Auto Insurance Local

Auto insurance is an essential aspect of vehicle ownership, providing financial protection and peace of mind to drivers across the globe. The specificities of auto insurance, however, can vary greatly depending on the local context, including regional laws, cultural norms, and economic factors. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of auto insurance, specifically focusing on its local variations, to offer a comprehensive understanding of this vital aspect of automotive life.
Understanding the Local Landscape of Auto Insurance

Auto insurance, in its most basic form, is a contract between an individual and an insurance company. The insured agrees to pay a premium, typically on a monthly or annual basis, and the insurer promises to financially protect the policyholder in the event of an accident or other covered incidents. However, the details of this contract, and the implications it has for drivers, can vary significantly from one region to another.
Legal Requirements and Regional Differences
One of the most fundamental ways auto insurance differs across locales is in the legal requirements surrounding it. In some countries or states, auto insurance is mandatory, with minimum coverage levels dictated by law. For instance, in the United States, auto insurance is a legal requirement in all 50 states, with each state setting its own minimum coverage requirements. In contrast, in countries like the Netherlands, auto insurance is not mandatory, though it is strongly recommended.
Even within countries where auto insurance is mandatory, the specifics can vary. For example, in the UK, drivers must have at least third-party liability insurance, which covers damage to other people's vehicles and property, as well as any injury caused to others. However, fully comprehensive insurance, which also covers the driver's own vehicle, is not legally required.
| Region | Type of Insurance Required |
|---|---|
| United States | Varies by State: Minimum Liability Insurance is Common |
| United Kingdom | Third-Party Liability Insurance |
| Netherlands | Not Mandatory, but Strongly Recommended |
Cultural and Economic Factors
Beyond legal requirements, auto insurance is also shaped by cultural and economic factors. In countries with a high incidence of vehicle theft or vandalism, for example, comprehensive insurance policies that cover these risks might be more prevalent and affordable. Similarly, regions with a high population density and frequent traffic jams might see higher premiums due to the increased risk of accidents.
Economic factors also play a significant role. In areas with a strong economy and high disposable income, drivers might be more willing and able to pay for comprehensive insurance policies that offer a wider range of coverage. Conversely, in regions with a struggling economy, drivers might opt for basic liability-only policies to keep costs down.
Local Variations in Auto Insurance Coverage

