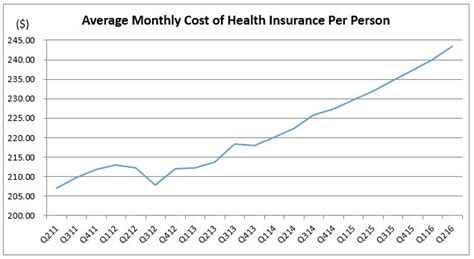
Approximate Cost Of Health Insurance
Understanding the Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of personal finance and healthcare, one of the most crucial considerations is the cost of health insurance. This essential coverage safeguards individuals and families from the financial burdens of unexpected medical expenses. However, determining the approximate cost of health insurance can be a complex endeavor, as it involves a myriad of factors that contribute to the final premium.
In this in-depth analysis, we will delve into the various aspects that influence the price of health insurance, providing a comprehensive guide to help you understand and navigate this crucial aspect of your financial well-being. By the end of this article, you'll have a clearer picture of the factors at play and be better equipped to make informed decisions about your health insurance coverage.
Demographic Factors: The Foundation of Insurance Premiums
When insurers calculate health insurance premiums, they begin with a foundation of demographic factors. These variables are used to assess the risk profile of an individual or a group and play a significant role in determining the cost of coverage.
Age
Age is one of the most influential demographic factors in health insurance pricing. Generally, younger individuals are considered lower-risk, as they are less likely to require extensive medical care. As a result, insurance companies typically offer lower premiums for younger enrollees. Conversely, older individuals, who may have a higher propensity for health issues, often face higher premiums to reflect the increased risk.
For instance, let's consider two individuals: Jane, a 25-year-old healthy adult, and John, a 60-year-old with a history of heart disease. Due to their respective ages and health conditions, Jane would likely pay a significantly lower premium than John. This age-based differentiation is a common practice in the health insurance industry and is often reflected in the structure of premium rates.
| Age Group | Average Premium |
|---|---|
| Under 30 | $250 - $400 per month |
| 30 - 40 | $300 - $500 per month |
| 40 - 50 | $400 - $650 per month |
| 50 and above | $500 - $1,000+ per month |

Gender
Historically, gender has been a factor in health insurance pricing, with insurers charging different rates for men and women. This practice, known as gender rating, has been based on the premise that men and women have different health needs and risks. However, this approach has faced scrutiny and legal challenges, leading to changes in some regions.
In the United States, for example, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits gender rating, ensuring that men and women pay the same premiums for the same coverage. This means that a man and a woman of the same age and health status would typically pay the same amount for their health insurance plan, regardless of their gender.
Location
The geographic location of an individual also impacts health insurance costs. Healthcare costs can vary significantly between different regions, influenced by factors such as the cost of living, availability of healthcare services, and local regulations. As a result, insurance premiums can differ substantially from one state or city to another.
For instance, consider the difference in healthcare costs between a rural area with limited medical facilities and a major metropolitan city with advanced healthcare infrastructure. The cost of healthcare services, and consequently, the insurance premiums, would likely be higher in the city due to the increased demand and the higher cost of maintaining state-of-the-art facilities.
Health Status and Medical History: The Impact on Premiums
An individual's health status and medical history are key factors that insurance companies consider when determining health insurance premiums. These variables help insurers assess the likelihood of an individual requiring medical treatment and the potential cost of that treatment.
Pre-existing Conditions
Pre-existing conditions are medical issues that an individual has had prior to applying for health insurance. These conditions can significantly impact insurance premiums, as they often require ongoing medical care and treatment. Insurers typically view individuals with pre-existing conditions as higher-risk, which can result in higher premiums.
For example, someone with a history of diabetes or heart disease may face higher insurance costs compared to someone without these conditions. The increased risk associated with pre-existing conditions often translates to a higher premium to cover the potential costs of ongoing medical management and potential complications.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices can also influence health insurance premiums. Insurance companies may consider factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, diet, and exercise habits when assessing an individual's risk profile. Unhealthy lifestyle choices can lead to an increased risk of certain health conditions, which in turn can impact insurance costs.
