What Is Premium In Insurance

In the world of insurance, the concept of premium is a fundamental and crucial aspect. It serves as the lifeblood of the insurance industry, driving the entire system and ensuring its smooth operation. Understanding the true essence of an insurance premium is essential for both consumers and professionals alike, as it forms the basis for the financial relationship between policyholders and insurance companies.
This comprehensive guide aims to delve deep into the world of insurance premiums, exploring its intricacies, its impact on the insurance ecosystem, and its significance in risk management and financial planning. By the end of this article, readers will possess a thorough understanding of insurance premiums, their role, and their implications.
The Definition and Role of Insurance Premium
At its core, an insurance premium is the amount of money an individual or entity pays to an insurance company for a specific coverage or policy. It is the cost of protection against potential risks and uncertainties, such as accidents, illnesses, property damage, or other defined perils. The premium is the price one pays to transfer the financial burden of these risks to the insurance provider.
The insurance premium is not a one-size-fits-all fee. It is tailored to the individual or business's specific needs and the level of risk they present. The higher the perceived risk, the higher the premium is likely to be. This personalized nature of premiums ensures that the insurance policy adequately addresses the insured's unique circumstances and requirements.
For instance, consider a young driver seeking auto insurance. Due to their lack of experience and the higher likelihood of accidents, their insurance premium is typically higher than that of a more seasoned driver. Similarly, a business operating in a high-risk industry, such as manufacturing or construction, will face higher premiums than a low-risk business like a software development firm.
Key Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
- Risk Assessment: Insurance companies thoroughly evaluate the risk associated with each policy. This involves analyzing the insured’s medical history, driving record, property location, business operations, and more. The higher the risk, the higher the premium.
- Coverage Level: The extent of coverage chosen by the policyholder also affects the premium. Comprehensive coverage plans with higher limits and additional benefits generally command higher premiums.
- Deductibles and Co-Payments: Policyholders can opt for higher deductibles (the amount they pay out of pocket before insurance coverage kicks in) or co-payments (a fixed amount they pay for each claim) to reduce their premiums. However, this strategy shifts more financial responsibility to the policyholder.
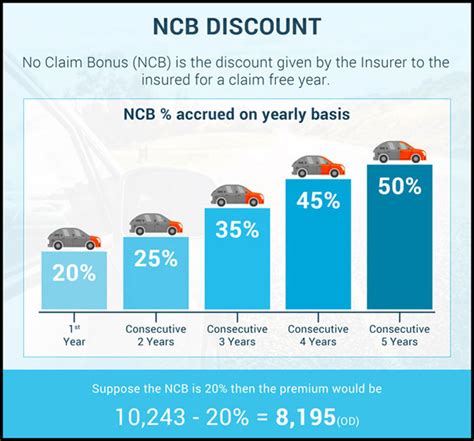
- Claims History: Insurance companies consider the policyholder’s claims history. Frequent claims can lead to higher premiums or even non-renewal of the policy.
- Location and Demographic Factors: The location of the insured property or residence can impact premiums. Areas prone to natural disasters or with high crime rates often see higher insurance costs. Demographic factors like age and gender also play a role, especially in certain types of insurance.
- Policy Type and Provider: Different insurance policies (auto, health, life, etc.) have varying premium structures. Additionally, insurance companies set their own rates based on their risk evaluation models and market positioning.
The Premium Payment Process