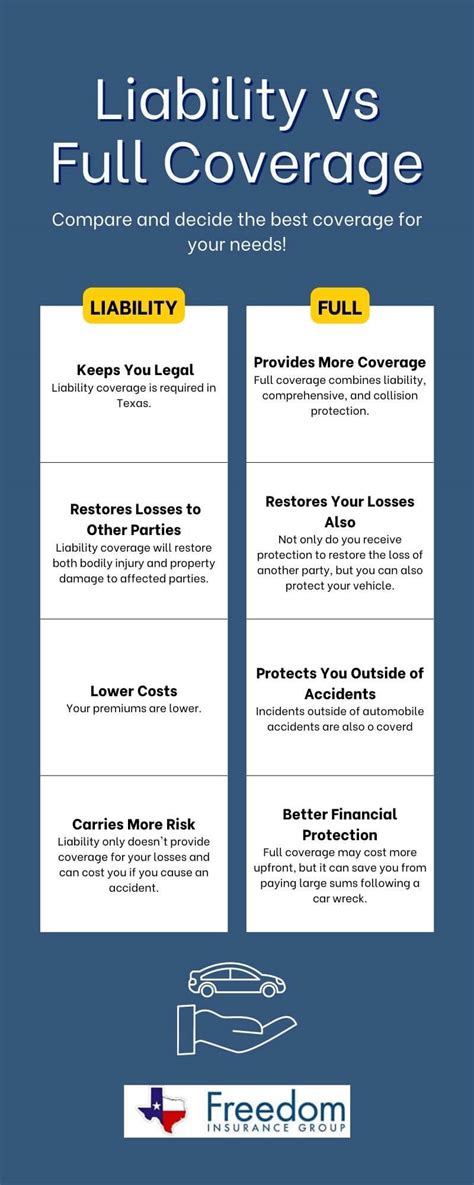
Liability Insurance
Liability insurance is a fundamental component of auto insurance policies worldwide. It covers the policyholder in the event they are found at fault for an accident, protecting them from financial liability for any damage or injury caused to others. The specific coverage limits and conditions, however, can vary significantly based on local laws and customs.
In the United States, for example, liability insurance is typically broken down into two categories: bodily injury liability and property damage liability. The former covers medical expenses and lost wages for people injured in an accident, while the latter covers damage to other people's vehicles and property. The coverage limits for these policies can vary greatly based on the state and the individual's choice.
Collision and Comprehensive Insurance
Collision and comprehensive insurance, often referred to as “full coverage,” offer additional protection beyond liability insurance. Collision insurance covers damage to the policyholder’s vehicle in the event of an accident, regardless of fault. Comprehensive insurance, on the other hand, covers damage to the vehicle from non-collision incidents, such as theft, vandalism, fire, or natural disasters.
The availability and popularity of collision and comprehensive insurance can vary widely depending on the region. In areas with a high incidence of theft or natural disasters, comprehensive insurance might be more prevalent and affordable. Conversely, in regions where accidents are relatively rare, collision insurance might be less common.
| Coverage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Liability Insurance | Covers damage and injury caused to others |
| Collision Insurance | Covers damage to the policyholder's vehicle in an accident |
| Comprehensive Insurance | Covers damage from non-collision incidents (theft, fire, natural disasters) |
Additional Coverages and Add-ons
Auto insurance policies can often be customized with additional coverages and add-ons to suit the individual’s needs. These can include personal injury protection (PIP), which covers medical expenses for the policyholder and their passengers regardless of fault; uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage, which protects the policyholder if they’re involved in an accident with a driver who has little or no insurance; and rental car coverage, which provides a rental car if the insured vehicle is being repaired or is deemed a total loss.
The availability and popularity of these additional coverages can vary based on local factors. For instance, in regions with a high incidence of uninsured drivers, uninsured motorist coverage might be more common. Similarly, in areas prone to natural disasters, coverage for wind or hail damage might be a popular add-on.
The Role of Technology in Local Auto Insurance
Telematics and Usage-Based Insurance
Advancements in technology have brought about new ways of insuring vehicles, particularly through the use of telematics and usage-based insurance (UBI). Telematics involves the use of devices installed in vehicles or smartphone apps that track driving behavior, such as speed, braking, and mileage. This data is then used to calculate insurance premiums, offering drivers the potential for significant discounts if they drive safely and responsibly.
Usage-based insurance takes this concept a step further, with insurance rates being adjusted based on real-time driving data. This means that the safer you drive, the more you can save on your insurance premiums. This approach is particularly beneficial for young drivers, who often face high insurance premiums due to their lack of driving experience, and for drivers who only use their vehicles occasionally.
Digital Platforms and Direct-to-Consumer Insurance
The rise of digital platforms and direct-to-consumer insurance models has also significantly impacted the local auto insurance landscape. These platforms, often powered by sophisticated algorithms and machine learning, offer customers a fast, efficient, and often cheaper way to purchase insurance. They can provide instant quotes, compare rates across multiple insurers, and even facilitate the purchase of a policy, all from the convenience of a smartphone or computer.
For insurers, these platforms offer a way to reach a wider audience, particularly tech-savvy millennials and Generation Z, who are increasingly comfortable with digital transactions and comparison shopping. By leveraging these platforms, insurers can also streamline their operations, reduce overhead costs, and pass on these savings to customers in the form of lower premiums.
Future Trends and Innovations in Local Auto Insurance
Connected Cars and Data-Driven Insurance
The increasing prevalence of connected cars, equipped with advanced telematics systems and data-sharing capabilities, is set to revolutionize the auto insurance industry. These vehicles can generate vast amounts of data about driving behavior, vehicle performance, and even road conditions, offering insurers a wealth of information to assess risk and set premiums.
This data-driven approach to insurance is expected to lead to more personalized and precise insurance policies. For instance, insurers might offer customized rates based on the driver's specific routes, the time of day they typically drive, or even the weather conditions they frequently encounter. This level of granularity could lead to more accurate risk assessments and potentially lower premiums for responsible drivers.
Autonomous Vehicles and the Future of Insurance
The impending arrival of autonomous vehicles (AVs) is another significant trend that will likely reshape the auto insurance landscape. As AVs become more prevalent, the nature of vehicle accidents and liabilities could change dramatically. With fewer driver errors, there might be a reduction in the number and severity of accidents, potentially leading to lower insurance premiums.
However, the introduction of AVs also raises new questions and challenges for the insurance industry. For instance, who is liable in the event of an accident involving an AV: the vehicle owner, the manufacturer, the software developer, or the ride-sharing company, if applicable? The answers to these questions will have significant implications for the structure and cost of auto insurance policies in the future.
Conclusion

Auto insurance is a vital component of vehicle ownership, and its local variations are shaped by a myriad of factors, including legal requirements, cultural norms, and economic conditions. Understanding these local differences is essential for drivers, insurers, and policymakers alike, as it allows for informed decisions and the development of policies that are both effective and equitable.
As the auto insurance landscape continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and emerging trends, staying informed and adapting to these changes will be key to ensuring that drivers are adequately protected and that the industry remains sustainable and responsive to the needs of its customers.
How do legal requirements affect auto insurance rates in different regions?
+Legal requirements can significantly impact auto insurance rates. In regions where insurance is mandatory and minimum coverage levels are high, insurers might have to spread their risk across a larger pool of policyholders, potentially leading to lower individual premiums. Conversely, in areas with lower mandatory coverage levels, insurers might face a higher concentration of risk, which could result in higher premiums.
What are some common factors that can increase auto insurance premiums?
+Several factors can increase auto insurance premiums, including the driver’s age, gender, and driving history. Younger drivers, particularly males, often face higher premiums due to their higher risk profile. Similarly, drivers with a history of accidents or traffic violations might also see increased rates. Other factors include the type of vehicle insured, its value, and the location where the vehicle is primarily driven.
How can technology, such as telematics and UBI, benefit drivers and insurers?
+Technology like telematics and usage-based insurance (UBI) can benefit both drivers and insurers. For drivers, these technologies offer the potential for significant discounts on insurance premiums by encouraging safer driving behavior. For insurers, telematics and UBI provide a more accurate assessment of risk, allowing them to offer competitive rates to good drivers while also identifying and managing higher-risk policyholders more effectively.