For instance, a smoker may pay a higher premium than a non-smoker due to the increased risk of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases associated with smoking. Similarly, individuals with unhealthy diets or sedentary lifestyles may face higher premiums, as these factors can contribute to conditions like obesity, which is linked to various health issues.
Family Medical History
An individual's family medical history can provide insights into potential genetic predispositions to certain health conditions. While this factor may not directly influence premiums, it can impact the types of coverage an individual may require. For example, if an individual has a family history of cancer, they may seek out insurance plans with comprehensive cancer coverage.
While family medical history doesn't typically affect the premium itself, it can impact the overall cost of healthcare, especially if an individual requires specialized treatments or procedures related to their family's health history.
Plan Type and Coverage: Tailoring Your Insurance
The type of health insurance plan and the level of coverage it provides are significant factors in determining the cost of your insurance. Different plan types offer varying levels of coverage, benefits, and out-of-pocket costs, all of which impact the overall premium.
Plan Types
There are several types of health insurance plans available, each with its own structure and benefits. The most common types include:
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs typically offer a network of healthcare providers, and enrollees must choose a primary care physician (PCP) to coordinate their care. These plans often have lower out-of-pocket costs but may have more restrictions on provider choices.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs provide a broader network of providers, and enrollees can visit any healthcare provider within the network without a referral. These plans offer more flexibility but may have higher out-of-pocket costs.
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): EPOs are similar to PPOs but with a narrower network of providers. Enrollees can visit any provider within the network without a referral, but services outside the network are not covered.
- Point-of-Service (POS) Plans: POS plans combine features of HMOs and PPOs. Enrollees have a PCP but can also visit out-of-network providers with an increased out-of-pocket cost.
- High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs): HDHPs have higher deductibles and lower premiums. They are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing enrollees to save pre-tax dollars for medical expenses.
Coverage and Benefits
The level of coverage and the specific benefits included in a health insurance plan are key determinants of the premium. Plans with more comprehensive coverage, including a wide range of services and benefits, typically have higher premiums.
For example, a plan that covers preventive care, prescription drugs, mental health services, and dental and vision care may have a higher premium compared to a plan that only covers basic medical services. The more comprehensive the coverage, the more costly the plan tends to be.
| Coverage Type | Average Premium Increase |
|---|---|
| Prescription Drugs | +10% - +20% |
| Mental Health Services | +5% - +15% |
| Dental and Vision Care | +5% - +10% |
| Preventive Care | +3% - +8% |
Out-of-Pocket Costs: Understanding Deductibles, Copays, and Coinsurance
In addition to the premium, health insurance plans come with various out-of-pocket costs that can impact the overall financial burden. Understanding these costs is essential for managing healthcare expenses effectively.
Deductibles
A deductible is the amount an individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance company starts covering costs. Deductibles can vary significantly, with some plans offering low deductibles and others requiring higher amounts. Higher deductibles typically result in lower premiums, while lower deductibles lead to higher premiums.
For instance, a plan with a $2,000 deductible may have a lower premium than a plan with a $500 deductible. This is because the insurance company assumes less financial risk with the higher deductible, which can lead to cost savings for the insurer and, subsequently, lower premiums for the enrollee.
Copays
Copays are fixed amounts an individual pays for a specific service or visit, typically after meeting the deductible. Copays can vary depending on the type of service and the plan's structure. For example, a copay for a primary care physician visit may be $25, while a copay for a specialist visit could be $50.
Copays can help manage healthcare costs by providing a fixed, predictable expense for certain services. This allows individuals to budget for their healthcare needs more effectively and can reduce the financial burden of unexpected medical bills.
Coinsurance
Coinsurance is the percentage of a covered healthcare service that an individual pays after meeting the deductible. For instance, if a plan has an 80/20 coinsurance structure, the insurance company pays 80% of the cost of a covered service, while the individual pays the remaining 20%.
Coinsurance can vary between different types of services and plans. Some plans may have different coinsurance rates for in-network and out-of-network providers, further impacting the overall cost of healthcare.
Market Competition and Insurance Provider Factors
The health insurance market is influenced by a range of competitive and provider-specific factors that can impact the cost of insurance premiums.
Market Competition
In a competitive market, insurance providers may offer lower premiums to attract customers. This competition can drive down prices, benefiting consumers. However, in less competitive markets, insurers may have more flexibility in setting premiums, potentially leading to higher costs.
