply.
Common Scenarios for MSI Eligibility
MSI is particularly relevant in the following situations:
- Active Employees: Individuals who are actively employed and have access to employer-sponsored health insurance can use MSI to ensure their Medicare coverage complements their primary insurance.
- Retirees: Retirees who have retiree health insurance plans can utilize MSI to maximize their healthcare coverage. This is especially beneficial for those who wish to maintain their retirement income without sacrificing comprehensive healthcare.
- Spouses' Coverage: Spouses of individuals who have employer-sponsored insurance can also take advantage of MSI. In this case, the spouse's insurance acts as the primary coverage, and Medicare serves as the secondary payer.
- Union Members: Union members who have access to union-sponsored health insurance plans can leverage MSI to ensure their Medicare coverage is optimized.
Enrollment and Coordination of Benefits
Enrolling in Medicare Secondary Insurance involves a coordinated effort between the individual, their primary insurance provider, and Medicare. Here's an overview of the enrollment and coordination process:
Step 1: Determining Primary Insurance
The first step is to identify which insurance plan will act as the primary payer. This is typically determined by the individual's employment status, as employer-sponsored insurance plans are usually considered primary. However, in some cases, the individual's other insurance plan may be designated as primary due to specific coverage rules or regulations.
Step 2: Enrollment in Medicare
If an individual is eligible for Medicare, they must enroll in Part A and Part B. Enrollment can be done online through the Medicare website, by calling the Social Security Administration, or by visiting a local Social Security office. It's important to enroll during the appropriate Initial Enrollment Period to avoid late enrollment penalties.
Step 3: Coordinating Benefits
Once enrolled in Medicare, the individual should contact their primary insurance provider to coordinate benefits. The primary insurance company will work with Medicare to ensure that the coordination of benefits rules are followed. This process involves:
- Determining which services are covered by the primary insurance plan.
- Establishing the order of payment for covered services.
- Addressing any specific rules or requirements for coordinating benefits between the two plans.
Step 4: Understanding Out-of-Pocket Costs
With MSI in place, individuals need to understand their potential out-of-pocket costs. These costs can include deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. The primary insurance plan typically handles these expenses first, and Medicare may step in to cover additional costs if they are not met by the primary insurance.
Advantages and Considerations of MSI
Medicare Secondary Insurance offers several advantages, but it's important to consider the potential implications as well. Here's a breakdown of the key advantages and considerations:
Advantages of MSI
- Maximized Coverage: MSI allows individuals to leverage the benefits of both Medicare and their primary insurance plan, resulting in more comprehensive coverage.
- Reduced Out-of-Pocket Costs: By having two insurance plans, individuals can often reduce their out-of-pocket expenses, as Medicare steps in to cover remaining costs not met by the primary insurance.
- Flexibility: MSI provides flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, as individuals can utilize both Medicare-approved providers and those accepted by their primary insurance plan.
- Protection for High-Cost Services: MSI is particularly beneficial for individuals who require high-cost medical services, as it ensures they have additional coverage to help manage these expenses.
Considerations and Potential Challenges
- Coordination Complexity: Coordinating benefits between Medicare and the primary insurance plan can be complex, and individuals may need to navigate multiple sets of rules and regulations.
- Limited Medicare Coverage: In some cases, Medicare's coverage as the secondary payer may be limited, particularly for services that are not covered by the primary insurance plan.
- Potential Gaps in Coverage: While MSI aims to provide comprehensive coverage, there may still be gaps or exclusions that individuals need to be aware of. It's essential to carefully review both insurance plans to identify any potential gaps.
- Premium Costs: Individuals must consider the cost of premiums for both Medicare and their primary insurance plan. While MSI can reduce out-of-pocket expenses, the overall premium costs may still be significant.
Real-World Examples of MSI in Action
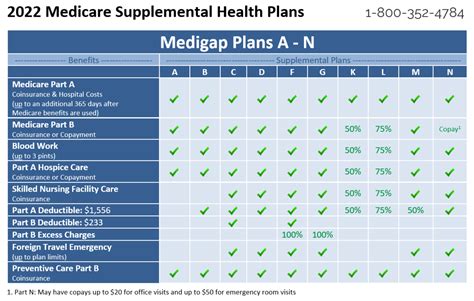
To illustrate how Medicare Secondary Insurance works in practice, let's explore a few real-world scenarios:
Scenario 1: Active Employee with Family Coverage
John, aged 63, is actively employed and has access to comprehensive health insurance through his employer. His insurance plan covers his family, including his wife, who is also 63, and their two adult children. When John and his wife turn 65, they enroll in Medicare Part A and Part B. With MSI in place, John's employer-sponsored insurance acts as the primary payer, covering the majority of their healthcare expenses. Medicare steps in to cover any remaining costs, ensuring that John and his family have comprehensive coverage without excessive out-of-pocket expenses.
