Fha Insured Loan
The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) plays a crucial role in the U.S. housing market by offering government-backed mortgage insurance to lenders, facilitating homeownership for millions of Americans. This insurance program, known as the FHA-insured loan, has been a cornerstone of the American dream, enabling individuals with lower credit scores and smaller down payments to purchase homes. With its flexible guidelines and affordable terms, FHA-insured loans have opened doors for first-time homebuyers, veterans, and those seeking to refinance their mortgages.
The Evolution of FHA-Insured Loans

The history of FHA-insured loans dates back to the Great Depression era when the U.S. government sought to stabilize the housing market and provide affordable housing opportunities. The FHA was established in 1934, and its primary mission was to encourage homeownership and stimulate the construction industry. Over the decades, the FHA loan program has evolved to meet the changing needs of the housing market and homebuyers.
One of the key advantages of FHA-insured loans is their accessibility. Unlike conventional loans, FHA loans have more lenient credit score requirements, allowing borrowers with scores as low as 580 to qualify for a 3.5% down payment. This accessibility has made FHA loans a popular choice for first-time homebuyers and those with limited savings.
Key Features of FHA-Insured Loans
FHA-insured loans offer a range of benefits and features that make them an attractive option for many homebuyers. Here are some of the key characteristics:
- Low Down Payment: As mentioned, FHA loans require as little as 3.5% down for borrowers with credit scores of 580 or higher. This is significantly lower than the typical 20% down payment required for conventional loans.
- Flexible Credit Guidelines: FHA loans are known for their flexible credit requirements. While a credit score of 580 is ideal, borrowers with scores as low as 500 may still qualify for a 10% down payment. Additionally, FHA loans consider various factors beyond credit score, such as employment history and debt-to-income ratio.
- Lower Interest Rates: FHA-insured loans often come with competitive interest rates, which can result in significant savings over the life of the loan. These rates are generally lower than those offered for conventional loans, making FHA loans more affordable for many borrowers.
- Insured by the Government: The FHA mortgage insurance program provides a layer of protection for lenders, which encourages them to offer loans to borrowers who may not meet the stringent requirements of conventional loans. This insurance also benefits borrowers, as it allows them to secure financing with more favorable terms.
- Refinancing Options: FHA loans offer various refinancing programs, including the FHA Streamline Refinance, which simplifies the refinancing process and allows borrowers to reduce their interest rates or switch from an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) to a fixed-rate mortgage.
It's important to note that while FHA-insured loans have their advantages, they also come with certain limitations and requirements. For instance, borrowers must pay mortgage insurance premiums, both upfront and annually, which can increase the overall cost of the loan. Additionally, FHA loans have specific property requirements and guidelines that borrowers must adhere to.
Eligibility and Requirements for FHA-Insured Loans