Market competition can also influence the range of plan options available. In more competitive markets, insurers may offer a wider variety of plans with different coverage levels and benefits, giving consumers more choices to find the plan that best suits their needs.
Insurance Provider Factors
Individual insurance providers may have unique business models, risk assessments, and cost structures that influence their premium rates. Some providers may specialize in certain types of plans or target specific demographics, which can impact the cost of their offerings.
For example, a provider that focuses on offering comprehensive coverage for families may have higher premiums compared to a provider that primarily offers basic coverage for individuals. The provider's business strategy, market position, and target audience can all play a role in determining the cost of their insurance plans.
Economic and Regulatory Influences: Shaping the Insurance Landscape
The broader economic and regulatory environment also plays a significant role in shaping the cost of health insurance. Economic conditions, government policies, and industry regulations can all impact insurance premiums and the overall healthcare landscape.
Economic Conditions
Economic factors, such as inflation, interest rates, and the overall economic climate, can influence the cost of healthcare services and, consequently, insurance premiums. For instance, during periods of high inflation, the cost of healthcare services may increase, leading to higher insurance premiums.
Economic downturns can also impact insurance costs. During a recession, healthcare providers may face financial challenges, which could lead to increased costs and, in turn, higher insurance premiums. Conversely, a strong economy may provide more stability and predictability in healthcare costs, potentially leading to more stable insurance premiums.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations can significantly impact the health insurance market. Laws and regulations can dictate the types of coverage that must be offered, the minimum benefits that must be included, and the rights and protections of consumers. These policies can influence the cost of insurance by affecting the scope and structure of health insurance plans.
For example, regulations that require insurance companies to cover pre-existing conditions without charging higher premiums can impact the overall cost of insurance. While this protects consumers with pre-existing conditions, it may also lead to higher premiums for everyone to ensure that these individuals can access affordable coverage.
Industry Trends and Innovations
The healthcare industry is continually evolving, with new technologies, treatments, and services emerging. These innovations can impact the cost of healthcare and, by extension, insurance premiums. For instance, the development of new, expensive medications or treatments can increase healthcare costs, which may be passed on to consumers through higher insurance premiums.
Additionally, industry trends such as the shift towards value-based care and the integration of technology into healthcare delivery can influence insurance costs. Value-based care models, which focus on delivering high-quality, cost-effective healthcare, may help control costs and potentially reduce insurance premiums over time.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexity of Health Insurance Costs
Understanding the approximate cost of health insurance involves considering a multitude of factors, from demographic variables and health status to plan types, coverage, and out-of-pocket costs. The market competition, insurance provider strategies, and broader economic and regulatory influences also play significant roles in shaping insurance premiums.
By familiarizing yourself with these factors and staying informed about changes in the healthcare industry and insurance landscape, you can make more informed decisions about your health insurance coverage. Remember, the cost of health insurance is a complex equation, and understanding its components can help you navigate this crucial aspect of your financial well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the average cost of health insurance in the United States?
+The average cost of health insurance in the United States can vary widely depending on various factors such as age, location, plan type, and coverage. According to recent data, the average monthly premium for an individual can range from 400 to 600, while family plans can cost upwards of $1,200 per month. However, these figures can vary significantly, and it’s important to get personalized quotes based on your specific circumstances.
How can I reduce the cost of my health insurance premiums?
+There are several strategies to potentially reduce your health insurance premiums. These include choosing a plan with a higher deductible (if you’re comfortable with higher out-of-pocket costs), enrolling in a health savings account (HSA) if eligible, or considering a plan that offers incentives for healthy behaviors. Additionally, shopping around and comparing quotes from different insurers can help you find the most cost-effective option for your needs.
Are there any government programs that can help with health insurance costs?
+Yes, there are government programs designed to assist individuals and families with health insurance costs. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) offers subsidies and tax credits to help lower- and middle-income individuals and families afford coverage. Additionally, Medicaid provides health coverage for eligible low-income adults, children, pregnant women, elderly adults, and people with disabilities. It’s important to check your eligibility and explore these options to potentially reduce your insurance costs.