Scenario 2: Retiree with Retiree Health Insurance
Sarah, aged 68, retired from her job a few years ago and has access to retiree health insurance through her former employer. This insurance plan provides her with primary coverage for her healthcare needs. When Sarah enrolled in Medicare Part A and Part B, she chose to utilize MSI. As a result, her retiree health insurance acts as the primary payer, covering most of her healthcare costs. Medicare, as the secondary payer, ensures that any remaining expenses, such as copayments or deductibles, are covered, providing Sarah with peace of mind regarding her healthcare expenses.
Scenario 3: Spouse's Coverage and Medicare
Michael, aged 66, is married to Emily, who is 64. Emily has access to health insurance through her employer, and they decide to use MSI to maximize their healthcare coverage. In this scenario, Emily's employer-sponsored insurance acts as the primary coverage for both Michael and Emily. When Michael enrolls in Medicare Part A and Part B, Medicare becomes the secondary payer, stepping in to cover any costs not met by Emily's insurance plan. This arrangement ensures that both Michael and Emily have robust healthcare coverage without unnecessary financial burdens.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
The landscape of healthcare and insurance is continually evolving, and Medicare Secondary Insurance is no exception. While MSI has provided valuable coverage options for many individuals, there are ongoing discussions and potential changes on the horizon:
Potential Changes to Medicare Benefits
The U.S. healthcare system is subject to various policy changes and reforms. As a result, Medicare benefits and coverage may undergo modifications in the future. These changes could impact the role of MSI and the coordination of benefits between Medicare and other insurance plans. It's essential for individuals to stay informed about any potential changes to Medicare and their implications on MSI.
Advancements in Healthcare Technology
Advancements in healthcare technology, such as electronic health records (EHRs) and improved data sharing between healthcare providers and insurance companies, have the potential to streamline the coordination of benefits process. These technological advancements could make it easier for individuals to navigate MSI and ensure seamless coverage.
Expanding Medicare Coverage
There are ongoing discussions and proposals to expand Medicare coverage to include additional services and benefits. If these expansions are implemented, it could impact the role of MSI and potentially reduce the need for individuals to rely on other insurance plans as primary coverage. Staying informed about these potential changes is crucial for individuals to make informed decisions regarding their healthcare coverage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if my primary insurance doesn't cover a specific medical service or procedure?
+If your primary insurance doesn't cover a specific medical service or procedure, Medicare may step in as the secondary payer to provide coverage. However, it's important to note that Medicare's coverage as a secondary payer may be limited, and there might be services or procedures that are not covered by either insurance plan. It's crucial to review both insurance policies to understand the potential gaps in coverage.
Can I have more than one secondary insurance plan in addition to Medicare?
+Yes, it is possible to have multiple secondary insurance plans in addition to Medicare. This is often the case for individuals who have access to multiple sources of insurance, such as through their own employer, a spouse's employer, or a union. Each insurance plan will have its own rules and regulations regarding coordination of benefits, so it's important to carefully review and understand all applicable policies.
Are there any situations where Medicare becomes the primary insurance instead of my employer-sponsored plan?
+Yes, there are specific situations where Medicare may become the primary insurance, even if you have employer-sponsored insurance. This typically occurs when you are eligible for Medicare due to a disability or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). In these cases, Medicare may be designated as the primary payer, and your employer-sponsored insurance would act as the secondary payer. It's important to understand your specific eligibility and the coordination of benefits rules in such situations.
How do I know if my insurance plan is considered "credible coverage" for MSI purposes?
+To determine if your insurance plan is considered "credible coverage" for Medicare Secondary Insurance purposes, you should review your insurance policy or contact your insurance provider. Credible coverage typically refers to health insurance plans that meet certain minimum standards for benefits and cost-sharing. These standards are set by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) to ensure that the insurance plan provides adequate coverage.
Can I switch between Medicare Secondary Insurance and Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) coverage?
+Switching between Medicare Secondary Insurance (MSI) and Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) coverage is possible, but it depends on your specific circumstances and eligibility. Generally, you can switch back to Original Medicare if you lose your other health insurance coverage, such as through a job change or retirement. However, it's important to understand the enrollment periods and potential implications of switching coverage types.
Medicare Secondary Insurance is a valuable tool for individuals who have access to other health insurance plans. By understanding the coordination of benefits and maximizing coverage, individuals can ensure they have the necessary healthcare coverage without excessive financial burdens. Staying informed about Medicare and insurance changes is crucial for making informed decisions about one’s healthcare and financial well-being.



