Bank Insurance On Deposits
Bank insurance on deposits is a critical component of the financial ecosystem, offering depositors a vital layer of protection and fostering trust in the banking system. In an industry where stability and security are paramount, understanding the intricacies of deposit insurance is essential. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of bank insurance, exploring its historical context, regulatory frameworks, and practical implications.
The Evolution of Deposit Insurance: A Historical Perspective

The concept of insuring bank deposits is not a recent development. Its origins can be traced back to the early 20th century, a period marked by significant financial crises and bank failures. These events highlighted the need for a safety net to protect depositors’ funds and prevent widespread panic, which could lead to further economic turmoil.
One of the earliest instances of deposit insurance emerged in the United States with the establishment of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) in 1933. The FDIC's creation was a direct response to the devastating impact of the Great Depression on the banking sector. By insuring deposits, the government aimed to restore confidence in the financial system and mitigate the risk of bank runs.
Since then, deposit insurance has become a global phenomenon, with numerous countries adopting similar systems to safeguard their citizens' savings. Each nation's approach, however, is unique, reflecting its specific economic, political, and cultural context. Some countries opt for a fully government-backed system, while others involve private sector participation.
The Mechanics of Bank Insurance: How It Works
At its core, bank insurance operates as a contractual agreement between a government agency or private insurer and a financial institution. The insurer agrees to protect depositors’ funds up to a certain limit in the event of the bank’s failure or insolvency.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a pivotal role in overseeing and enforcing deposit insurance schemes. These entities establish the rules and guidelines that govern the insurance process, ensuring fair practices and protecting the interests of depositors. They are responsible for setting the insurance limits, determining the eligibility criteria for institutions, and supervising the overall functioning of the system.
Funding Mechanisms
The funding of deposit insurance schemes varies widely. In some cases, governments fully subsidize the insurance, bearing the financial burden themselves. In others, a premium-based system is employed, where banks pay a fee to insure their deposits. This fee is often calculated based on the bank’s risk profile and the amount of insured deposits.
Additionally, some countries adopt a hybrid model, where both the government and the financial institutions contribute to the insurance fund. This approach aims to strike a balance between government support and market discipline, ensuring that banks remain vigilant about their risk management practices.
Deposit Insurance Limits
One of the most crucial aspects of deposit insurance is the establishment of coverage limits. These limits dictate the maximum amount of a depositor’s funds that are protected in the event of a bank failure. Setting an appropriate limit is a delicate task, as it must strike a balance between providing adequate protection and avoiding excessive moral hazard.
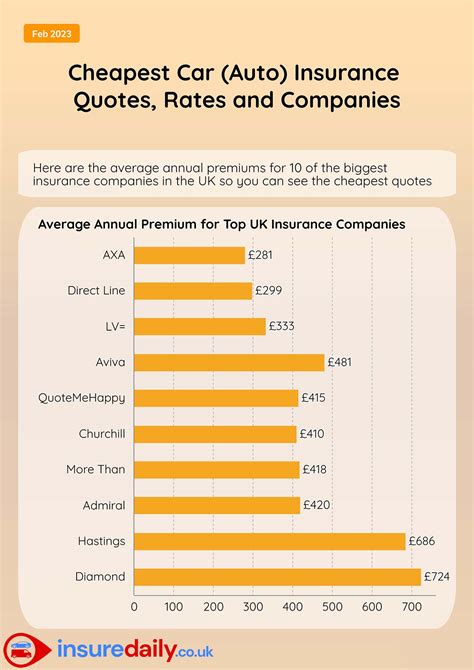
For instance, consider the case of the United States, where the FDIC currently insures deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank. This limit has been adjusted over time to keep pace with inflation and changing economic conditions. Other countries may have different limits, reflecting their unique economic landscapes and risk profiles.
The Impact of Deposit Insurance: Benefits and Considerations
The implementation of deposit insurance schemes has had far-reaching implications for the financial industry and the broader economy.
Stability and Confidence
Perhaps the most significant advantage of deposit insurance is its ability to instill confidence in the banking system. By providing a safety net for depositors, insurance schemes reduce the likelihood of bank runs and systemic crises. This stability encourages individuals and businesses to trust the financial system, facilitating economic growth and investment.