To qualify for an FHA-insured loan, borrowers must meet certain criteria set by the FHA. Here are the key eligibility factors:
- Credit Score: As mentioned, FHA loans have more flexible credit score requirements compared to conventional loans. Borrowers with credit scores as low as 500 may qualify, but a score of 580 or higher is ideal to take advantage of the lowest down payment option.
- Down Payment: The minimum down payment for an FHA loan is 3.5% of the purchase price for borrowers with credit scores of 580 or higher. For those with credit scores between 500 and 579, a 10% down payment is required.
- Debt-to-Income Ratio: The FHA generally allows a maximum debt-to-income ratio of 43%, which means that your total monthly debt payments, including your mortgage, should not exceed 43% of your gross monthly income.
- Property Requirements: FHA loans have specific guidelines for the properties they insure. The home must be the borrower's primary residence, and it must meet the FHA's minimum property standards, which ensure that the property is safe, secure, and structurally sound.
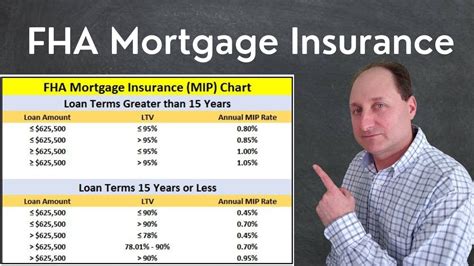
- Mortgage Insurance Premiums: Borrowers must pay mortgage insurance premiums to protect the lender in case of default. There is an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) of 1.75% of the loan amount, which can be financed into the loan, and an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP) that ranges from 0.45% to 1.05% of the loan amount, depending on the loan term and loan-to-value ratio.
How to Apply for an FHA-Insured Loan
The process of applying for an FHA-insured loan involves several steps. Here’s a general overview:
- Pre-Approval: Start by obtaining a pre-approval letter from an FHA-approved lender. This letter will outline the loan amount you qualify for based on your financial situation.
- Find a Property: Work with a real estate agent to find a suitable property that meets the FHA's minimum property standards. Remember that the property must be your primary residence.
- Submit Your Application: Once you've found a property, submit a formal loan application to your lender. This will involve providing detailed financial information, such as income statements, tax returns, and bank statements.
- Underwriting: The lender will then underwrite your loan application, verifying your financial information and assessing the property's value through an appraisal.
- Closing: If your loan is approved, you'll proceed to closing, where you'll sign the loan documents and finalize the purchase of your new home.
It's crucial to work with a reputable and experienced lender who can guide you through the process and ensure that you meet all the requirements for an FHA-insured loan.
The Impact of FHA-Insured Loans on the Housing Market
FHA-insured loans have had a significant impact on the U.S. housing market, particularly in terms of homeownership rates and economic stability. By making homeownership more accessible, FHA loans have contributed to a more diverse and inclusive housing market. They have played a crucial role in helping minority and low-to-moderate-income borrowers achieve their dreams of homeownership.
Moreover, FHA loans have been instrumental in stabilizing the housing market during economic downturns. By providing insurance to lenders, the FHA encourages lending even in challenging economic conditions, preventing a complete freeze in the mortgage market. This stability benefits not only borrowers but also the overall economy, as it supports the construction industry, creates jobs, and stimulates economic growth.
Future Prospects and Considerations
As the housing market continues to evolve, FHA-insured loans are likely to remain a vital component of the mortgage landscape. However, there are ongoing discussions and potential changes to the FHA loan program that borrowers and homebuyers should be aware of. These include:
- Changing Mortgage Insurance Premiums: The FHA periodically adjusts its mortgage insurance premiums to ensure the financial health of the program. Borrowers should stay informed about any changes to these premiums, as they can impact the overall cost of the loan.
- Property Value Appreciation: FHA loans are often used in markets with rising property values. Borrowers should consider the potential for appreciation when purchasing a home with an FHA loan, as it can impact their equity and refinancing options in the future.
- FHA Loan Limits: The FHA sets loan limits for different areas of the country. These limits are adjusted annually and can impact the maximum loan amount borrowers can qualify for. It's essential to understand these limits when planning to purchase a home with an FHA loan.
- FHA Loan Guidelines: The FHA periodically updates its guidelines and requirements. Borrowers should stay updated on these changes, as they may impact their eligibility and the terms of their loan.
Overall, FHA-insured loans remain a valuable tool for homebuyers seeking affordable and flexible mortgage options. By understanding the ins and outs of the program, borrowers can make informed decisions and take advantage of the many benefits FHA loans offer.
| FHA Loan Fact | Details |
|---|---|
| Minimum Credit Score | 500 (with 10% down) or 580 (with 3.5% down) |
| Down Payment | As low as 3.5% |
| Debt-to-Income Ratio | Up to 43% |
| Mortgage Insurance | Upfront and annual premiums required |
| Loan Limits | Varies by location, with limits set annually |

What is the maximum loan amount for an FHA-insured loan?
+
The maximum loan amount for an FHA-insured loan varies by location and is subject to FHA loan limits. These limits are set annually and take into account the average home price in a particular area. It’s important to consult with an FHA-approved lender to determine the specific loan limit for your location.
Can I use an FHA-insured loan to purchase a vacation home or investment property?
+
No, FHA-insured loans are intended for primary residences only. They are not available for vacation homes or investment properties.
How long do I have to occupy the property with an FHA loan?
+
FHA loans require that the borrower occupy the property as their primary residence for at least one year. After that, the borrower can choose to move or rent out the property, but they must meet certain criteria to do so.
Can I use an FHA loan to purchase a fixer-upper or a home that needs renovations?
+
Yes, FHA loans offer a special program called the 203(k) Rehabilitation Loan, which allows borrowers to finance both the purchase or refinance of a home, as well as the cost of repairs and renovations. This program is ideal for those who want to purchase a home that needs some work.
Are there any income restrictions for FHA-insured loans?
+
No, there are no specific income restrictions for FHA loans. However, borrowers must demonstrate the ability to repay the loan based on their income and debt obligations. The FHA assesses the borrower’s debt-to-income ratio to ensure they can afford the monthly mortgage payments.