Premium payments are typically made at the start of the policy period, which is often annually or semi-annually. Policyholders can choose to pay their premiums in one lump sum or in installments. Some insurance companies offer flexible payment plans to accommodate different financial situations.
Upon receiving the premium, the insurance company assumes the financial responsibility for covering the policyholder's risks as outlined in the insurance contract. This contract, or policy document, details the coverage, exclusions, deductibles, and other important terms and conditions.
Premium Financing
In certain cases, policyholders may opt for premium financing, especially for large commercial policies or specialized insurance products. Premium financing involves borrowing money to pay the premium upfront and then repaying the loan over time, often with interest. This approach is particularly useful for businesses that prefer to preserve their cash flow or for individuals with significant insurance needs.
The Impact of Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums have a profound impact on the insurance industry and the broader economy. They influence the availability and affordability of insurance coverage, which, in turn, affects people’s and businesses’ ability to manage and mitigate risks.
Industry Sustainability
Insurance companies rely on premiums to cover their operating costs, pay claims, and generate profits. Adequate premiums are crucial for the financial stability and sustainability of the insurance industry. Insurers use sophisticated actuarial models to calculate premiums, ensuring they can meet their obligations to policyholders.
Risk Management and Financial Planning
For individuals and businesses, insurance premiums are a vital tool for managing risks. By paying premiums, policyholders can transfer the financial burden of potential losses to insurance companies, providing peace of mind and financial protection. This risk management strategy is essential for long-term financial planning and stability.
Economic Implications
Insurance premiums also have wider economic implications. They can influence investment decisions, as insurance companies invest a portion of the premiums they collect. Additionally, insurance premiums can affect consumer spending patterns, as individuals and businesses must allocate funds for insurance coverage.
Strategies for Managing Insurance Premiums
While insurance premiums are primarily based on risk assessment, policyholders have some degree of control over their premiums. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Compare Quotes: Obtain quotes from multiple insurance providers to find the most competitive rates for your specific needs.
- Bundle Policies: Combining multiple insurance policies, such as auto and home insurance, can often result in discounted premiums.
- Improve Risk Profile: Take steps to reduce your risk exposure. For instance, maintain a clean driving record, install security systems, or adopt healthy lifestyle habits.
- Review Coverage Regularly: Regularly assess your insurance needs and coverage. As your circumstances change, you may be able to adjust your policy and premiums accordingly.
- Consider Higher Deductibles: Opting for higher deductibles can lower your premiums, but it's important to ensure you have the financial capacity to cover the deductible in the event of a claim.
The Future of Insurance Premiums

The insurance industry is evolving, and so are insurance premiums. Technological advancements, data analytics, and changing consumer expectations are shaping the future of insurance premiums.
Personalized Pricing
With the advent of big data and advanced analytics, insurance companies are increasingly able to offer personalized pricing. By leveraging data-driven insights, insurers can more accurately assess individual risks and offer premiums tailored to each policyholder’s unique circumstances.
Usage-Based Insurance
Usage-based insurance (UBI) is a growing trend, particularly in auto insurance. UBI policies use telematics devices to monitor driving behavior and reward safe drivers with lower premiums. This pay-as-you-drive model offers a more dynamic and fair pricing structure.
Insurtech Innovations
Insurtech startups are disrupting the traditional insurance model with innovative solutions. These companies often leverage technology to offer more efficient and transparent premium pricing, leveraging machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve risk assessment.
| Insurance Type | Average Annual Premium |
|---|---|
| Auto Insurance | $1,674 |
| Homeowners Insurance | $1,312 |
| Health Insurance | $7,739 (Individual) |
| Life Insurance | $2,000 (Term Life) |

Conclusion
Insurance premiums are a critical component of the insurance ecosystem, shaping the financial relationship between policyholders and insurance companies. Understanding the factors that influence premiums, the payment process, and the strategies to manage them empowers individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about their insurance coverage. As the insurance industry continues to evolve, staying abreast of premium trends and innovations will be crucial for both consumers and industry professionals.
How often do insurance premiums change?
+
Insurance premiums can change annually or even more frequently, depending on the policy and the insurance company. Factors like claims history, changes in risk assessment, and market conditions can lead to premium adjustments.
Can I negotiate my insurance premium?
+
While insurance premiums are largely based on risk assessment, some flexibility exists. You can negotiate with your insurance provider, especially if you have a long-standing relationship or if you bundle multiple policies. However, be prepared to provide justification for a lower premium, such as improved risk management practices.
What happens if I can’t afford my insurance premium?
+
If you’re facing financial difficulties and can’t afford your insurance premium, it’s important to communicate with your insurance provider as soon as possible. They may offer payment plans or suggest ways to reduce your premium, such as increasing your deductible. In some cases, you may need to consider switching to a more affordable policy or provider.