Risk Mitigation and Market Discipline
While deposit insurance offers protection, it also serves as a form of market discipline. Banks that participate in insurance schemes are incentivized to maintain strong risk management practices and adhere to regulatory standards. This fosters a culture of financial prudence and accountability, ultimately benefiting the entire financial ecosystem.
Challenges and Potential Pitfalls
Despite its benefits, deposit insurance is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is moral hazard, where the existence of insurance may encourage banks to engage in riskier behavior, believing that their deposits are guaranteed. To mitigate this risk, regulatory bodies often impose strict guidelines and conduct regular audits to ensure compliance.
Another challenge lies in the potential for insurance funds to become depleted in the event of widespread bank failures. This risk is often addressed through careful fund management and the establishment of reserve requirements. Additionally, some countries have contingency plans in place, such as access to government support or the ability to borrow from central banks, to ensure the ongoing viability of the insurance scheme.
Real-World Examples: Case Studies of Deposit Insurance in Action
To understand the practical implications of deposit insurance, let’s explore two case studies from different parts of the world.
Case Study 1: The FDIC and the U.S. Banking System
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) in the United States has been a cornerstone of the country’s financial stability since its inception. Over the years, the FDIC has successfully protected millions of depositors, even during times of economic turmoil.
One notable example is the 2008 financial crisis, where the FDIC played a critical role in mitigating the impact on depositors. Despite the widespread bank failures and market volatility, the FDIC's insurance coverage ensured that depositors' funds remained secure. This confidence in the system prevented a full-scale panic and contributed to the eventual recovery of the U.S. economy.
Case Study 2: The European Deposit Insurance Scheme (EDIS)
In Europe, the concept of deposit insurance has evolved through the establishment of the European Deposit Insurance Scheme (EDIS). EDIS aims to provide a unified safety net for depositors across the European Union, enhancing financial stability and integration.
Under EDIS, deposits up to €100,000 per depositor are fully guaranteed by the scheme. This harmonized approach ensures that depositors throughout the EU can rely on a consistent level of protection, regardless of their location. EDIS also promotes cooperation among EU member states, fostering a more resilient financial system.
The Future of Deposit Insurance: Emerging Trends and Innovations
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, so too must the strategies and approaches to deposit insurance.
Technological Innovations
The rise of digital banking and fintech innovations has prompted regulatory bodies to adapt their deposit insurance frameworks. Many countries are now exploring the use of blockchain technology and smart contracts to enhance the efficiency and security of insurance processes. These technologies can streamline record-keeping, improve transparency, and reduce the risk of fraud.
International Cooperation and Harmonization
With the increasing interconnectedness of global financial markets, there is a growing emphasis on international cooperation in deposit insurance. Regulatory bodies are collaborating to establish harmonized standards and practices, ensuring that depositors receive consistent protection regardless of where their funds are held. This cooperation is particularly vital in addressing cross-border banking and the movement of capital.
Dynamic Risk Assessment
Traditional deposit insurance models often rely on static coverage limits. However, emerging trends suggest a shift towards dynamic risk assessment, where insurance limits can be adjusted based on the real-time risk profile of individual banks. This approach allows for a more nuanced and responsive insurance framework, adapting to the evolving nature of financial risk.
| Country | Deposit Insurance Limit | Regulatory Body |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank | Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) |
| European Union | €100,000 per depositor | European Deposit Insurance Scheme (EDIS) |
| Canada | C$100,000 per depositor, per insured institution | Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation (CDIC) |
| Japan | ¥10 million per depositor | Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan (DICJ) |

How does deposit insurance benefit the economy as a whole?
+
Deposit insurance plays a crucial role in promoting economic stability and growth. By providing a safety net for depositors, it encourages individuals and businesses to save and invest, which fuels economic activity. Additionally, it reduces the likelihood of bank runs and systemic crises, maintaining confidence in the financial system.
Are there any disadvantages to deposit insurance schemes?
+
While deposit insurance offers significant advantages, it can also lead to moral hazard and encourage riskier behavior by banks. Additionally, the cost of insuring deposits may be passed on to consumers in the form of higher fees or reduced interest rates. Furthermore, the complexity of insurance schemes can create challenges in terms of transparency and public understanding.
What happens if a bank fails despite having deposit insurance?
+
In the event of a bank failure, the deposit insurance scheme steps in to protect insured depositors. The regulatory body overseeing the insurance will take control of the failed bank and ensure that eligible depositors receive their insured funds promptly. This process is designed to minimize disruption and maintain stability in the financial system.